Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2024; 16(4): 1532-1546
Published online Apr 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1532
Published online Apr 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1532
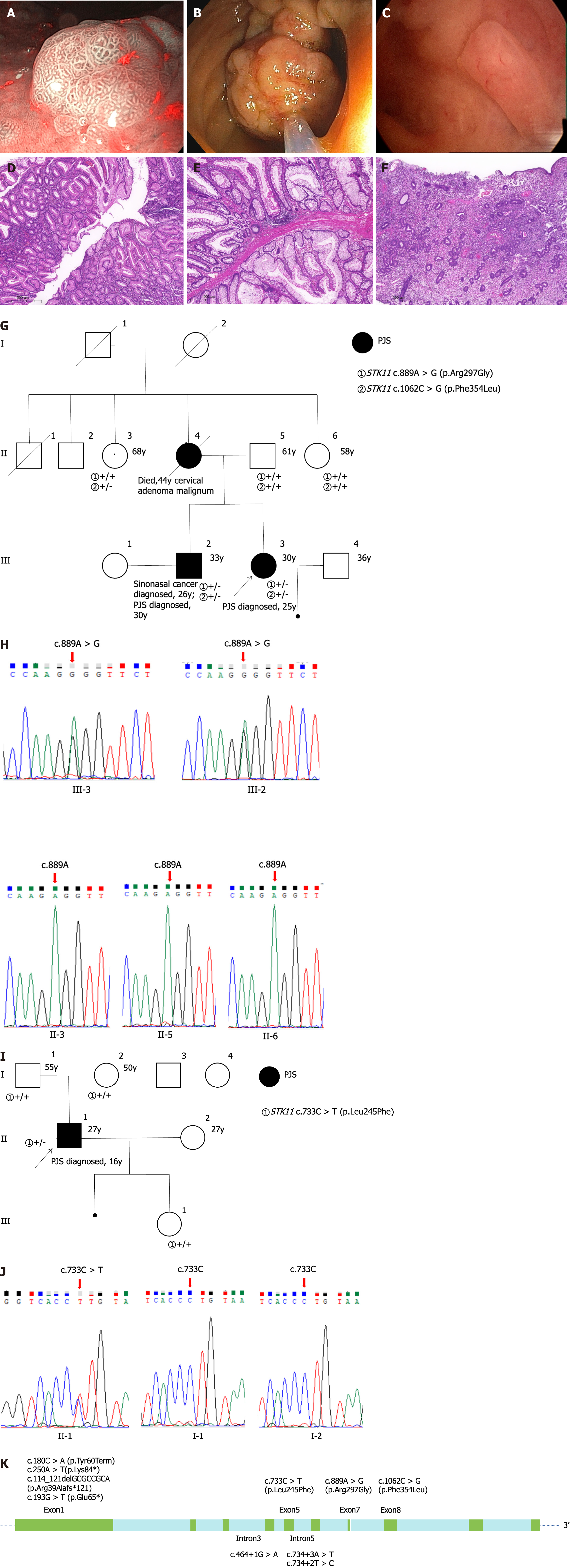
Figure 1 Clinical features and sequencing data of patients with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome.
A-F: Polyps and hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining of a patient with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (PJS). Gastroenteroscopy and hysteroscopy revealed and resected multiple polyps in the stomach, intestines, and uterus. Gastric polyp and HE (A and D), colon polyp and HE (B and E), endometrial polyp and HE (C and F), magnification, 5 × (D-F); G-J: Family pedigree and sequencing maps of two missense STK11 variants of uncertain significance (VUS) in two PJS patients; Family pedigree of a female patient with PJS who had STK11 c.889A>G (VUS) and c.1062C>G (likely benign) variations (G); The patient and her older brother had STK11 c.889A>G variation, but her father and two aunts were undetected (H); Family pedigree of a male patient with PJS who had STK11 c.733C>T (VUS) variations (I); The patient had STK11 c.733C>T variations, but his father and mother were undetected (J); K: Schematic representation of the STK11 gene structure and variations in 9 PJS families. Arg: Arginine; Gly: Glycine; Phe: Phenylalanine; Leu: Leucine; y: Years; Tyr: Tyrosine; Term: Termination; Lys: Lysine; del: Deletion; Glu: Glutamic acid.
- Citation: Liu J, Zeng SC, Wang A, Cheng HY, Zhang QJ, Lu GX. Two missense STK11 gene variations impaired LKB1/adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase signaling in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(4): 1532-1546
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i4/1532.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1532