Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 16, 2022; 10(23): 8344-8351
Published online Aug 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i23.8344
Published online Aug 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i23.8344
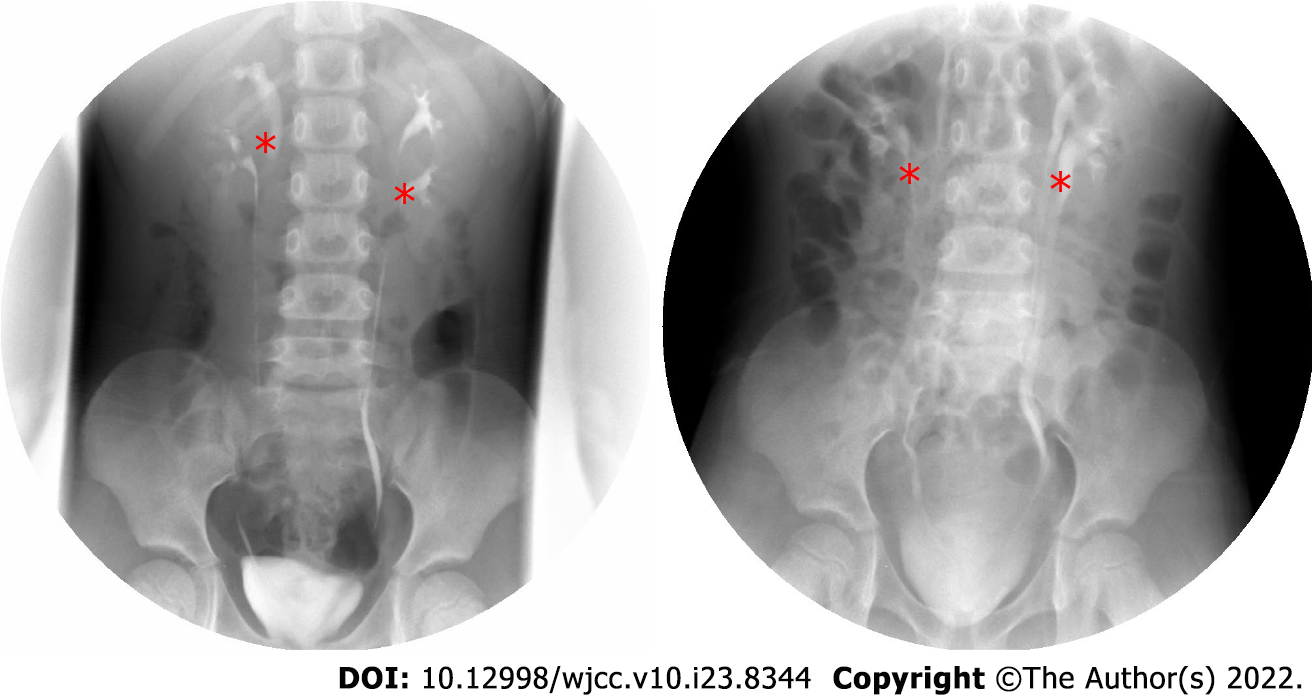
Figure 1 Intravenous urography.
The left side image was taken before operation. The right side image was taken three months after the operation. The double renal pelvis and double ureter malformations were identified by asterisk, and bilateral ureters were unobstructed and no hydronephrosis was found after operation.
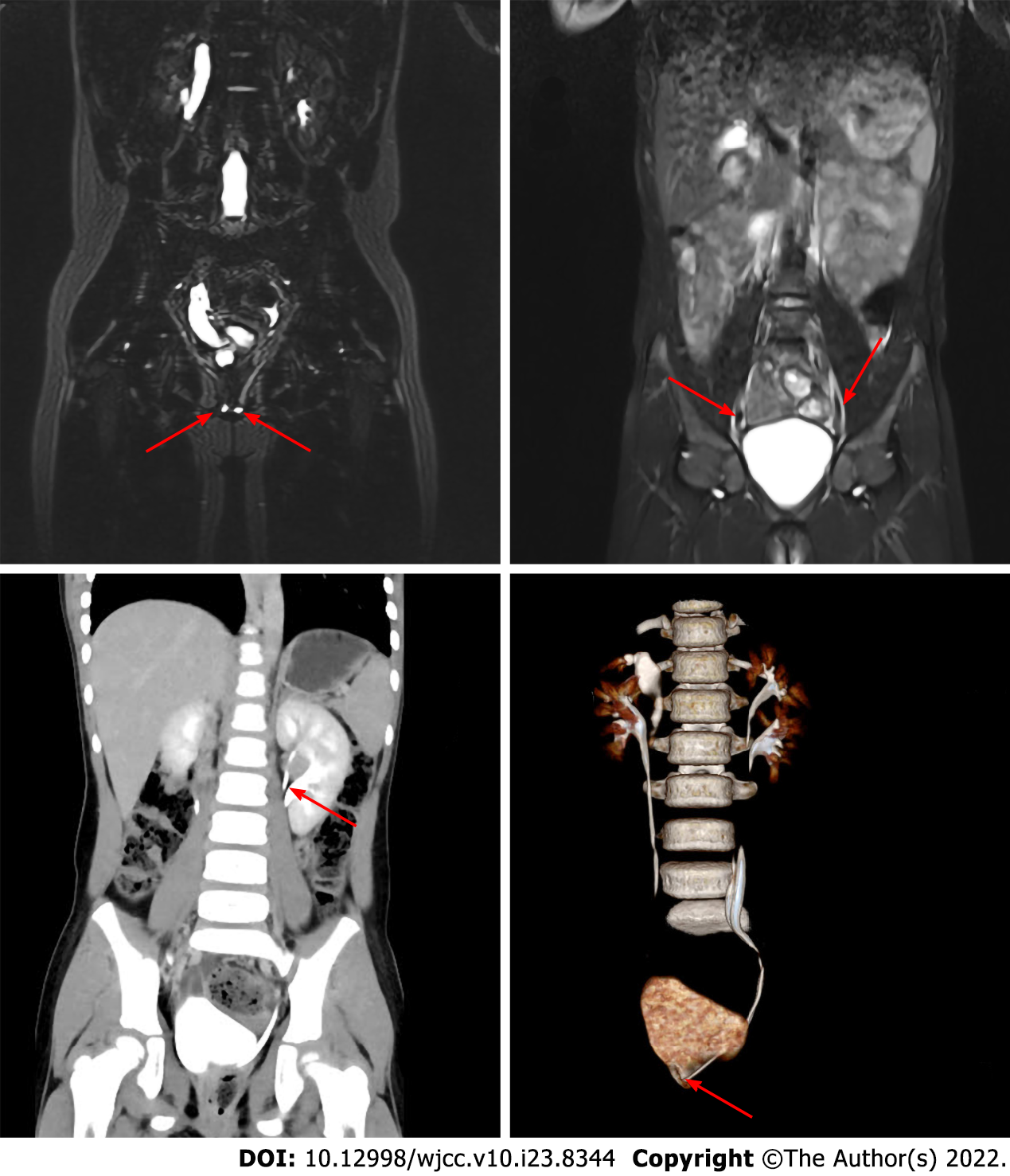
Figure 2 Imaging data.
A and B show abdomen magnetic resonance imaging, C and D show abdomen enhanced computed tomography. A: The arrow shows ectopic ureteral orifice; B: The arrow shows ureteral duplication; C: The arrow shows the duplication of the renal pelvis; D: The arrow shows the ectopic opening of the ureter.
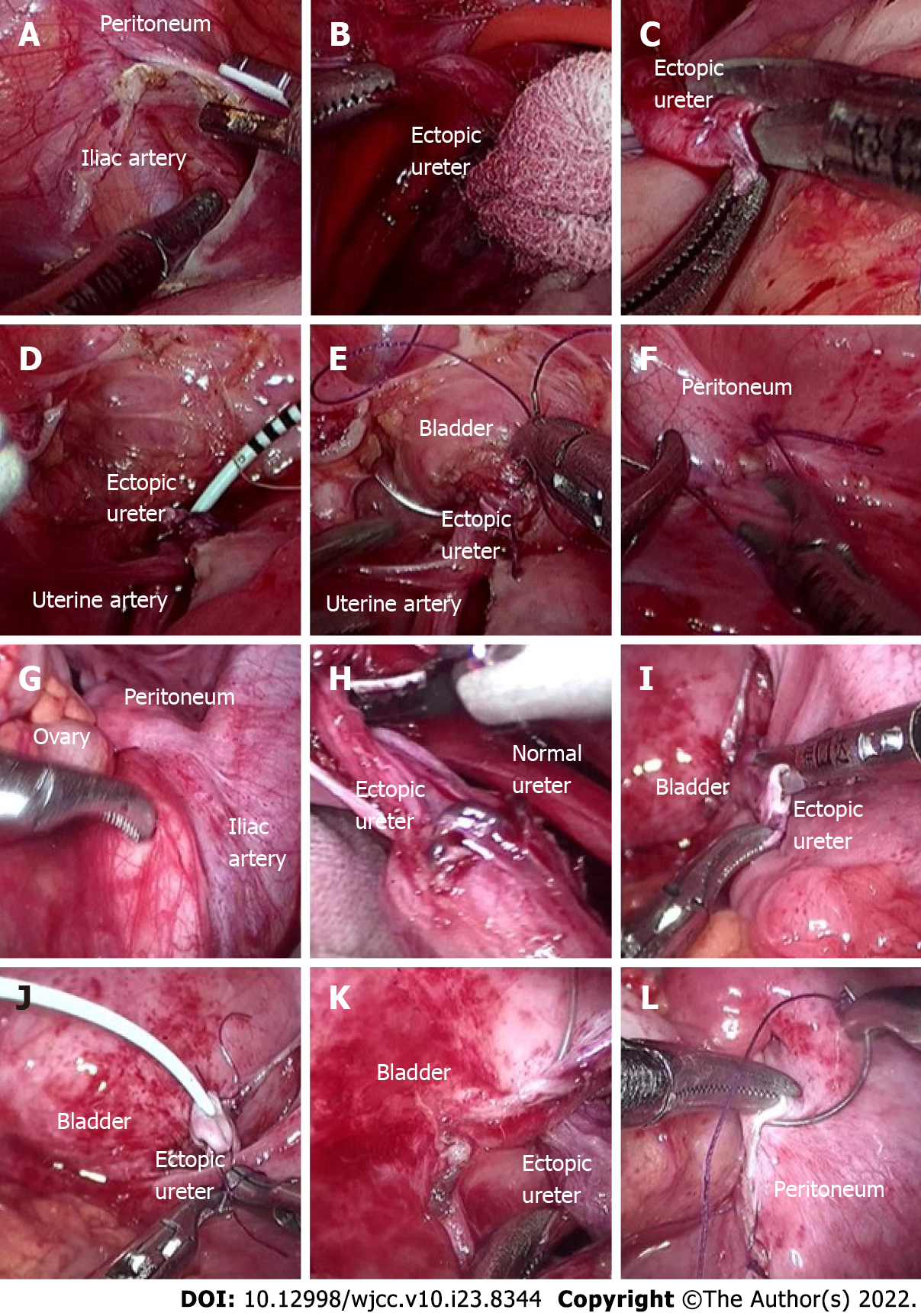
Figure 3 Intraoperative imaging.
A-F show left ureter operation, and G-L show right ureter operation. The operation process of right and left side was similar. A: The peritoneum was cut beside the iliac artery; B: Two parallel ureters on the left side were found and dissociated; C: The ectopic ureter was cut off, and the broken end was trimmed. The 1.5 cm ureter was turned out in sleeve shape to form "nipple"; D: A 5 Fr ureteral stent (D-J tube) was inserted through the broken end of the ureter; E: The bladder was filled with 200 mL normal saline through the catheter. Then the ectopic ureter was completely released from the pelvic peritoneal, the lateral posterior wall of the bladder was fully incised about 1.0 cm, and the urine in the bladder was sucked out. Then, the ureteral "nipple" was completely inserted into the bladder through the incision of the lateral posterior wall of the bladder. Finally, 4-0 absorbable suture was used to intermittently suture the bladder incision and ureteral "nipple", with a total of 4-6 stitches. One or two stitches were used to reinforce the bladder seromuscular layer; F: 4-0 absorbable suture was used to continuously suture the pelvic peritoneal incision, and the bladder ureteral anastomosis was wrapped outside the peritoneum.
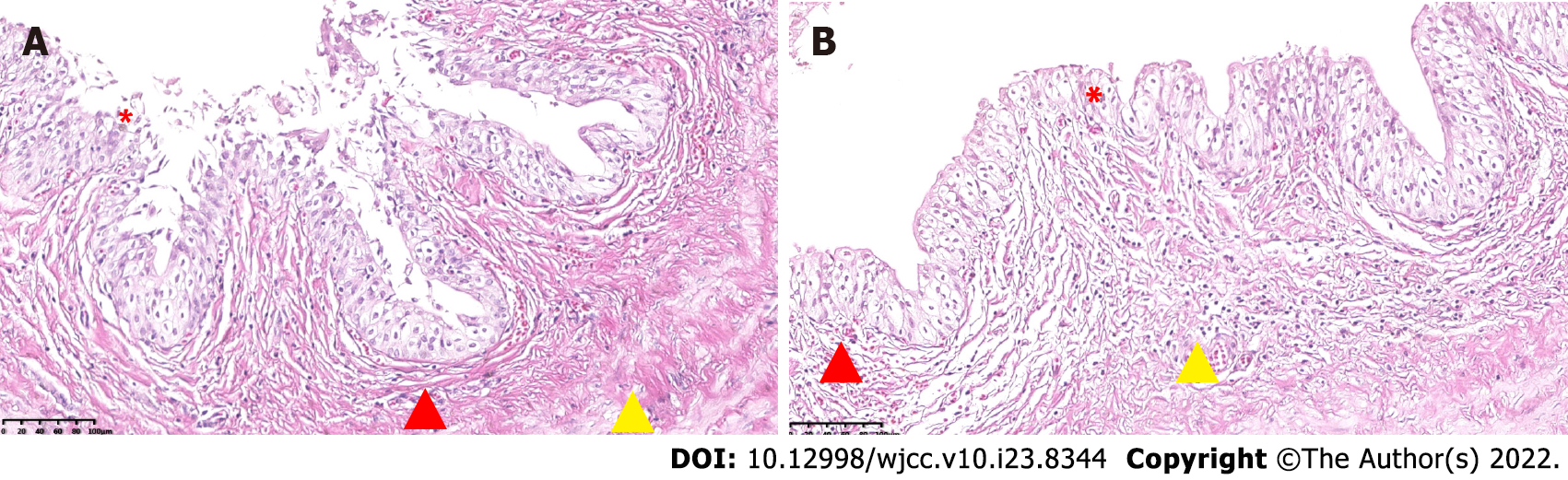
Figure 4 Pathological results.
A and B: The left and right renal pelvis pathological results. The wall of the sample tube is lined with urothelium (by asterisk), there is little inflammatory cell infiltration in the stroma (by triangle in red), and the blood vessels are congested (by triangle in yellow) (HE, 20 ×).
- Citation: Wang SB, Wan L, Wang Y, Yi ZJ, Xiao C, Cao JZ, Liu XY, Tang RP, Luo Y. Laparoscopic treatment of bilateral duplex kidney and ectopic ureter: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(23): 8344-8351
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i23/8344.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i23.8344