Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2024; 16(4): 1532-1546
Published online Apr 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1532
Published online Apr 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1532
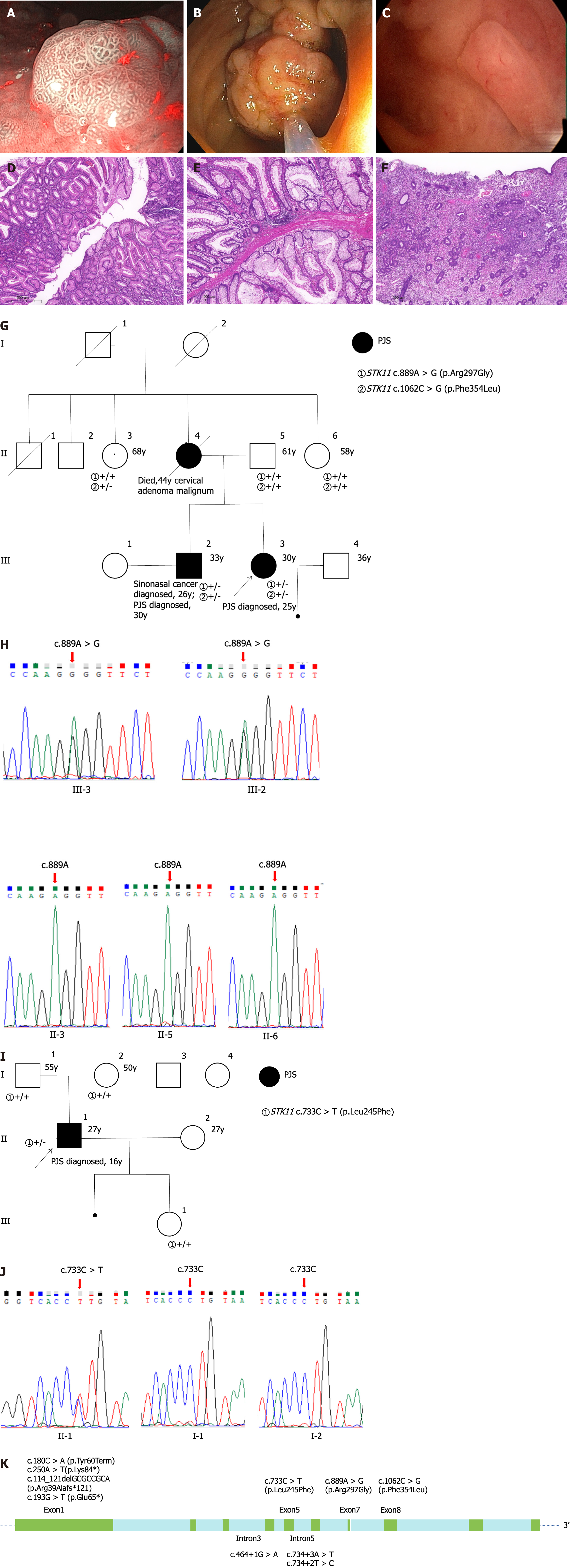
Figure 1 Clinical features and sequencing data of patients with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome.
A-F: Polyps and hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining of a patient with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (PJS). Gastroenteroscopy and hysteroscopy revealed and resected multiple polyps in the stomach, intestines, and uterus. Gastric polyp and HE (A and D), colon polyp and HE (B and E), endometrial polyp and HE (C and F), magnification, 5 × (D-F); G-J: Family pedigree and sequencing maps of two missense STK11 variants of uncertain significance (VUS) in two PJS patients; Family pedigree of a female patient with PJS who had STK11 c.889A>G (VUS) and c.1062C>G (likely benign) variations (G); The patient and her older brother had STK11 c.889A>G variation, but her father and two aunts were undetected (H); Family pedigree of a male patient with PJS who had STK11 c.733C>T (VUS) variations (I); The patient had STK11 c.733C>T variations, but his father and mother were undetected (J); K: Schematic representation of the STK11 gene structure and variations in 9 PJS families. Arg: Arginine; Gly: Glycine; Phe: Phenylalanine; Leu: Leucine; y: Years; Tyr: Tyrosine; Term: Termination; Lys: Lysine; del: Deletion; Glu: Glutamic acid.
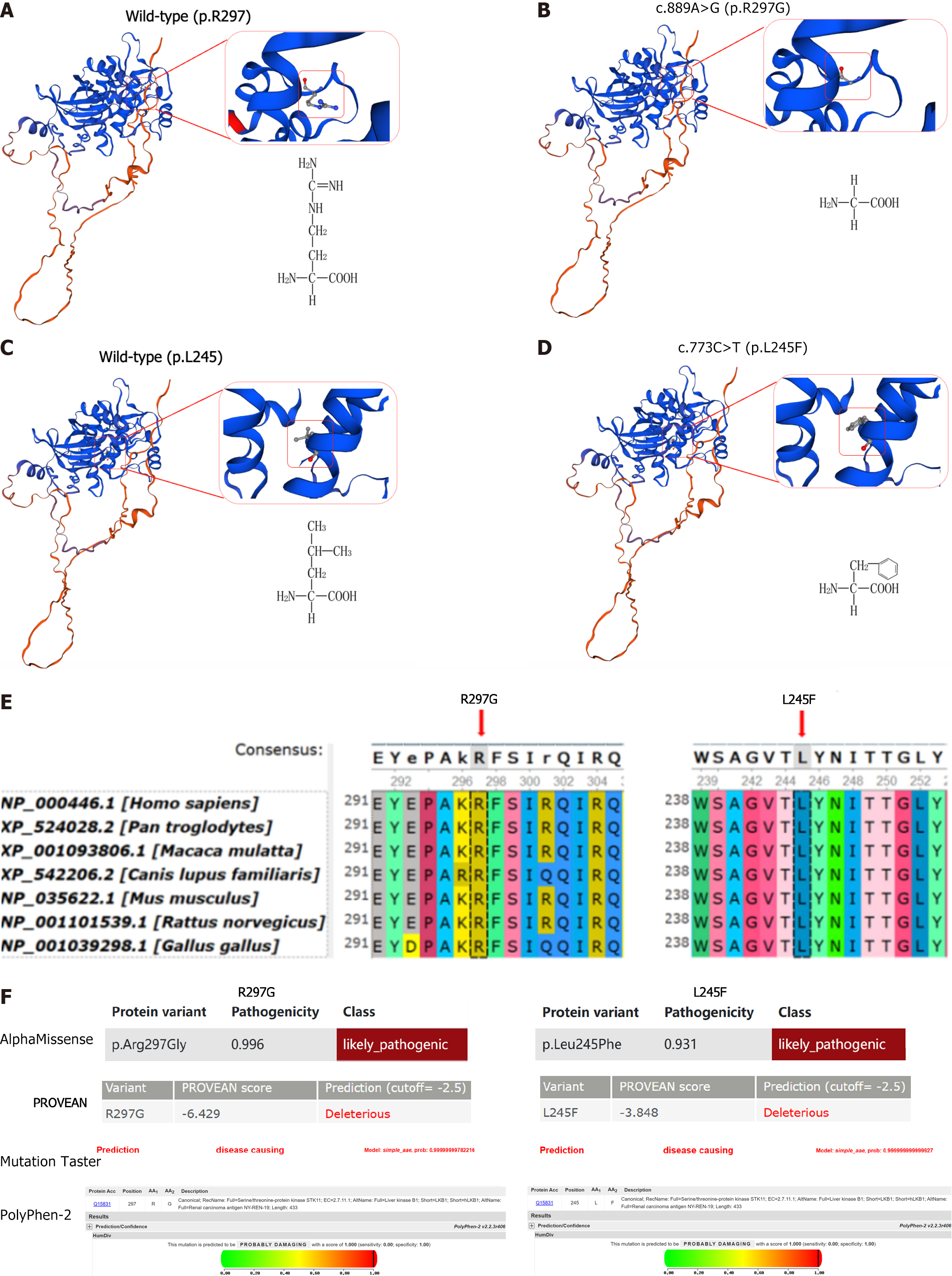
Figure 2 Multiple software predict the pathogenicity of these variations.
A-D: Three-dimensional model of the protein structure of liver kinase B1 and amino acid molecular structure formula. These variations result in significant changes in the properties of amino acids, which may be harmful; E: Evolutionary conservation shows that the variation sites (p.R297G and p.L245F) are highly conserved across different species; F: Four software assessed the pathogenicity of these variations, all of which were likely pathogenic or pathogenic. “R” represents arginine; “G” represents glycine; “L” represents leucine; and “F” represents phenylalanine.
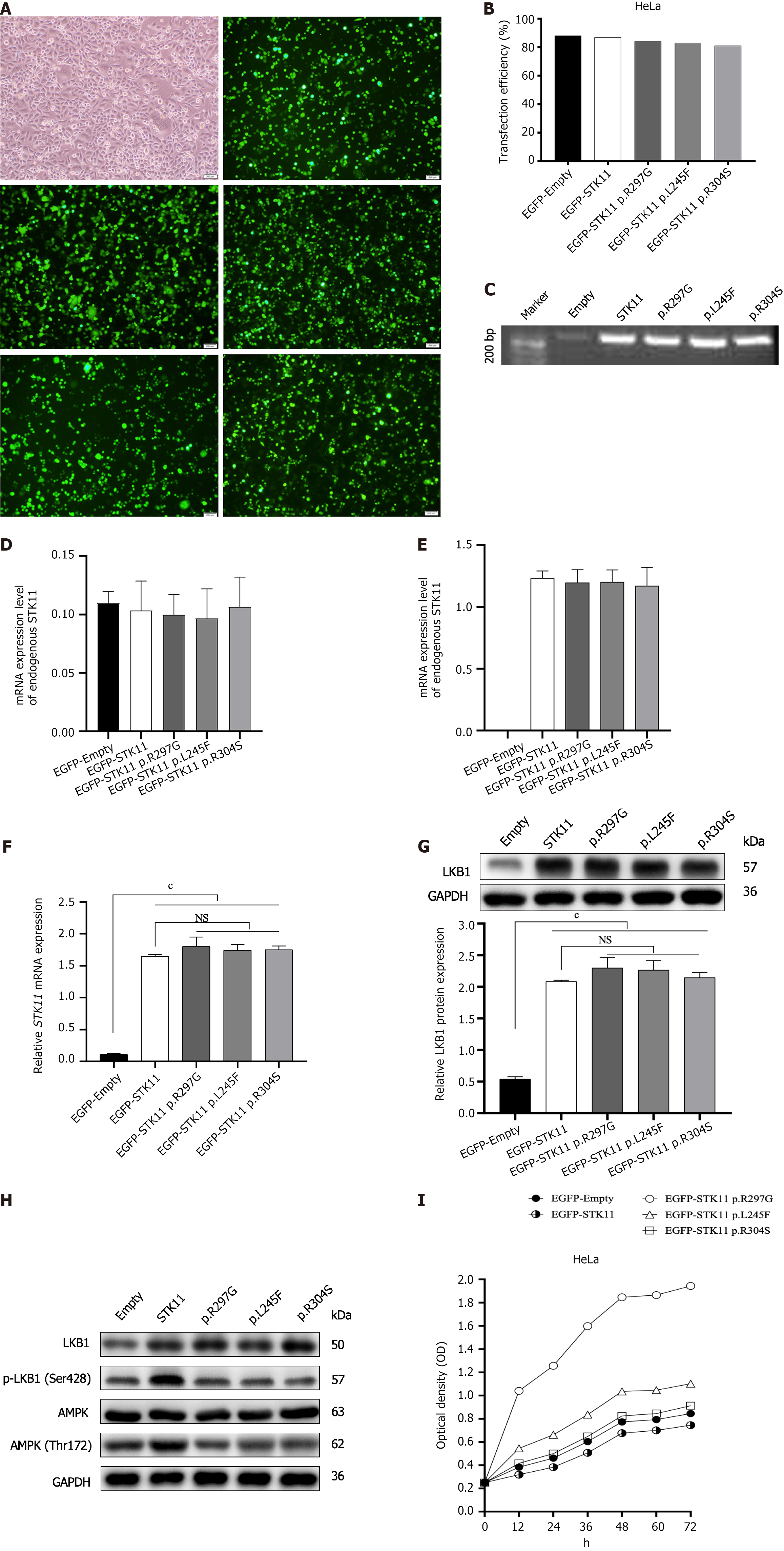
Figure 3 Expression and functional analysis of STK11.
A: Plasmids were successfully transfected into HeLa cells. HeLa cell-Lipofectamine 3000; and HeLa cell transfected with enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP)-Empty, EGFP-N1-STK11, EGFP-N1-STK11 c.889A>G (p.Arg297Gly), EGFP-N1-STK11 c.733C>T (p.Leu245Phe) and EGFP-N1-STK11 c.910C>T (p.Arg304Trp) plasmid vectors, Magnification: 10 ×; B: Plasmid transfection efficiency was high; C: PCR gel electrophoresis confirmed that the transfected plasmid was correct; D: The endogenous expression of STK11 gene was low in HeLa cells; E: The exogenous expression of STK11 gene in HeLa cells after transfection; F: These missense variants do not affect gene transcription; G: These variations do not affect the function of gene translation into proteins; H: These missense variants disrupted the phosphorylation of liver kinase B1 and adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; I: These missense variants promote cell proliferation, cP < 0.0001. “R” represents arginine; “G” represents glycine; “L” represents leucine; “F” represents phenylalanine; and “S” represents serine. Independent sample results were obtained after at least three experiments and then obtained statistically. NS: Not significant; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; LKB1: Serine/threonine kinase 11.
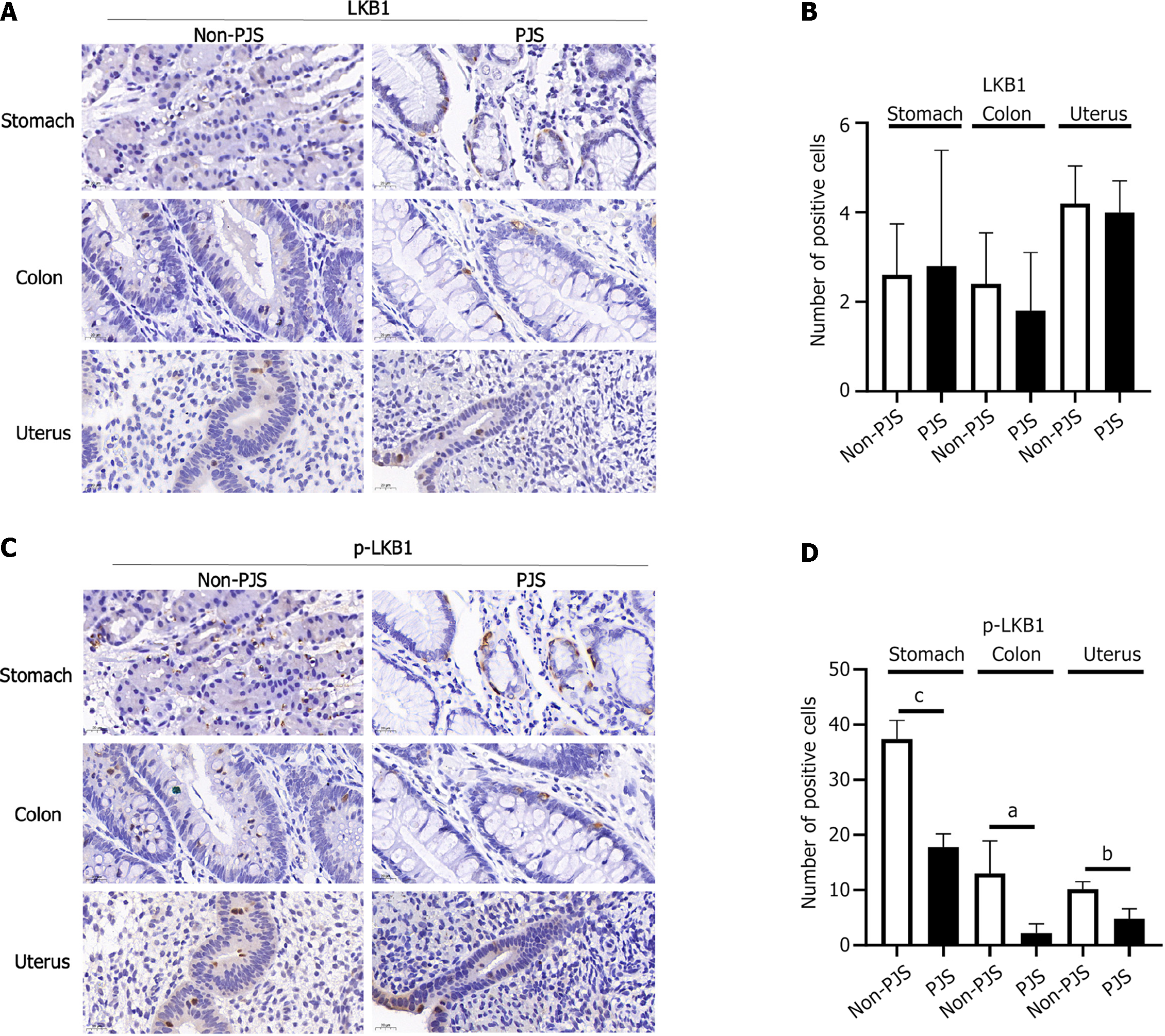
Figure 4 Expression of the serine/threonine kinase 11 in polyps of Peutz-Jeghers syndrome and non-Peutz-Jeghers syndrome patients.
A-D: The phosphorylation levels of liver kinase B1 in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (PJS) patients polyps were significantly lower than those in non-PJS patients polyps. PJS: Peutz-Jeghers syndrome; LKB1: Liver kinase B1. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.001; cP < 0.0001.
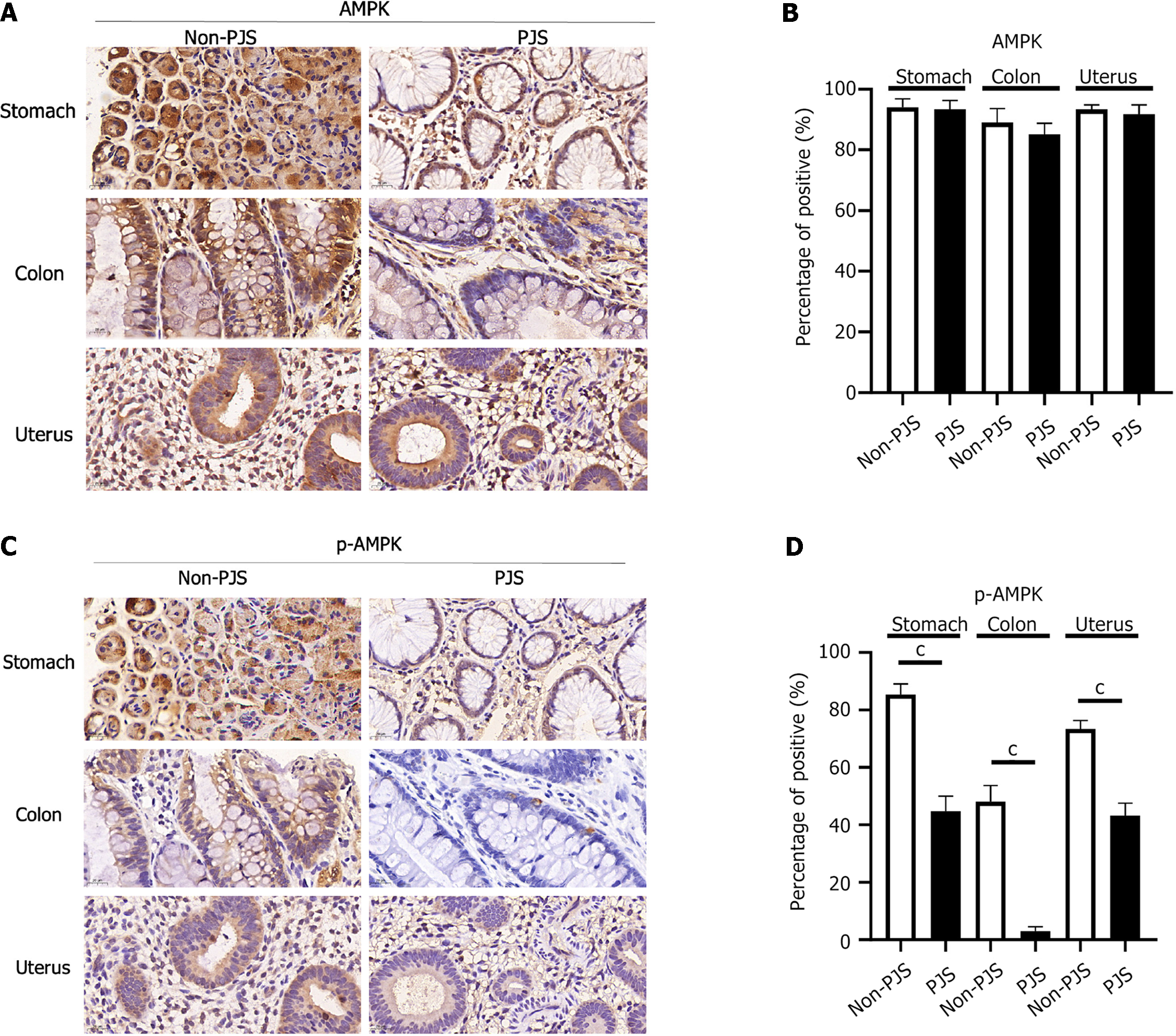
Figure 5 Expression of the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase in polyps of Peutz-Jeghers syndrome and non-Peutz-Jeghers syndrome patients.
A-D: The phosphorylation levels of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase in Peutz-Jeghers (PJS) patients polyps were significantly lower than those in non-PJS patients polyps. Magnification: 70 ×. Results of independent samples were calculated by using five randomly selected visual fields. Independent sample results were obtained after at least three experiments and then obtained statistically. PJS: Peutz-Jeghers syndrome; AMPK: Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase. cP < 0.0001.
- Citation: Liu J, Zeng SC, Wang A, Cheng HY, Zhang QJ, Lu GX. Two missense STK11 gene variations impaired LKB1/adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase signaling in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(4): 1532-1546
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i4/1532.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1532