Copyright
©The Author(s) 2002.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 15, 2002; 8(1): 135-138
Published online Feb 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i1.135
Published online Feb 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i1.135
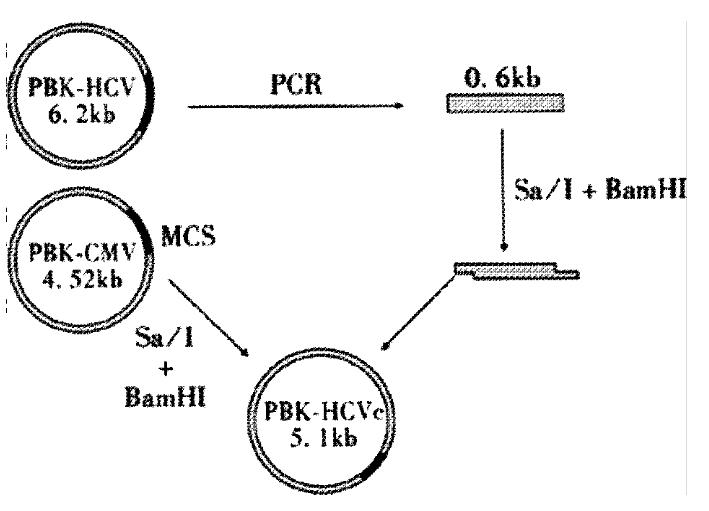
Figure 1 Construction of plasmid PBK-HCVC.
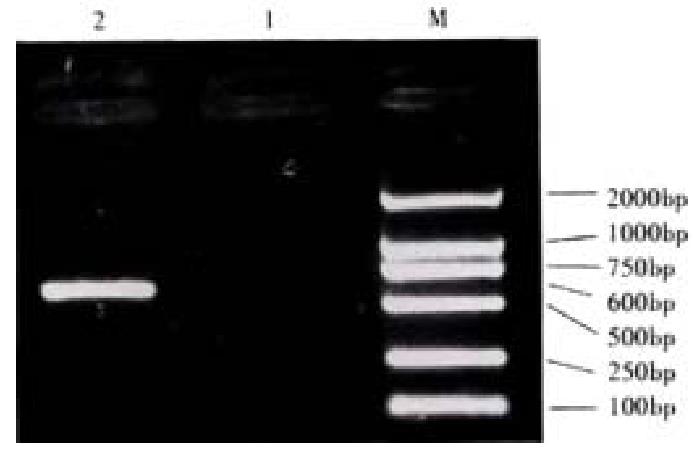
Figure 2 Electrophoretic analysis of PCR product.
M:Marker DL2000; 1:Negative control; 2:PCR product
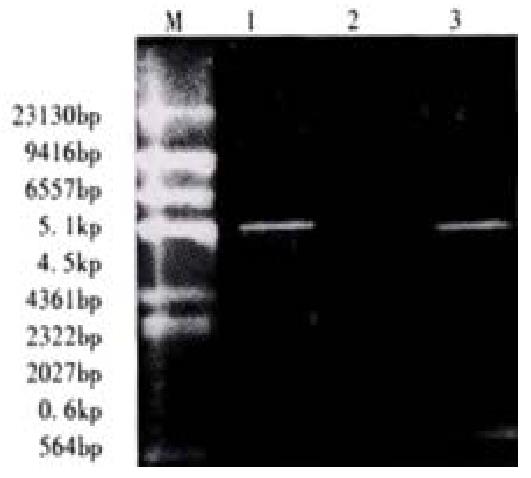
Figure 3 The restriction mapping of PBK-HCVC.
M: Maker; ëDNA/Hind¢ó; 1:PBK-CMV; 2:PBK-HCVC; 3:PBK-HCVC restricted by SalI and BamHI
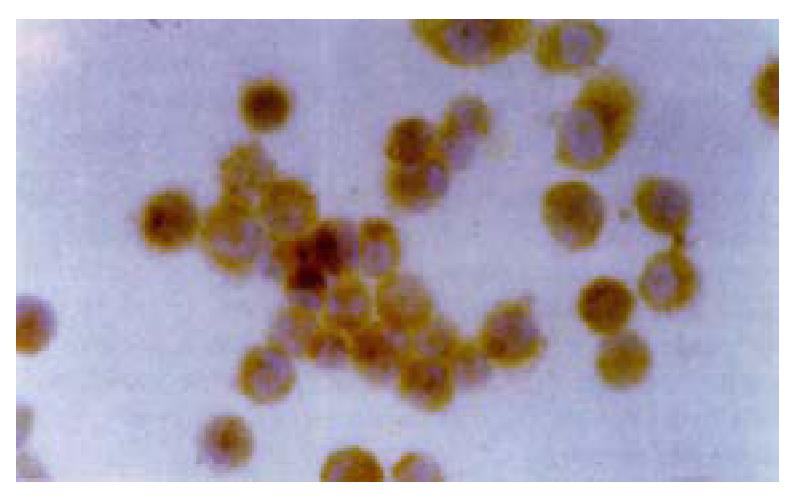
Figure 4 Detection of expressed HCV C antigen by immunocytochemistry.
× 200
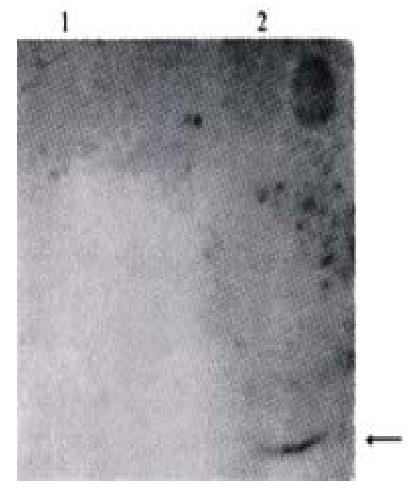
Figure 5 Western blotting detection of the expressed HCV-C protein.
1:Transfected QBC939 cells with PBK-CMV£» 2:Transfected QBC939 cells with PBK-HCVC
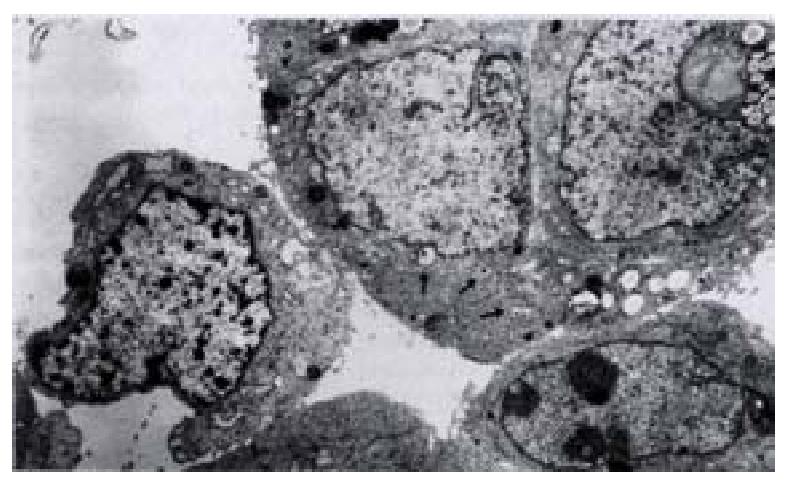
Figure 6 Morphology of QBC939-HCVC cells by TEM.
× 6500
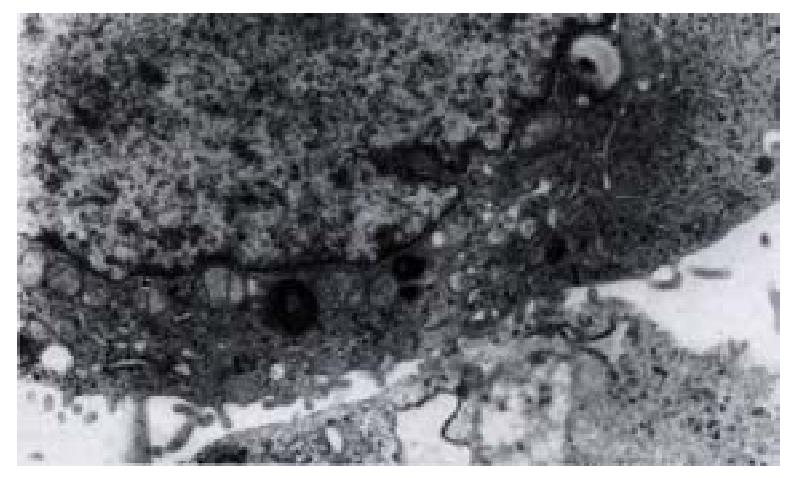
Figure 7 Morphology of QBC939-HCVC cells by TEM.
× 60000
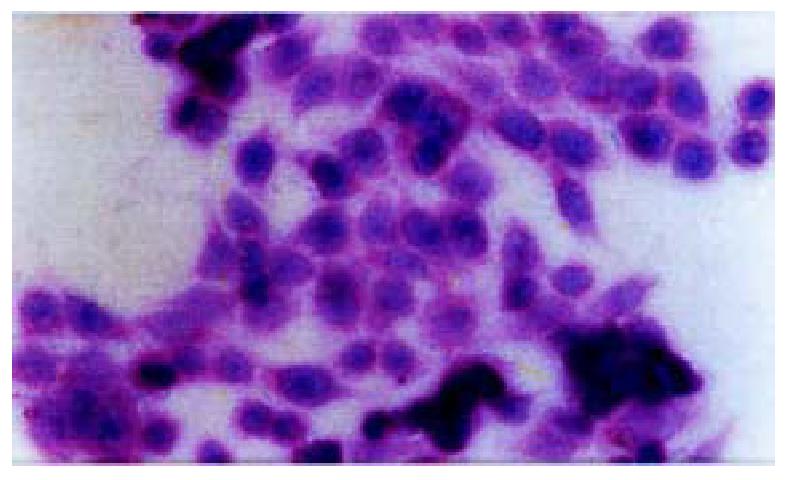
Figure 8 The morphologic alteration of the transfected cells HE.
× 200
- Citation: Liu XF, Zou SQ, Qiu FZ. Construction of HCV-core gene vector and its expression in cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2002; 8(1): 135-138
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v8/i1/135.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v8.i1.135