Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 16, 2025; 13(23): 107096
Published online Aug 16, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i23.107096
Published online Aug 16, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i23.107096
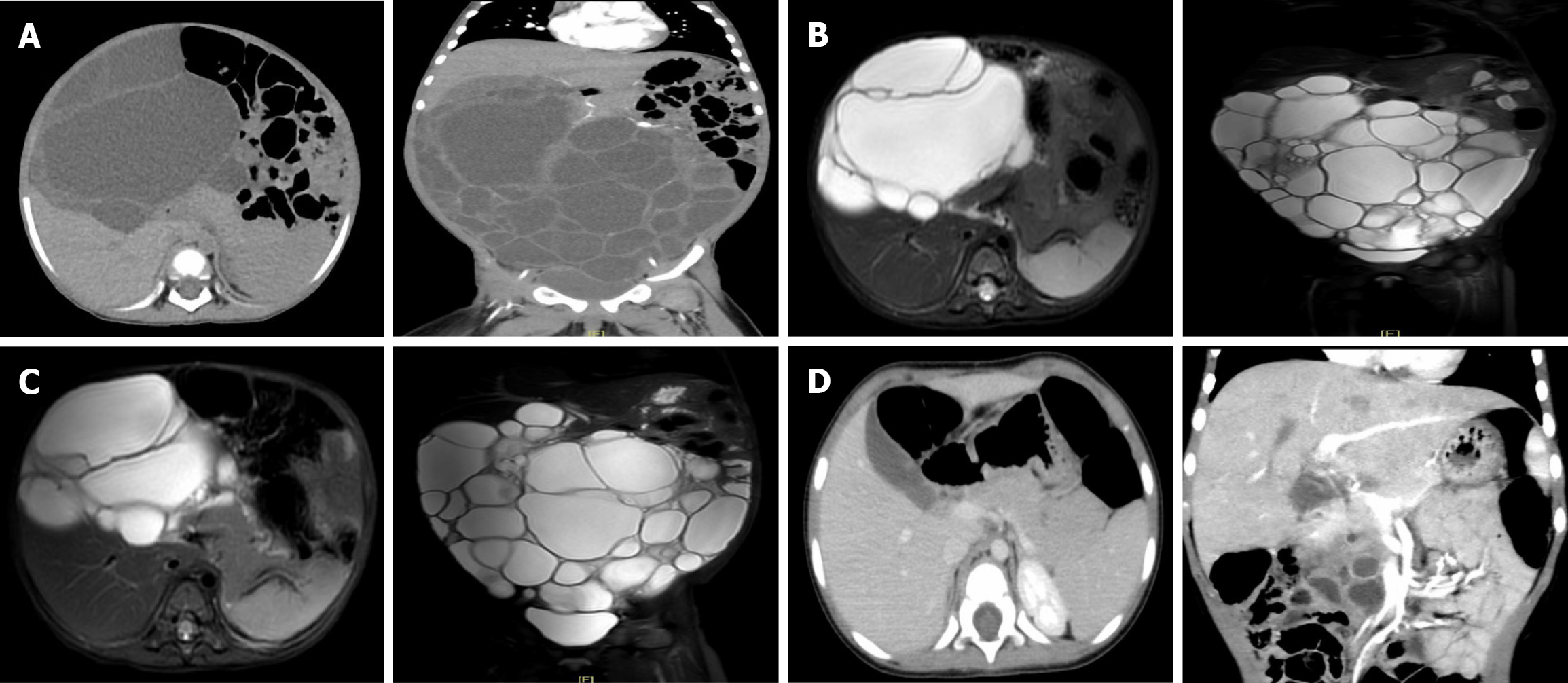
Figure 1 Abdominal computed tomography and magnetic resonance images.
A: Abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan completed on March 22, 2023. Large multiloculated, multiseptated cystic mass (21.7 cm × 16.8 cm × 8.9 cm); B: Abdominal magnetic resonance (MR) completed on April 27, 2023. The size of the cyst was similar to previous CT (18.0 cm × 10.0 cm × 21.0 cm); C: Abdominal MR completed on June 27, 2023. The size of the cyst was similar to previous MR (17.9 cm × 11.0 cm × 21.0 cm); D: Abdominal CT scan completed on February 26, 2024. Pancreatic head cyst was significantly reduced (4.6 cm × 4.3 cm × 2.0 cm).
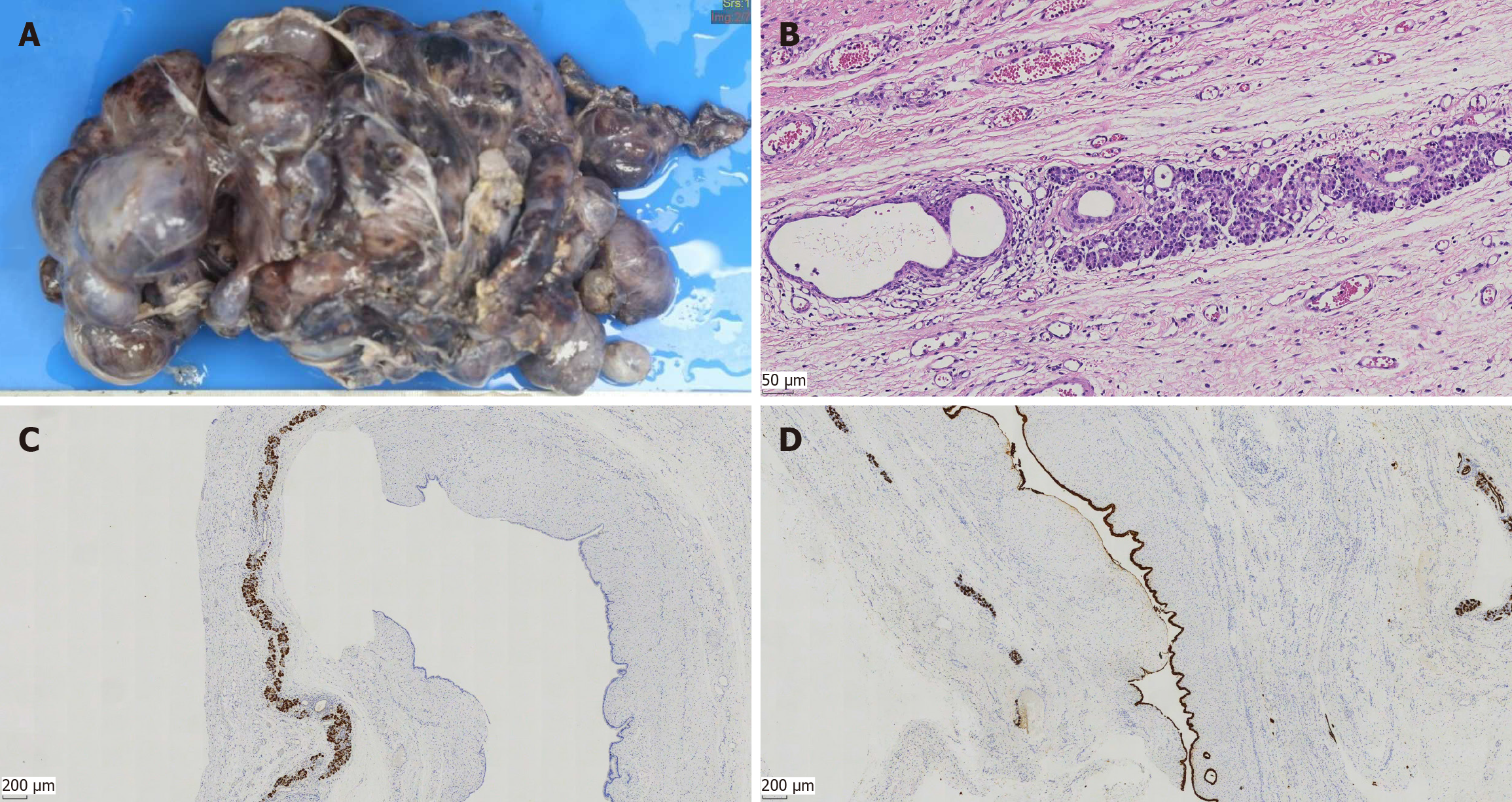
Figure 2 Gross morphology and microscopic images of resection specimen.
A: Gross morphology of resection specimen; B: Resection specimen consisting of multiple variable-sized cysts. The lesion is lined by cells with acinar differentiation, which have apical eosinophilic cytoplasmic granules and uniform nuclei. Cytologic atypia and mitotic figures are absent (hematoxylin and eosin, 200× magnification); C: Immunohistochemical positivity for the pancreatic enzyme trypsin is seen in the acinar cells (40× magnification); D: The lining cells are positive for CK19 and have strong and diffuse cytoplasmic staining for CK19 (40× magnification).
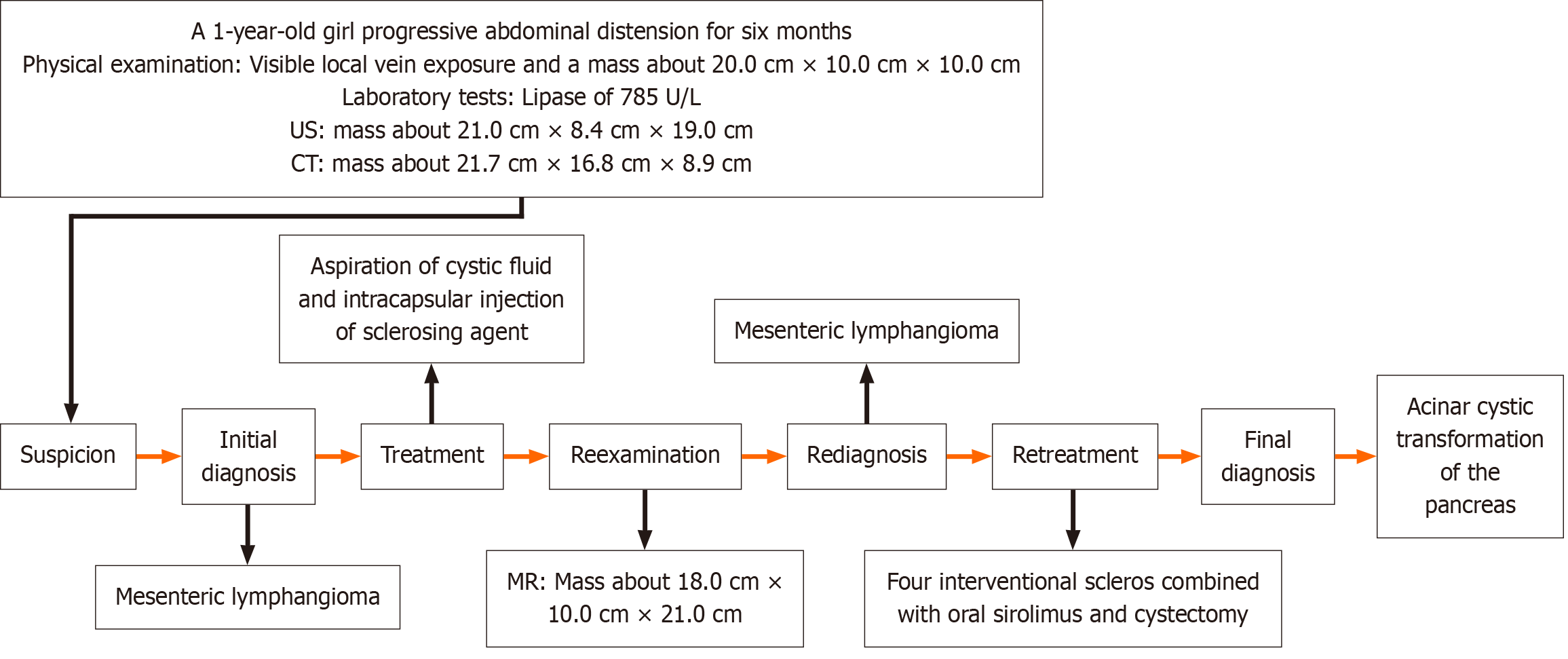
Figure 3 Diagnosis and treatment flow chart.
CT: Computed tomography; US: Ultrasound; MR: Magnetic resonance.
- Citation: Zhong XY, Liang ZJ, Lan ML, Xu XG, Yuan L, Zeng JX. Acinar cystic transformation of the pancreas: A rare case report. World J Clin Cases 2025; 13(23): 107096
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v13/i23/107096.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v13.i23.107096