Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 16, 2022; 10(23): 8352-8359
Published online Aug 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i23.8352
Published online Aug 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i23.8352
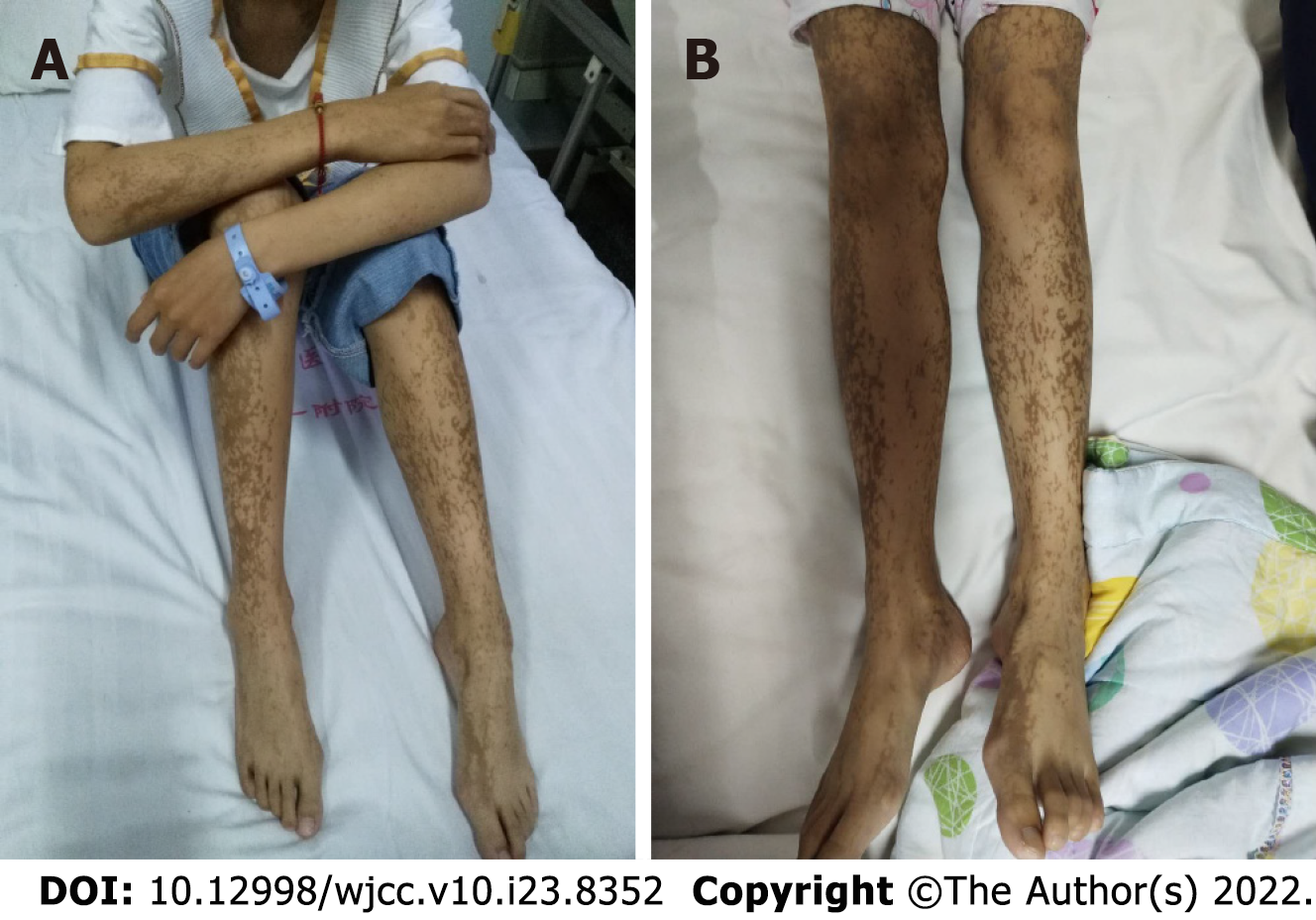
Figure 1 Presentation at the initial clinic visit.
A: Ink-splattered and streak-like brown hyperpigmentation all over the trunk and extremities; B: Linear lesion of the lower limbs and feet with hyperpigmentation.
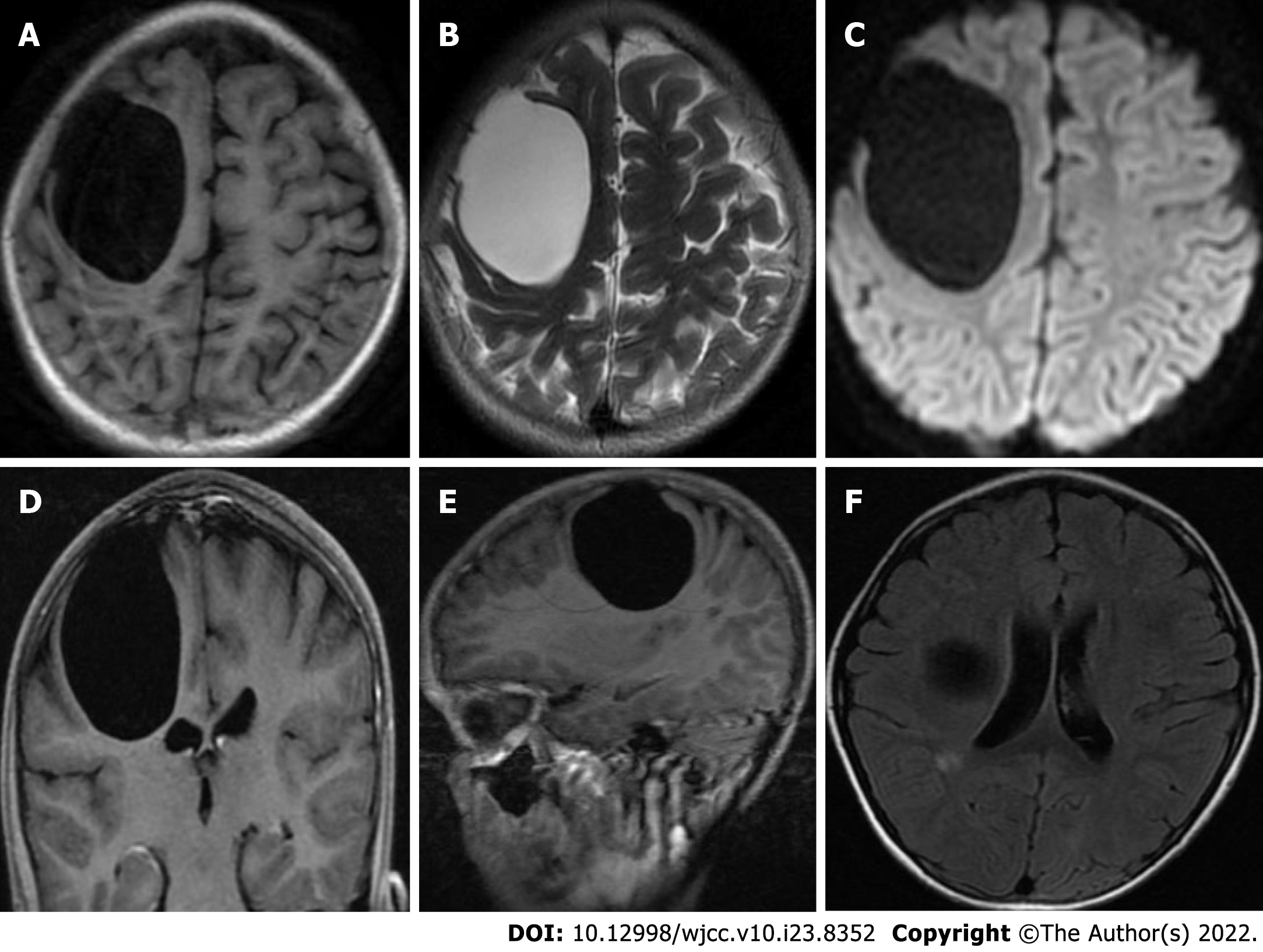
Figure 2 Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging examination.
A: A large, circular, homogeneous sac-like signal was observed in the right frontal brain area, approximately 49.3 mm × 58.5 mm × 54.0 mm, with clear boundaries, and the adjacent brain sulci were compressed and narrowed. Long T1-weighted imaging (T1WI) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) signal showed a capsule shadow; B: Long T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) MRI signal showed a capsule shadow; C: Diffusion weighted imaging images showed a low signal; D: The right lateral ventricle was deformed by compression; E: with no obvious enhancement on the enhanced scan; F: There was a small patchy long T1WI and long T2WI signal next to the posterior horn of the right lateral ventricle, T2 fluid-attenuated inversion recovery showed a slightly high signal, and no obvious enhancement was found on the enhanced scan. Radiological diagnosis of the right frontal lobe was a cystic mass, which was considered a possible intracranial arachnoid cyst, and small ischemic foci next to the posterior horn of the right lateral ventricle were noted.
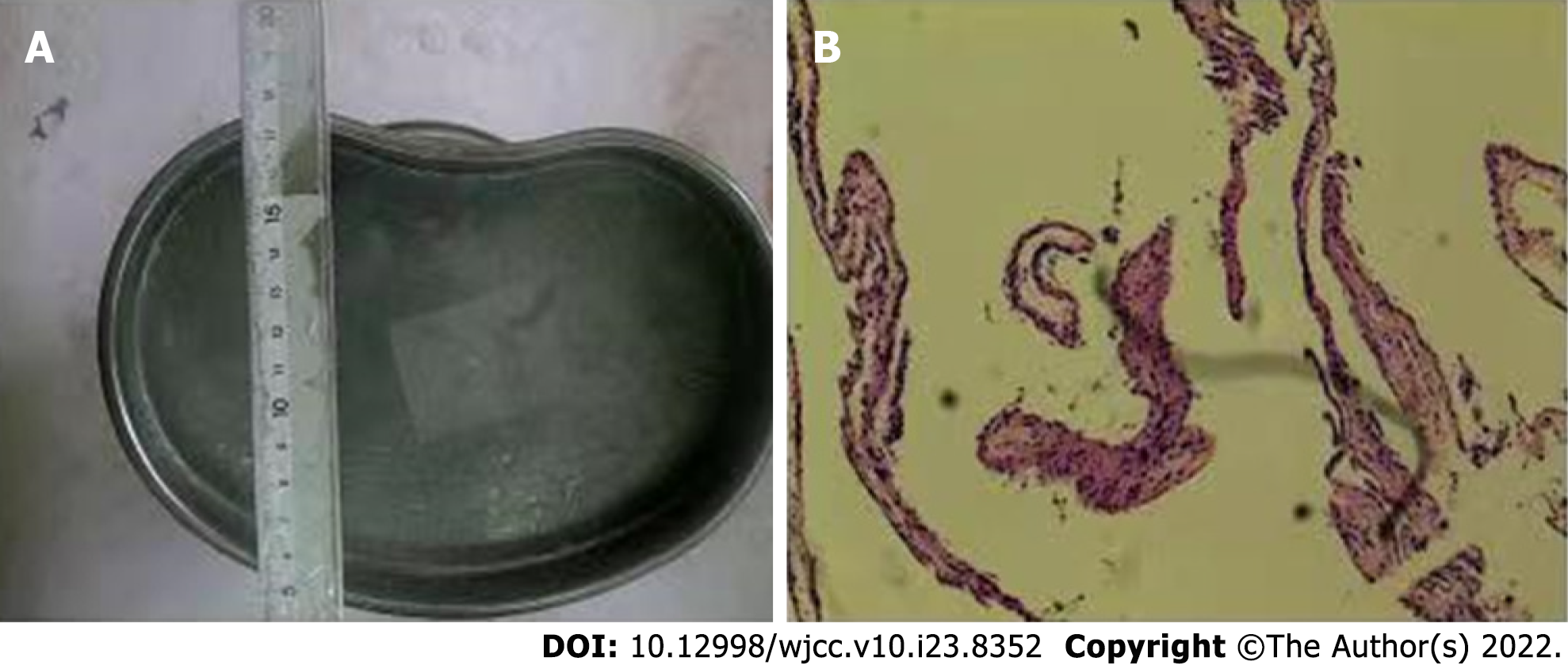
Figure 3 Pathological examination of the tumor tissue.
A: Gray tissue with a diameter of 0.2 cm was observed; B: Immunohistochemical results revealed an arachnoid cyst on hematoxylin-eosin staining.
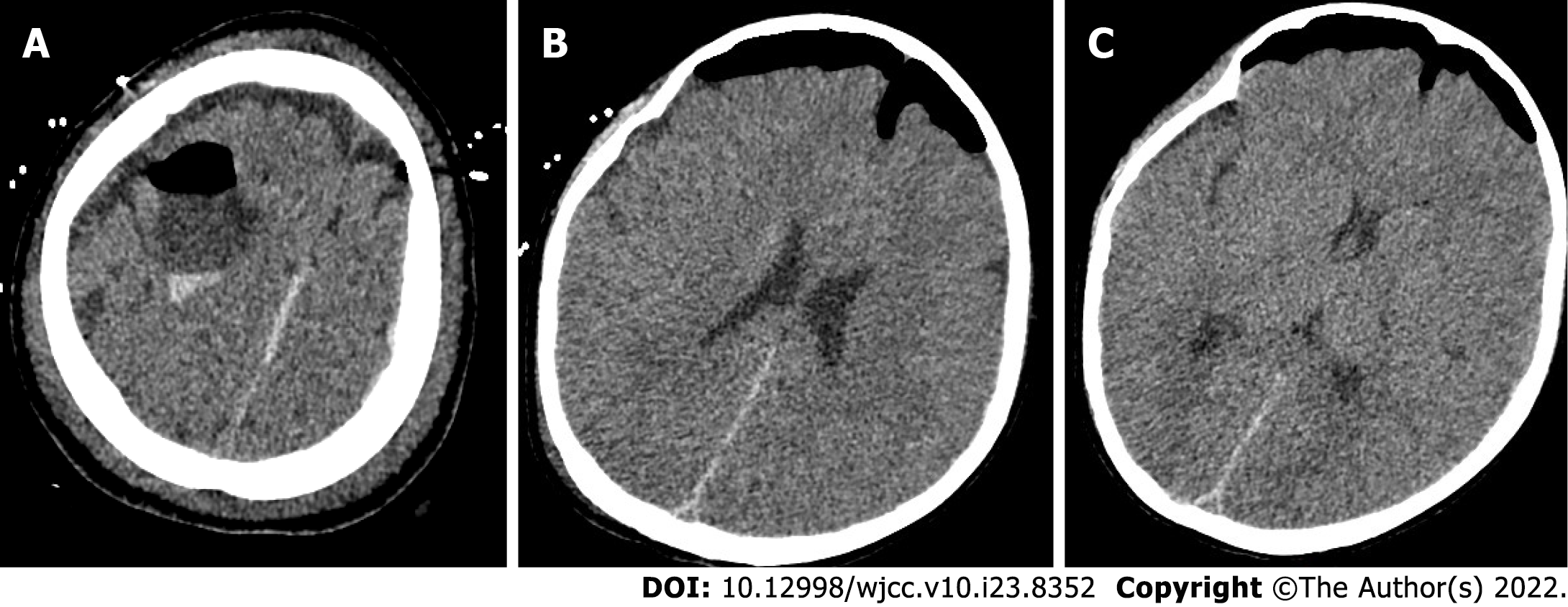
Figure 4 Postoperative head computed tomography.
A: The local bone of the right frontal area showed postoperative changes; B: The pressure in the arachnoid cyst was released; C: Right lateral ventricle and the brain tissue that was compressed and deformed before surgery gradually rebounded.
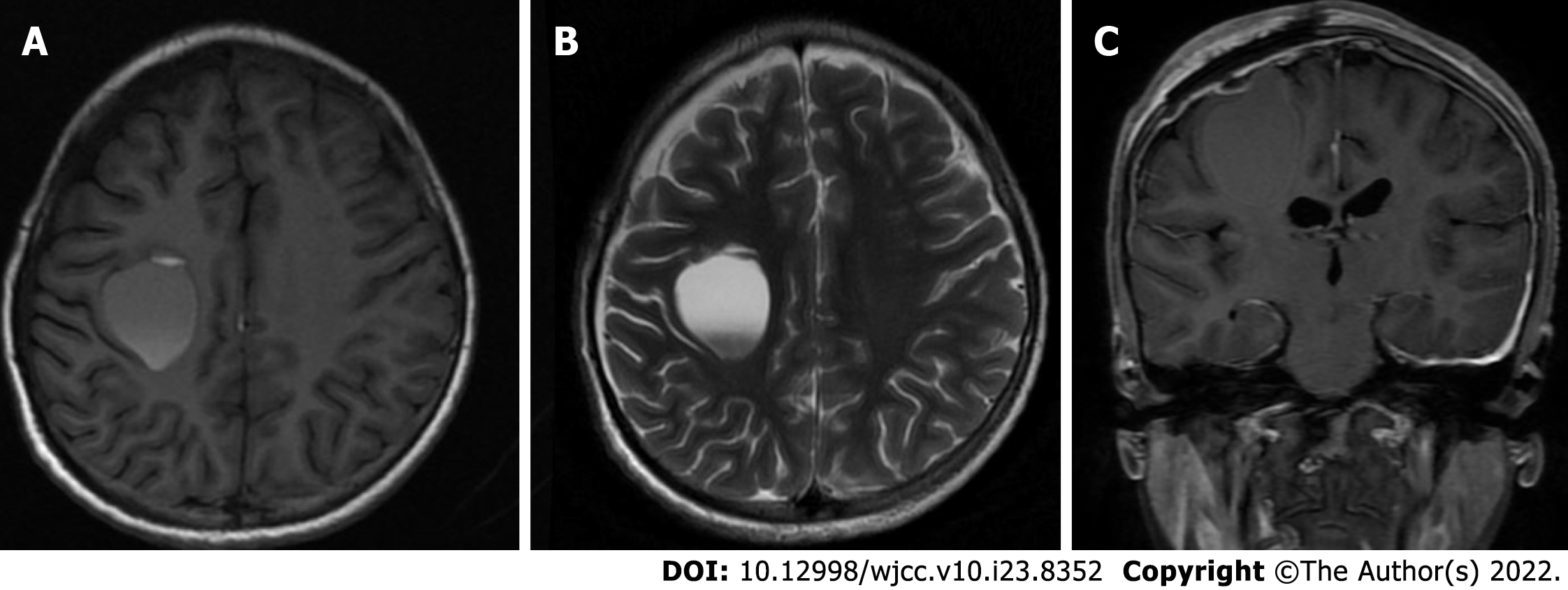
Figure 5 Imaging changes during patient follow-up.
A: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examination show the cystic shadow in the surgical area was significantly smaller than that before surgery; B: Long T2-weighted imaging MRI signal showed a capsule shadow and was approximately 23.8 mm × 30.0 mm × 28.5 mm; C: Lateral ventricle and the brain tissue that was compressed before surgery furtherly rebounded.
- Citation: Li WC, Li ML, Ding JW, Wang L, Wang SR, Wang YY, Xiao LF, Sun T. Incontinentia pigmenti with intracranial arachnoid cyst: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(23): 8352-8359
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i23/8352.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i23.8352