Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2020; 26(28): 4094-4107
Published online Jul 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i28.4094
Published online Jul 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i28.4094
Figure 1 Effect of thioacetamide and celecoxib on liver fibrosis.
A: Macroscopic analysis of liver tissue. Celecoxib improved pathological changes in the liver, as shown by hematoxylin-eosin and Sirius red (SR) staining (original magnification: × 100; scale bar = 400 μm); B: Ishak’s score based on histology and SR staining as well as alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, and hydroxyproline levels. The data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 15, aP < 0.05 vs TAA + celecoxib group; bP < 0.01 vs control group). TAA: Thioacetamide; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; HE: Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
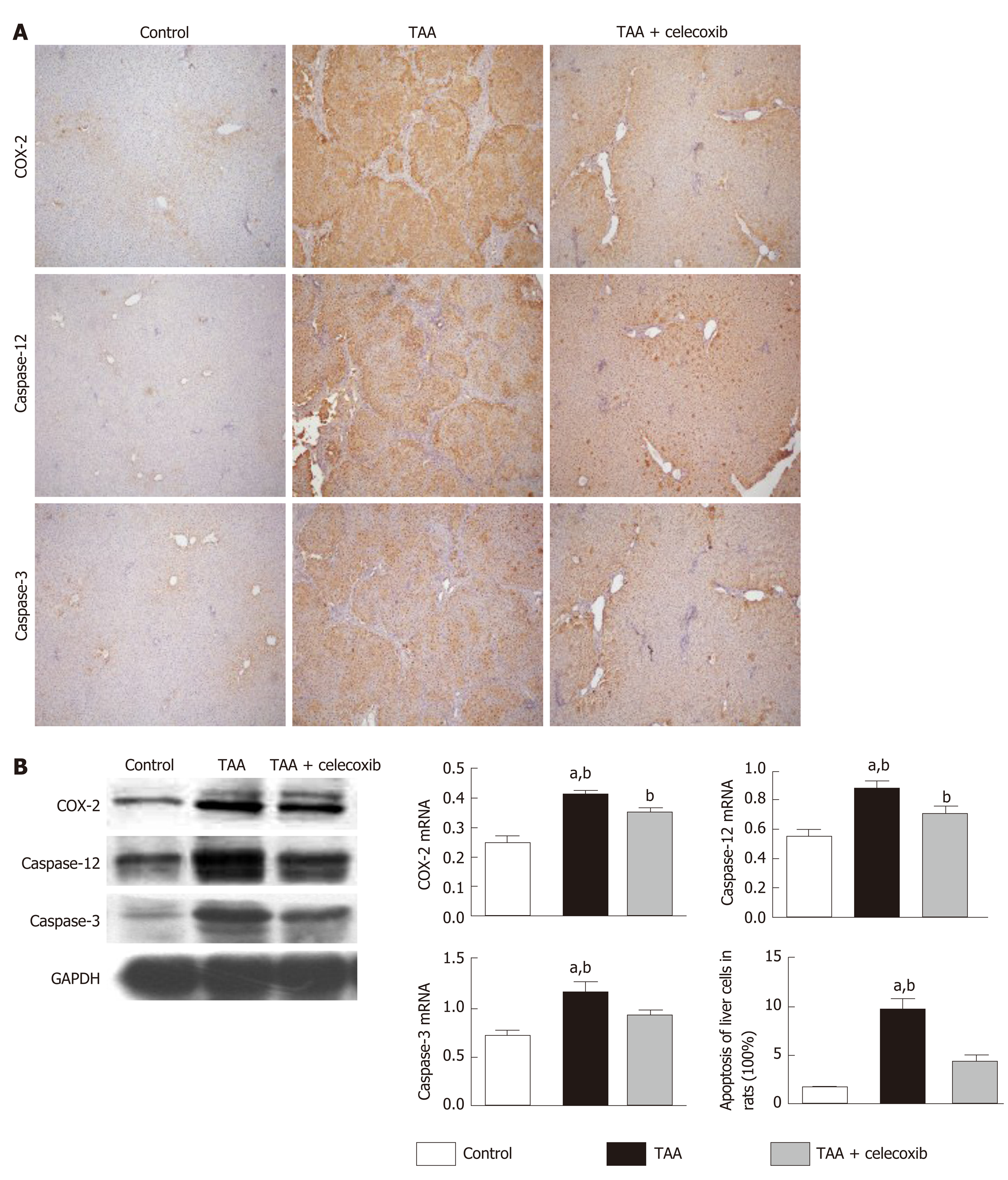
Figure 2 Celecoxib inhibits apoptosis of hepatocytes and expression of caspase-3 and caspase-12 in thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis.
A: Immunohistochemical staining (100 ×) for collagen III, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), caspase-12, and caspase-3 in the three groups of rats. Positive rates were analyzed using Image-Pro Plus 6.0. The data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 15, aP < 0.05 vs TAA + celecoxib group; bP < 0.01 vs control group). The scale bar is 200 μm; B: Western blot results showing collagen III, COX-2, caspase-3, and caspase-12 expression in the three groups. aP < 0.05 vs TAA + celecoxib group; bP < 0.01 vs control group. TAA: Thioacetamide; COX-2:Cyclooxygenase-2; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
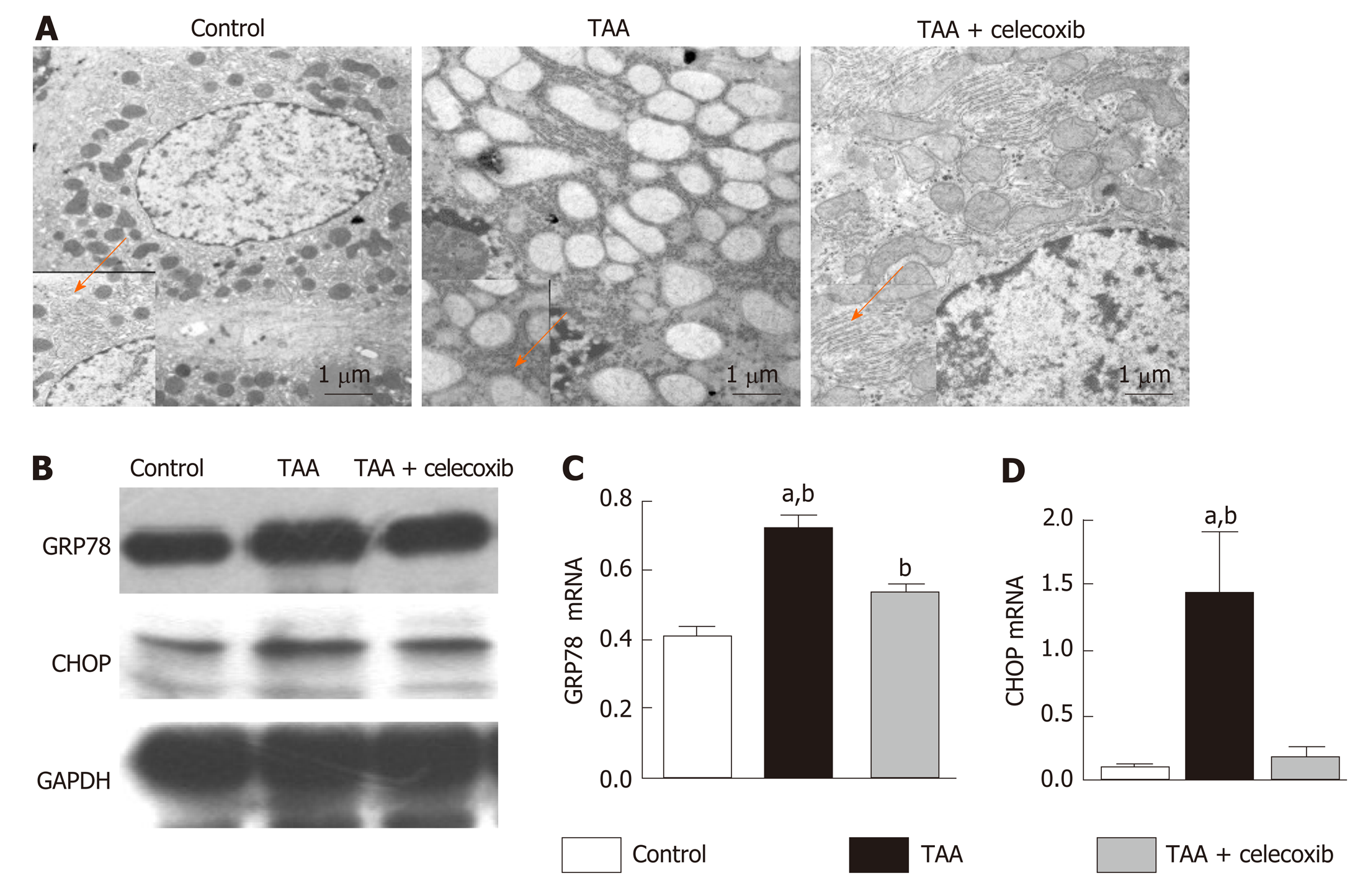
Figure 3 Celecoxib inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress.
A: Hepatocytes in the thioacetamide (TAA) and TAA + celecoxib groups (transmission electron microscopy, × 6000-10000); B: Hepatic glucose-regulated protein 78 and CCAAT/enhancer binding protein homologous protein expression measured by Western blot. n = 6/group; C and D: Quantitative Western blot results. aP < 0.05 vs TAA + celecoxib group; bP < 0.01 vs the control group. GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GRP78: Glucose-regulated protein 78; CHOP: CCAAT/enhancer binding protein homologous protein. TAA: Thioacetamide.
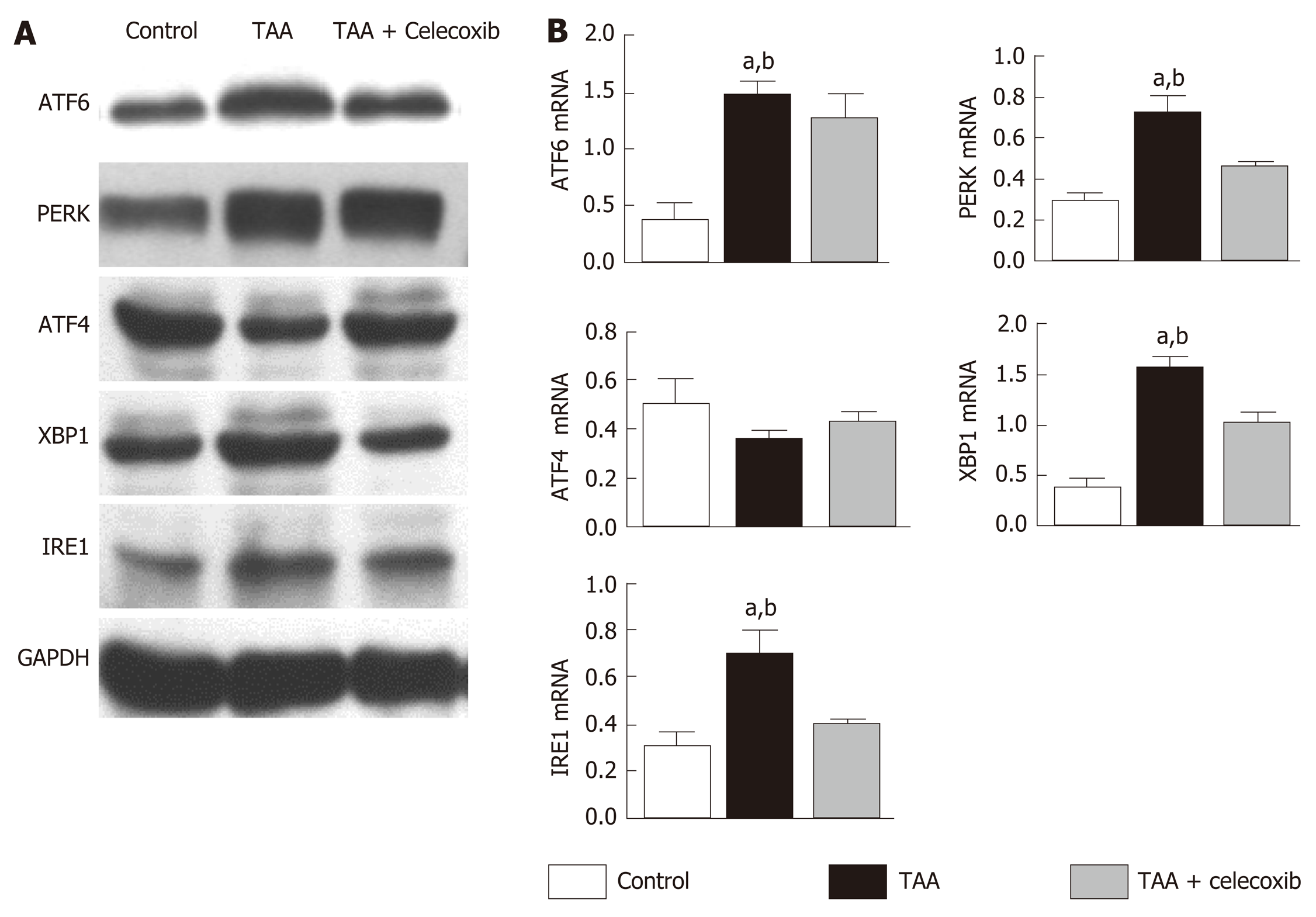
Figure 4 Celecoxib attenuates hepatocyte apoptosis by inhibiting the expression of unfolded protein response-related pathway proteins.
A: Hepatic activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6), PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum protein kinase, ATF4, X-box binding protein-1, and inositol-requiring enzyme 1 protein expression measured by Western blot. n = 6/group; B: Quantitative Western blot results. aP < 0.05 vs TAA + celecoxib group; bP < 0.01 vs control group. GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; ATF6: Activating transcription factor 6; PERK: PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum protein kinase; XBP1: X-box binding protein-1; IRE1: Inositol-requiring enzyme 1; TAA: Thioacetamide.
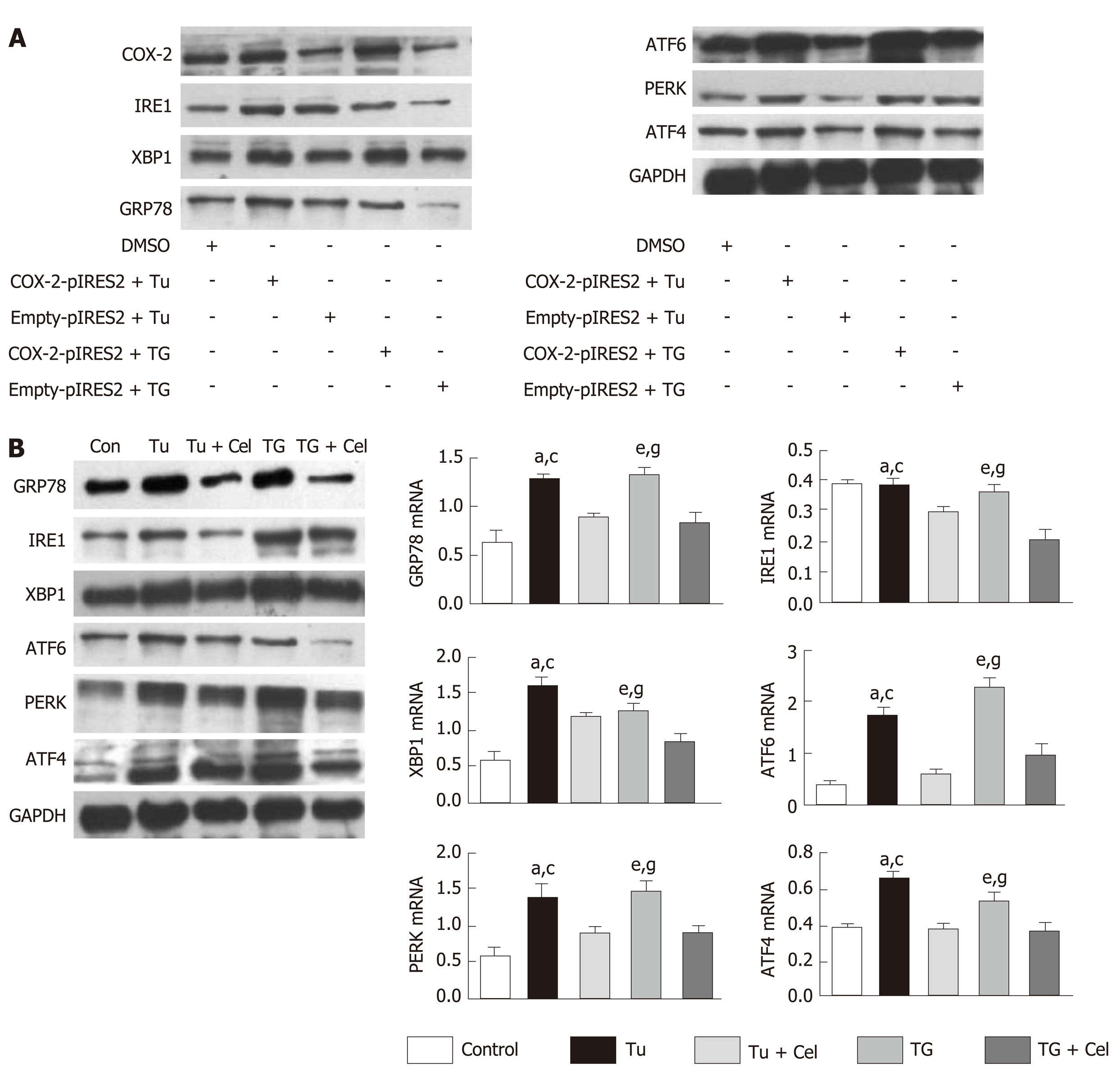
Figure 5 Celecoxib regulates the endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling pathway.
A: Western blot analysis of glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78), inositol enzyme 1 (IRE1), X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1), activated transcription factor 6 (ATF6), PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum protein kinase (PERK), and ATF4 levels in L02 cells transfected with a cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) expressing plasmid and treated with endoplasmic reticulum stress inducers tunicamycin (Tu) and thapsigargin (TG); B: Western blot analysis of GRP78, IRE1, XBP1, ATF6, PERK and ATF4 levels in LO2 cells treated with celecoxib and/or Tu and TG. aP < 0.05 between Tu group and control group, cP < 0.05 between Tu group and Tu + celecoxib group, eP < 0.05 between TG group and control group, gP < 0.05 between TG group and control group TG + celecoxib group (n = 6). Con: Control; Tu: Tunicamycin; TG: Thapsigargin; Tu + Cel: Tu + celecoxib; TG + Cel: TG + celecoxib; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GRP78: Glucose-regulated protein 78; ATF6: Activating transcription factor 6; PERK: PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum protein kinase; XBP1: X-box binding protein-1; IRE1: Inositol-requiring enzyme 1; TAA: Thioacetamide; COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2.
- Citation: Su W, Tai Y, Tang SH, Ye YT, Zhao C, Gao JH, Tuo BG, Tang CW. Celecoxib attenuates hepatocyte apoptosis by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress in thioacetamide-induced cirrhotic rats. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(28): 4094-4107
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i28/4094.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i28.4094