Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2018; 24(23): 2468-2481
Published online Jun 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i23.2468
Published online Jun 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i23.2468
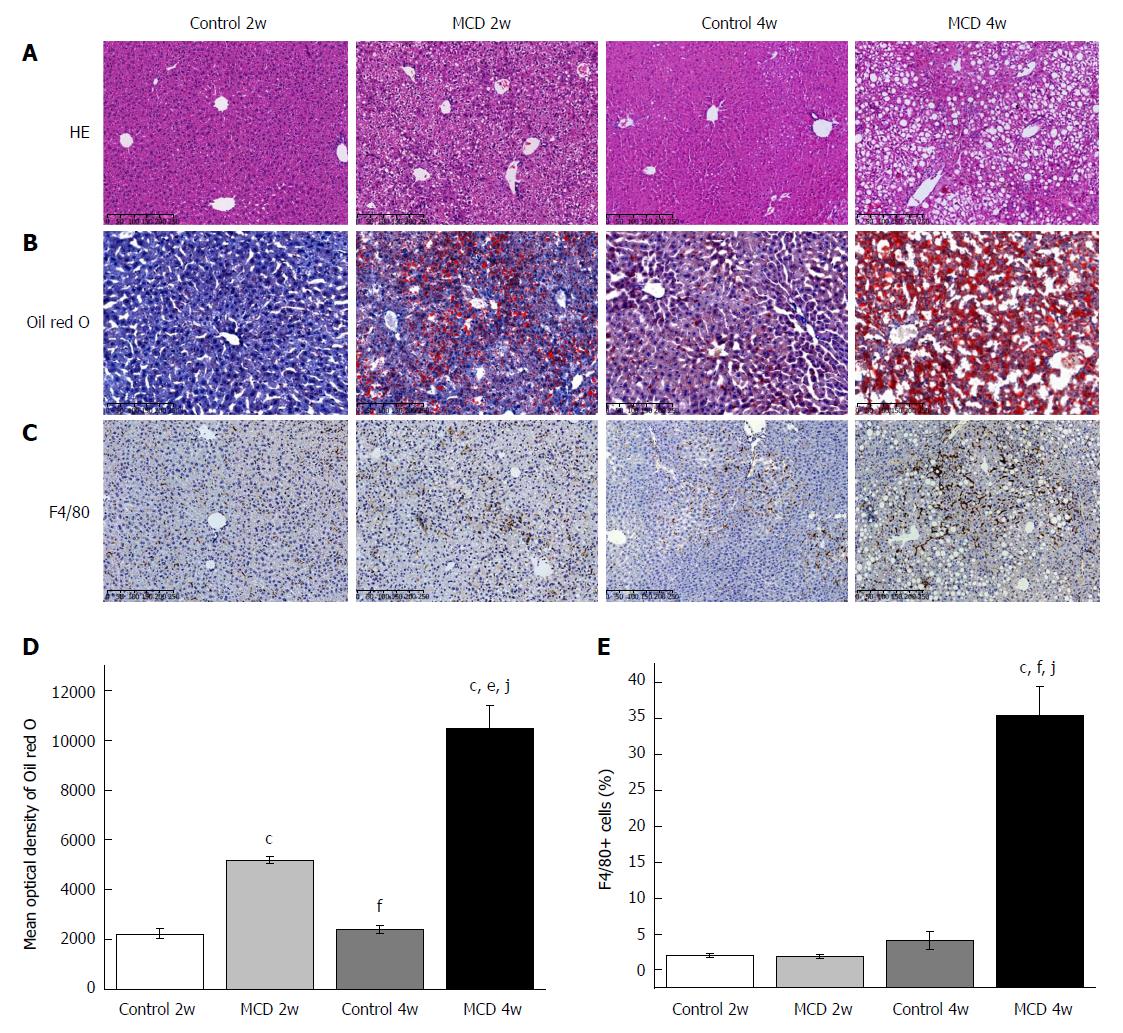
Figure 1 Methionine-choline-deficient diet induced hepatic injury, fat accumulation, and macrophage infiltration.
A-C: Representative liver histology assessed by HE staining (A), Oil red O staining (B), and macrophages (F4/80) staining (C). Scale bar: 250 μm. D: Representative staining intensities of Oil red O as designated by mean optical density. E: Percentage of F4/80 positive cells. The data are given as the means ± SEM. n = 6 per group. cP < 0.001 vs Control 2w group, eP < 0.01 and fP < 0.001 vs MCD 2w group, jP < 0.001 vs Control 4w group by post hoc ANOVA one-way statistical analysis. MCD: Methionine-choline-deficient.
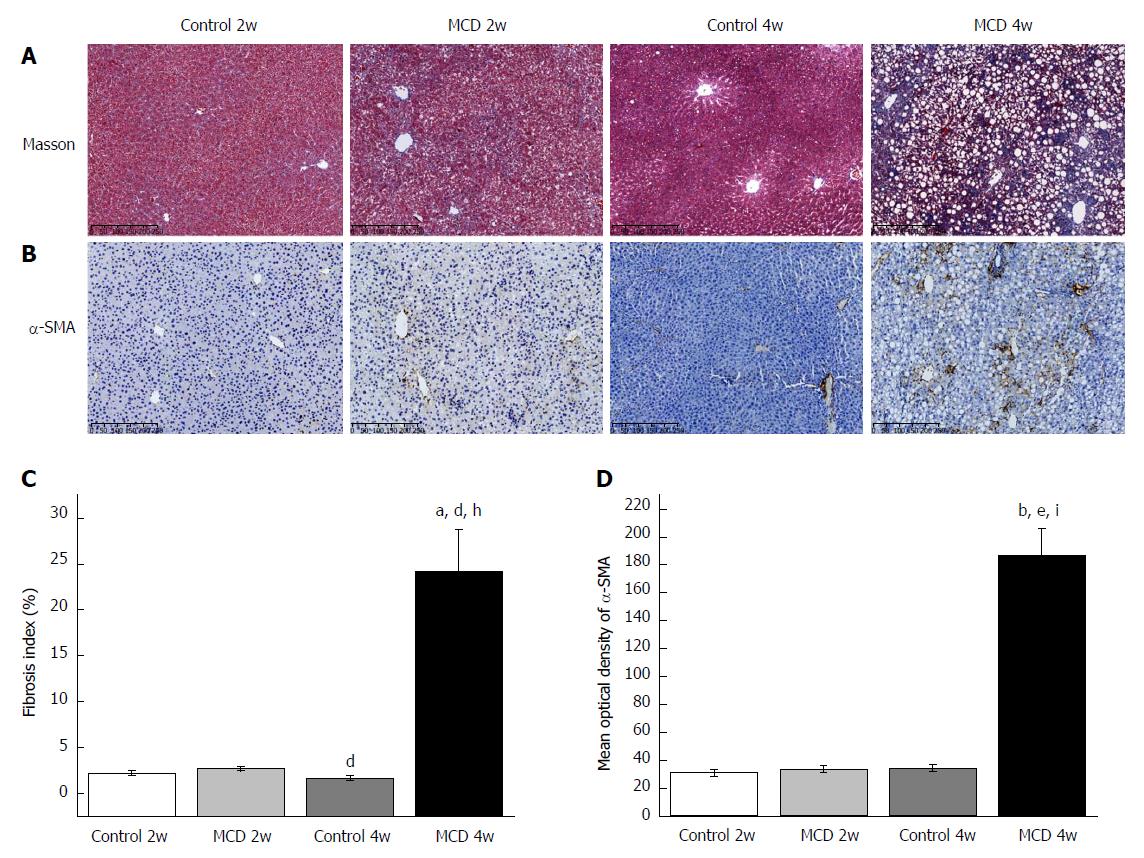
Figure 2 Methionine-choline-deficient diet induced liver fibrosis after 4 wk of feeding.
A-B: Representative liver histology assessed by Masson’s trichrome staining (A) and α-SMA staining (B). Scale bar: 250 μm. C: Percent of Masson’s trichrome-stained area as indicated by the fibrosis index (%). D: Representative staining intensities of α-SMA as designated by the mean optical density. The data are given as the means ± SEM. n = 6 per group. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs Control 2w group, dP < 0.05 and eP < 0.01 vs MCD 2w group, hP < 0.05 and iP < 0.01 vs Control 4w group by post hoc ANOVA one-way statistical analysis. MCD: Methionine-choline-deficient.
Figure 3 Methionine-choline-deficient diet resulted in gradual intestinal barrier impairment.
Representative colon histology was assessed by ZO-1 immunofluorescence staining. Scale bar: 100 μm. The data are given as the means ± SEM. MCD: Methionine-choline-deficient.
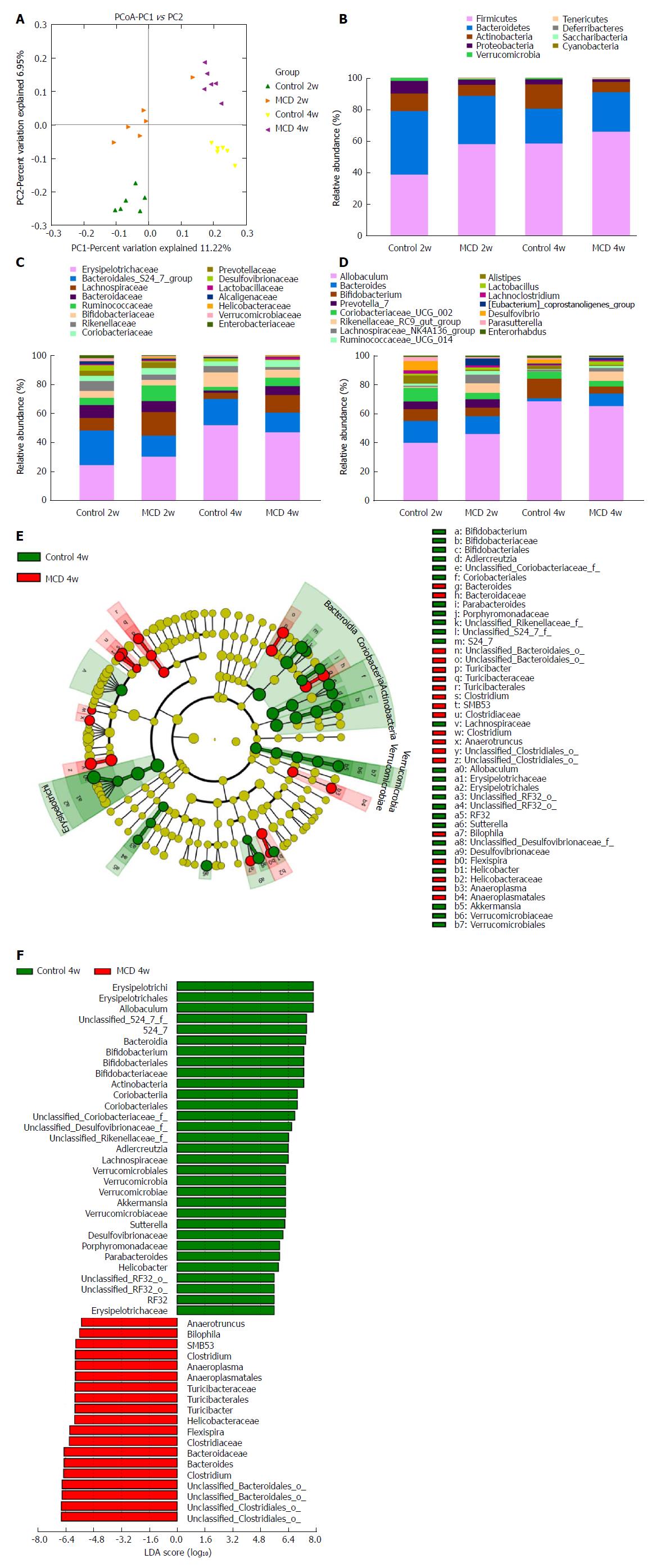
Figure 4 Methionine-choline-deficient diet induced gut microbiota dysbiosis.
A: PCoA plot of the microbiota based on unweighted UniFrac metric. Each symbol represents one sample (n = 6 per group). B-D: Top most abundant taxa at the phylum (B), family (C), and genus (D) levels. E: LEfSe cladogram represented taxon enriched in the Control 4w group (green) and in the MCD 4w group (red). Rings from the inside out represented taxonomic levels from phylum to genus. Sizes of the circles indicate the relative abundance levels of the taxa. F: Discriminative biomarkers with an LDA score > 4.8. MCD: Methionine-choline-deficient.
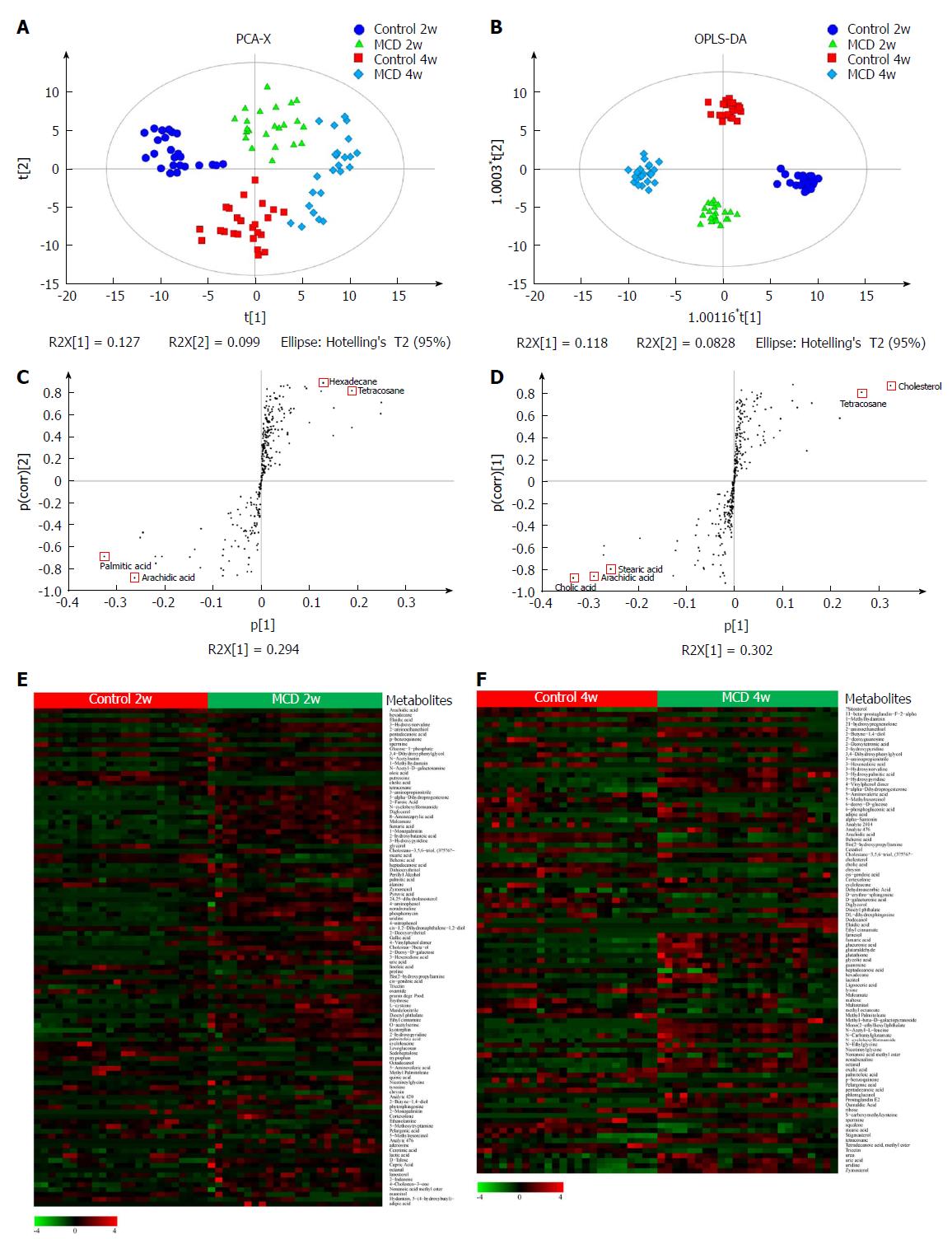
Figure 5 Methionine-choline-deficient diet altered the fecal metabolomic profile during nonalcoholic steatohepatitis progression.
A: 4-state model of a PCA plot comparing between the Control 2w (cycle), MCD 2w (triangle), Control 4w (square), and MCD 4w groups (diamond). B: OPLS-DA score scatter plot comparing the Control 2w (cycle), MCD 2w (triangle), Control 4w (square), and MCD 4w groups (diamond). Each symbol represents one sample (n = 24 per group, with a quadruplicate technical replicates of 6 samples per group). C-D: S-plot constructed from the OPLS-DA model at 2 wk (C) and 4 wk (D). The selected metabolites (red triangles) are located in the upper far right and lower far left with considerable potential as biomarkers and marked discrimination between the groups. E-F: Euclidean distance hierarchical clustering analysis visualizing the different intensity levels of characteristic metabolites at 2 wk (E) and 4 wk (F). PCA: Principal component analysis; MCD: Methionine-choline-deficient; OPLS-DA: Orthogonal partial least-squares-discriminant analysis.
- Citation: Ye JZ, Li YT, Wu WR, Shi D, Fang DQ, Yang LY, Bian XY, Wu JJ, Wang Q, Jiang XW, Peng CG, Ye WC, Xia PC, Li LJ. Dynamic alterations in the gut microbiota and metabolome during the development of methionine-choline-deficient diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(23): 2468-2481
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i23/2468.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i23.2468