Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 15, 2003; 9(12): 2711-2714
Published online Dec 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i12.2711
Published online Dec 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i12.2711
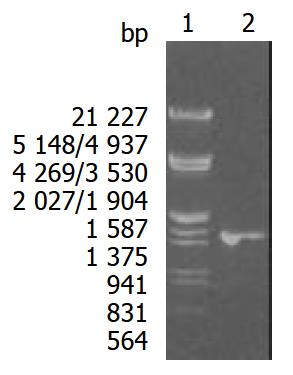
Figure 1 Eight g·L-1 agarose gels electrophoreses of Hsp60 DNA fragment amplified by PCR from H pylori.
Lane1: Nucleotide marker, Lane2: PCR products.
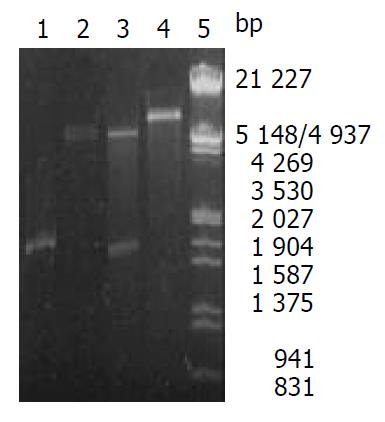
Figure 2 Identification of recombinant plasmid by restriction enzyme digestion.
Lane1: PCR products, Lane2: pET22b (+)/ Not I, Lane3: Recombinant plasmid/Not I and Nco I, Lane4: Recombinant plasmid/Not I, Lane5: Nucleotide marker.
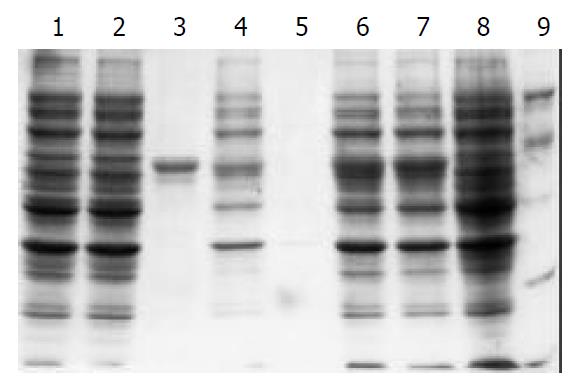
Figure 3 100 g·L-1 SDS-PAGE analysis of the fusion protein expressed in BL21(DE3).
Lane1: control strain BL21(pET) be-fore induction, Lane2: control strain BL21(pET) after 3 h in-duction with IPTG, Lane3: purified recombinant protein Hsp60, Lane4: sonicated supernatant of BL21(pET-Hsp60) cells after 3 h induction with IPTG, Lane5: BL21(pET-Hsp60) cell periplasm protein after 3 h induction with IPTG, Lane6: BL21 (pET- Hsp60) cells after 5 h induction with IPTG, Lane7: BL21 (pET- Hsp60) cells after 3 h induction with IPTG, Lane8: BL21 (pET-Hsp60) cells before induction, Lane9: molecular weight marker (20,30,43,67,94)×103
-
Citation: Bai Y, Li LR, Wang JD, Chen Y, Jin JF, Zhang ZS, Zhou DY, Zhang YL. Expression of
Helicobacter pylori Hsp60 protein and its immunogenicity. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(12): 2711-2714 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i12/2711.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i12.2711