Published online Dec 16, 2015. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v3.i12.1011
Peer-review started: May 5, 2015
First decision: August 19, 2015
Revised: August 29, 2015
Accepted: September 29, 2015
Article in press: September 30, 2015
Published online: December 16, 2015
Processing time: 220 Days and 5.8 Hours
Burkitt’s lymphoma (BL) is an aggressive form of non-Hodgkin’s B-cell lymphoma with three variants namely endemic, sporadic, and immunodeficiency-associated types. It is endemic in Africa and sporadic in other parts of the world. While the endemic form is widely reported to occur in early childhood and commonly involves the jaw bones, the sporadic form typically presents as an abdominal mass. This presentation reports a rare case of sporadic form of BL clinically manifesting as a generalized gingival enlargement in an immunocompetent adult male which demonstrated an aggressive behavior. The patient reported with a prominent anterior gingival swelling of 6 mo duration which slowly enlarged in size and associated with multiple lymph node involvement. Microscopic examination of the lesion using H, E and immunohistochemical diagnosis confirmed the diagnosis as BL. The patient succumbed to the disease before any therapy could be instituted. Since a wide array of causes can be attributed to gingival enlargements, it is necessary to consider malignancies as one of the important differential diagnosis so as to facilitate the need for appropriate diagnosis and prompt treatment.
Core tip: Burkitt’s lymphoma (BL) is an aggressive form of non-Hodgkin’s B-cell lymphoma with three variants namely endemic, sporadic, and immunodeficiency-associated types. It is endemic in Africa and sporadic in other parts of the world. We report a rare case of sporadic BL presenting as generalized gingival enlargement. The purpose of this case report is to illustrate the fact that gingival enlargements may be caused by any benign non-neoplastic lesions or aggressive malignancies like BL and bespeaks the need for prompt recognition and life-saving referral by the dental practitioner.
- Citation: Patankar S, Venkatraman P, Sridharan G, Kane S. Burkitt’s lymphoma of maxillary gingiva: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2015; 3(12): 1011-1016
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v3/i12/1011.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v3.i12.1011
Lymphomas are malignant neoplasms of lymphocyte cell lines and ranks second to squamous cell carcinoma in frequency of occurrence in head and neck. They are of two types: Hodgkin’s (HL) and Non-Hodgkin’s (NHL). HL often presents as a nodal disease with predilection for head and mediastinal nodes. NHL are heterogenous group of neoplasms arising primarily within the lymph nodes but up to 24%-40% cases occur in extra nodal sites such as gastrointestinal tract, skin, bone and Waldeyer’s ring[1].
Burkitt’s lymphoma (BL) is an aggressive form of non-Hodgkin’s B-cell lymphoma that is endemic in Africa and sporadic in other parts of the world. It is usually diagnosed in children and young adults but rarely in middle-aged adults. The endemic form typically involves the mandible, maxilla, and abdomen. BL of orofacial region typically occurs in the jaw bones associated with tooth mobility, dental pain and jaw expansion. Sudden and unexpected development of life threatening complications such as airway and abdominal obstruction and acute renal failure has been reported with BL[2]. In contrast, the sporadic form commonly presents as an abdominal mass involving the mesenteric lymph nodes or ileocecal region. Jaw involvement occurs in only a small number of sporadic cases[3].
A wide range of local and systemic lesions may manifest in the form of gingival enlargements. The most common cause occurs secondary to prolonged exposure to dental plaque resulting as a consequence of poor oral hygiene[4]. Other causes include drug induced enlargement; conditioned enlargements secondary to pregnancy, puberty, vitamin C deficiency; idiopathic enlargements and those associated with chronic microbial infections. While majority of the causes are benign and non-neoplastic in nature, malignant neoplasms also at time manifest in the form of gingival enlargements. Gingival enlargement is an important manifestation of malignancies like leukemia and lymphoma encountered by a dental specialist[5]. In the oral cavity lymphomas of the NHL type occurs as a primary disease or in conjunction with disseminated disease. All the variants of NHL occur in older patients except BL which usually occurs in children. The patient may present with nonspecific pain parasthesia, bony swelling with eventual perforation and soft tissue enlargement[6].
The present article reports a sporadic form of BL in an imuunocompetent adult male manifesting with atypical clinical presentation primarily involving the oral soft tissue.
A 38-year-old male patient reported to Oral Pathology clinic at our center for evaluation of an oral mass. Patient’s chief complaint was painful swelling in the anterior gingiva with difficulty in eating. He noticed the swelling 6 mo back in the upper anterior gingiva which progressively increased in size and gradually involved the entire gingiva of both the arches. Patient visited a local dentist and oral prophylaxis was performed. No clinical changes were evident post prophylaxis and the lesion attained the present size within seven days. The patient’s medical and dental history was insignificant. Personal history included regular tobacco chewing along with lime 5-6 times a day for the past 7-8 years accompanied with occasional alcohol consumption.
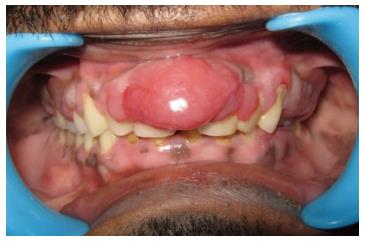
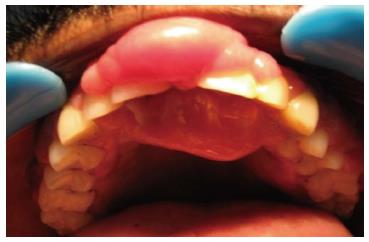
On extra-oral examination mild facial asymmetry with elevation of upper lip was noted. No abnormalities were detected on TMJ examination. Multiple, ipsilateral, nontender, matted, submandibular lymph nodes of approximate size 2.5 cm2 along with superficial cervical lymph nodes of approximate 1.5-2 cm2 were palpable on right side. Intra oral examination revealed generalized diffuse enlargement of both maxillary and mandibular gingiva. The swelling was particularly prominent in the anterior maxillary region involving both the palatal and labial gingiva extending from right maxillary lateral incisor to left maxillary lateral incisor, of size 3 cm × 3 cm, covering 2/3 of the crown portion of the incisors (Figures 1 and 2). The maxillary central incisors were displaced. The anterior lesion possessed smooth, shiny, non-stippled surface and was red in color. The other areas were red, edematous, stippled with non ulcerated surface. On palpation the texture was soft with bleeding in few areas and fibrous in others. There was no evidence of pulsation or thrill. Generalized Grade 1 mobility of the teeth was present. Oral hygiene status of the patient was poor. A provisional diagnosis of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) associated gingival enlargement or neoplastic gingival enlargement was considered.
Orthopantamographic examination revealed a generalized horizontal alveolar bone loss. The mass was primarily located in the soft tissues. No other bony changes related to the swelling were observed.
Routine blood investigation was performed and all parameters were within normal limits. ELISA and Western blot were negative for HIV. Peripheral blood smear stained with Leishman-Romanowsky stain showed atypical lymphocytes with pale cytoplasm and nuclei at the periphery with coarse chromatin and multiple nucleoli (Table 1).
| Test | Values |
| HB | 14.1 g/dL |
| RBC | 5.1 million/mm3 |
| Neutrophils | 26 |
| Lymphocytes | 41 |
| Eosinophils | 4 |
| Monocytes | 3 |
| Abnormal cells | 26 |
| Platelet count | 23000 |
| HIV | Negative |
| HBs Ag | Negative |
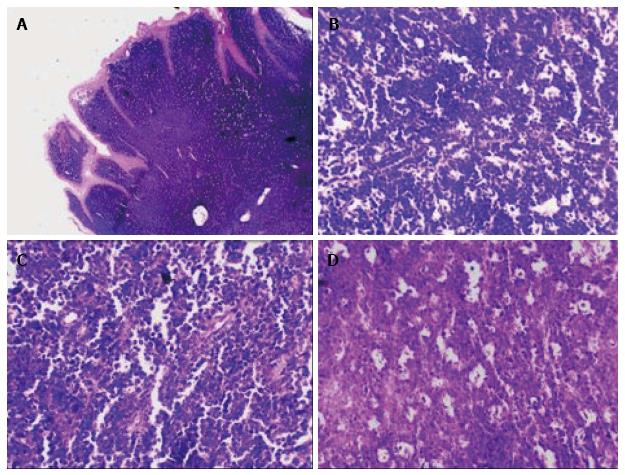
The light microscopic examination of the H and E stained tissue section under low power magnification showed a dense infiltrate of monotonous appearing darkly stained round cells, which appeared to be of lymphoid origin, with minimal stroma in the submucosal region. On a higher magnification the tumor cells were homogenous in size and shape with round to oval intensely basophilic nuclei and minimal cytoplasm. They were separated by thin fibrous septae with scattered large pale staining macrophages resembling starry sky pattern. The neoplastic cells showed nuclei with coarse chromatin and several nucleoli indicating a high mitotic index. Microscopically the morphological picture was consistent with NHL. Based on the histopathological findings a diagnosis of NHL probably BL was made (Figure 3).
Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis was performed with a panel of antibodies to confirm the diagnosis (Table 2). A negative cytokeratin staining along with diffuse positivity of LCA confirmed the lymphoid origin. Granulocytic origin was ruled out by MPO negativity. CD3 positivity in scattered cells revealed that the cells were not of T-cell lineage. The origin of B cells was confirmed with CD10 positivity. Tdt was negative which indicated the presence of mature cells and not blast cells. CD 20 was focally positive which confirmed the presence of mature B cells. MIB 1 was > 95% positive which confirmed increased DNA synthesis and increased mitotic activity. Plasma cell neoplasms were ruled out on CD 138 negativity.
| Marker | Expression | Interpretation |
| LCA | Diffusely positive | Suggestive of lymphoma |
| Cytokeratin | Negative | Excludes undifferentiated carcinoma |
| MPO | Negative | Ruled out granulocytic origin |
| Tdt | Negative | Rules out blast cell origin |
| CD3 | Positive in scattered T cells | Excludes T-lymphocyte predominance |
| CD20 | Focally positive | Indicates mature cell origin |
| CD10 | Positive | Indicative of B-cell origin |
| CD138 | Negative | Excludes plasma cell origin |
| MIB 1 | Positive (almost 100%) | Indicative of aggressiveness |
The histopathological picture along with IHC findings confirmed the diagnosis of BL.
The patient’s condition deteriorated with the platelet count falling below 10000 within few days and he succumbed to the disease.
A wide range of etiological factors are responsible for gingival enlargements. They may result from acute or chronic inflammatory changes, systemic diseases such as Wegener’s granulomatosis[7] tuberculosis and sarcoidosis or neoplastic enlargements which may clinically mimic inflammatory enlargements[8]. Malignant neoplasms of epithelial origin are more common in gingivobuccal area[9] and are to be primarily considered followed by leukemia[6]. The present case manifested in the form of gingival enlargement with aggressive behavior and poor clinical outcome.
Lymphoma is a malignant neoplasm of lymphocytic cell lines and includes two clinical types namely HL and NHL lymphoma. HL often presents as a nodal disease with predilection for head, neck and mediastinal lymph nodes. NHL is a heterogenous group of neoplasms arising primarily within the lymph nodes but up to 24%-40% cases occur in extra nodal sites[1]. Oral lesions are often a component of disseminated disease process that may involve regional lymph nodes or may at times represent the primary extra nodal form of the disease[10]. Isolated oral lymphoma is extremely rare and oral NHL in Indian sub population is more aggressive compared with western population[11].
BL is an aggressive childhood to early adulthood variant of NHL which is endemic in Africa and is often associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Majority of the endemic form occurs in children 5 years or lesser[12], suggesting a stimulatory effect from the growth factors associated with jaw or tooth development[13]. The sporadic form has no geographic predilection and most commonly develops in adults as an abdominal mass[14]. BL of orofacial region typically occurs in the jaw bones associated with tooth mobility, dental pain and jaw expansion. Sudden and unexpected development of life threatening complications such as airway and abdominal obstruction and acute renal failure has been reported with BL[2]. BL affecting the gingival soft tissue only, has been occasionally reported in the literature while the present article present an unique case with diffuse enlargement involving both maxillary and mandibular gingiva.
BL is classified as a highly aggressive peripheral B cell tumor and demonstrating the highest proliferation rate of any neoplasms in humans, with a potential doubling time of 24 h and a growth fraction of nearly 100%[15]. It is further classified morphologically by WHO into classical BL and two variants namely BL with plasmacytoid differentiation and atypical Burkitt’s like lymphoma[16]. All cases of BL show characteristic translocation between IgH locus on either chromosome 14/2/22 and the c-MYC gene on chromosome 8. An increase in c-Myc expression results from the translocation. This c-MYC dysregulation seems to be the defining abnormality that eventuates into BL[17].
The microscopic features of typical BL shows tumor cells that are monotonous, intermediate sized with round nuclei containing coarse chromatin, multiple small nucleoli admixed with tingible body macrophages creating starry-sky pattern visible at low power. Mitotic and apoptotic activity are typically a prominent feature. Expression of pan B-cell markers as well as Bcl-6 and CD-10 suggests a germinal centre origin for the tumor cells[16]. Histologically oral BL has to be differentiated from diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and plasmablastic lymphomas (PBL). DLBCL is predominant variant in oral cavity and this is explained by its proclivity to present at single extra nodal site[18]. The characteristic microscopic feature of PBL is a diffuse sub mucosal proliferation of monomorphic large sized tumor cells with deep ulceration of the overlying mucosa. PBL is characterized by a diagnostic triad of predilection for gingivobuccal complex mucosa, classical plasmablastic morphology with lack of neoplastic plasma cells and a limited histochemical panel including a high Mib-1 index[19].
This paper presents a unique sporadic case of BL in a HIV adult male with the oral lesion limited to the gingival soft tissue only without involvement of the jaw bones. Diffuse involvement of gingiva on both the arches along with rapid growth showed the aggressiveness of the lesion. This lesion has clinical characteristics that mimicked a variety of other aggressive orofacial pathologies including malignant neoplasms and illustrates the inherent difficulty in diagnosis based on the lesion’s uncharacteristic clinical appearance. Biopsy and histopathological examination of the tissue with immunohistochemistry was mandatory to arrive at a diagnosis.
Gingival enlargement is a common pathology in the general population caused by a variety of local and systemic factors. While plaque induced inflammation is the most important cause, enlargement can also be induced by non-neoplastic and neoplastic factors of systemic origin. The clinician can often diagnose the cause of enlargement by careful history, by location and by clinical presentation. It is imperative that the clinician maintain a high degree of suspicion and act promptly in lesions with unusual appearance and behavior. A detailed investigation including biopsy is mandatory to correctly diagnose and treat such lesions. Our case reported some unusual presentation of gingival involvement secondary to malignancy and thus highlights the importance of considering such lesions in the differential diagnosis of gingival enlargements.
A 38-year-old male patient reported with a chief complaint of painful swelling in the upper anterior gingiva with difficulty in eating since 6 mo.
Human immunodeficiency virus associated gingival enlargement was considered as the provisional diagnosis.
Neoplastic gingival enlargement, chronic granulomatous lesion and oral lesions secondary to systemic diseases like leukemia.
All lab findings were within normal limits.
Orthopantamographic examination revealed a generalized horizontal alveolar bone loss without any other relevant changes.
Burkitt’s lymphoma (BL).
Patient succumbed to the disease before institution of therapy.
BL in an adult immunocompetent individual is less reported in literature and needs to be treated early owing to its aggressive nature.
BL is a malignant neoplasm belonging to group of non-Hodgkin’ss lymphoma with aggressive behavior and poor prognosis.
Oral manifestations of malignant neoplasms such as leukemia and lymphoma should be considered in the differential diagnosis of rapid gingival enlargements and clinical practitioners should be aware of its consequences.
It’s a simple case report about oral BL concurrency associated with gingival enlargement. This is a well written case report with a very rare pathology.
P- Reviewer: Adrian K, Jorge V, Santos FA S- Editor: Qiu S L- Editor: A E- Editor: Lu YJ
| 1. | Durmuş E, Oz G, Güler N, Avunduk M, Calişkan U, Blanchaert RH. Intraosseous mandibular lesion. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003;61:246-249. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Jan A, Vora K, Sándor GK. Sporadic Burkitt’s lymphoma of the jaws: the essentials of prompt life-saving referral and management. J Can Dent Assoc. 2005;71:165-168. [PubMed] |
| 3. | Regezi JA, Sciubba JJ, Jordan RCK. Oral Pathology: Clinical Pathologic Correlations. 4th ed. St. Louis: W.B Saunders 2003; 179-180. |
| 4. | Newman MG, Takei HH, Klokkevold PR, Carranza FA. Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology. 10th ed. St. Louis: Saunders 2006; 373-388. |
| 5. | Demirer S, Ozdemir H, Sencan M, Marakoglu I. Gingival hyperplasia as an early diagnostic oral manifestation in acute monocytic leukemia: a case report. Eur J Dent. 2007;1:111-114. [PubMed] |
| 6. | Ferry JA. Burkitt’s lymphoma: clinicopathologic features and differential diagnosis. Oncologist. 2006;11:375-383. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 217] [Cited by in RCA: 216] [Article Influence: 11.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Redman RS, Chauhan S, Paul BF. Slowly enlarging gingival mass in a 50-year-old man. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2013;116:135-141. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Spatafore CM, Keyes G, Skidmore AE. Lymphoma: an unusual oral presentation. J Endod. 1989;15:438-441. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Boyd BC, Au J, Aguirre A, Votta TJ. Rapidly enlarging nodular lesion of the anterior maxilla. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011;112:626-631. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Rajendran R, Sivapathasundaram B. Shafer’s textbook of Oral Pathology. 6th ed. St. Louis: W.B. Saunders Elsevier 2009; 173-178. |
| 11. | Shah GH, Panwar SK, Chaturvedi PP, Kane SN. Isolated primary extranodal lymphoma of the oral cavity: A series of 15 cases and review of literature from a tertiary care cancer centre in India. Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol. 2011;32:76-81. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Tadanobu S, Tamotsu U, Hiroyuki U, Mashahiko H. A case of Burkitt lymphoma involving the right maxillary gingiva in a 2-year-7-month-old infant. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2001;47:174-177. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Marx RE, Stern D. Oral and maxillofacial pathology: A rationale for diagnosis and treatment. 1st ed. Germany: Quintessence publishing 2003; . |
| 14. | Martinelli-Kläy CP, Martinelli CR, Martinelli C, Dias JB, Cheade TC, Lombardi T. Primary extranodal non-Hodgkin lymphoma of the gingiva initially misdiagnosed as dental abscess. Quintessence Int. 2009;40:805-808. [PubMed] |
| 15. | Kemp S, Gallagher G, Kabani S, Noonan V, O’Hara C. Oral non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: review of the literature and World Health Organization classification with reference to 40 cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008;105:194-201. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 113] [Cited by in RCA: 129] [Article Influence: 7.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Balasubramaniam R, Goradia A, Turner LN, Stoopler ET, Alawi F, Frank DM, Greenberg MS. Burkitt lymphoma of the oral cavity: an atypical presentation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009;107:240-245. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, Bouquot JE. Soft tissue tumors. Oral and Maxillofacial pathology. 3rd ed. St. Louis: W.B. Saunders Elsevier 2009; 557-559. |
| 18. | van der Waal RI, Huijgens PC, van der Valk P, van der Waal I. Characteristics of 40 primary extranodal non-Hodgkin lymphomas of the oral cavity in perspective of the new WHO classification and the International Prognostic Index. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005;34:391-395. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 75] [Cited by in RCA: 90] [Article Influence: 4.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Kane S, Khurana A, Parulkar G, Shet T, Prabhash K, Nair R, Gujral S. Minimum diagnostic criteria for plasmablastic lymphoma of oral/sinonasal region encountered in a tertiary cancer hospital of a developing country. J Oral Pathol Med. 2009;38:138-144. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |