Published online Aug 6, 2021. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6418
Peer-review started: February 18, 2021
First decision: March 11, 2021
Revised: March 23, 2021
Accepted: June 1, 2021
Article in press: June 1, 2021
Published online: August 6, 2021
Processing time: 159 Days and 20.1 Hours
Pancreatic inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) is a relatively rare disease that is often confused with pancreatic cancer or pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. The histological features of IMTs show that tissue from this type of tumor contains an intermingling of fibroblast and myofibroblast proliferation, accompa
The management of an IMT occurring at the neck of the pancreas is presented in this paper. A 66-year-old female patient was diagnosed with a pancreatic neck mass after a series of tests. The patient underwent enucleation of the pancreatic neck tumor after a pathological diagnosis of IMT. Previous research on the clinical features, pathological diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic IMTs was reviewed. Compared with previous reports, this is a unique case of enucleation of a pancreatic IMT.
The enucleation of pancreatic IMTs may be a safe and efficient surgical method for managing such tumors with a better prognosis. Further cases are required to explore surgical measures for pancreatic IMTs.
Core Tip: Pancreatic inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) is a relatively rare disease that is often confused with pancreatic cancer or pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. We present herein a 66-year-old female patient who was diagnosed with a pancreatic neck mass after a series of tests. The patient underwent enucleation of a pancreatic neck tumor after pathological diagnosis of IMT. Compared with previous reports, this is a unique case of enucleation of a pancreatic IMT. We conclude that the enucleation of pancreatic IMTs may be a safe and efficient surgical method for managing such tumors with a better prognosis.
- Citation: Chen ZT, Lin YX, Li MX, Zhang T, Wan DL, Lin SZ. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the pancreatic neck: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2021; 9(22): 6418-6427
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v9/i22/6418.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6418
An inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) is a rare mesenchymal tumor of unknown pathogenesis and aggressive malignant potential with a global incidence of less than 1%[1,2]. IMTs most commonly occur in the lungs of children and young adults, followed by the head and neck[3], liver[4], pancreas[5], genitourinary tract[6] and thyroid[7]. The clinical presentation of pancreatic IMTs varies depending on their anatomic location, and the final diagnosis of most lesions requires a pathological examination. The pancreatic head is the most common site for pancreatic IMTs and may be the first choice for surgical resection. Of 29 cases of pancreatic IMT reported in the English literature, none have been treated by enucleation of the tumor. Herein, an unusual pancreatic neck IMT occurring in a 66-year-old female patient is presented, and this may be the first case of enucleation of a pancreatic IMT. Pancreatic IMTs have a relatively low incidence and unspecific manifestations. The clinical and histological features of pancreatic IMTs, as well as their diagnosis and treatment, are discussed in this paper.
A 66-year-old female patient was admitted to Shulan (Hangzhou) Hospital on January 13, 2020 for a pancreatic mass.
Abdominal ultrasonography of the patient showed hyperechoic foci in the neck of the pancreas after a follow-up examination in the local hospital 4 d prior, and then the patient was transferred to our department for further treatment.
The patient had a history of right pulmonary wedge resection for adenocarcinoma in 2014 and right hemicolectomy for colon cancer in 2018.
The physical examination was unremarkable.
Laboratory examinations, including complete blood count, C-reactive protein and tumor markers, were all within the normal range.
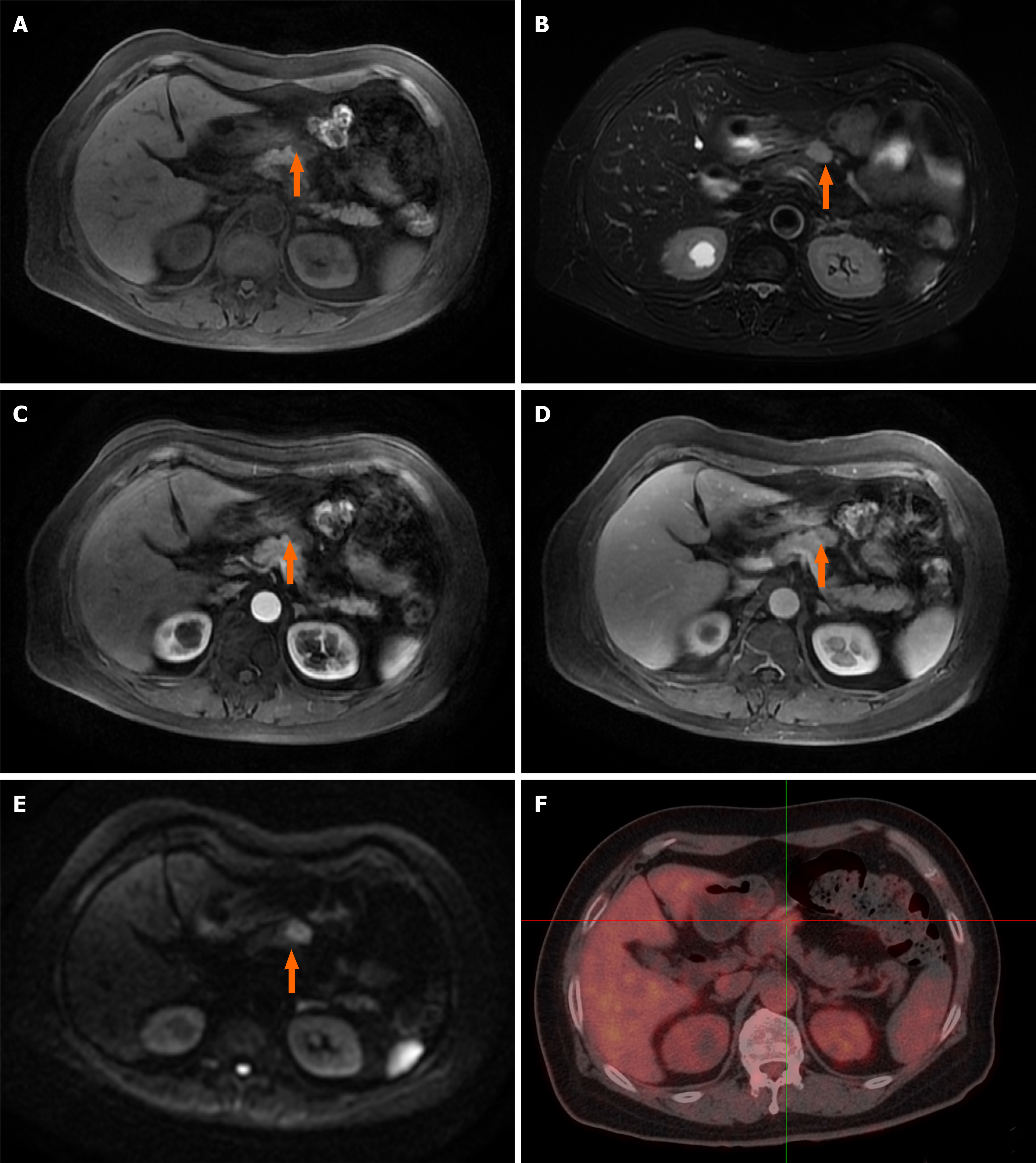
However, the ultrasound scan revealed a 2.5 cm × 1.5 cm mass in the neck of the pancreas. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging scan showed an abnormal soft tissue heterogeneous mass in the neck of the pancreas, which appeared hyperintense on the T1-weighted image and mildly hyperintense on the T2-weighted image. A centripetal enhancement pattern was observed during the delayed phase of contrast imaging (Figure 1A-E). Whole-body 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography/computed tomography (CT) examination revealed a 2.3 cm × 1.4 cm, mild-to-moderate FDG uptake nodule in front of the pancreatic neck (SUVmax 3.87) with normal scans of the head, neck, chest and colon (Figure 1F). The imaging findings were highly suggestive of pancreatic IMT. However, the possibility of a metastatic tumor could not be ruled out due to the history of lung and colon cancer.
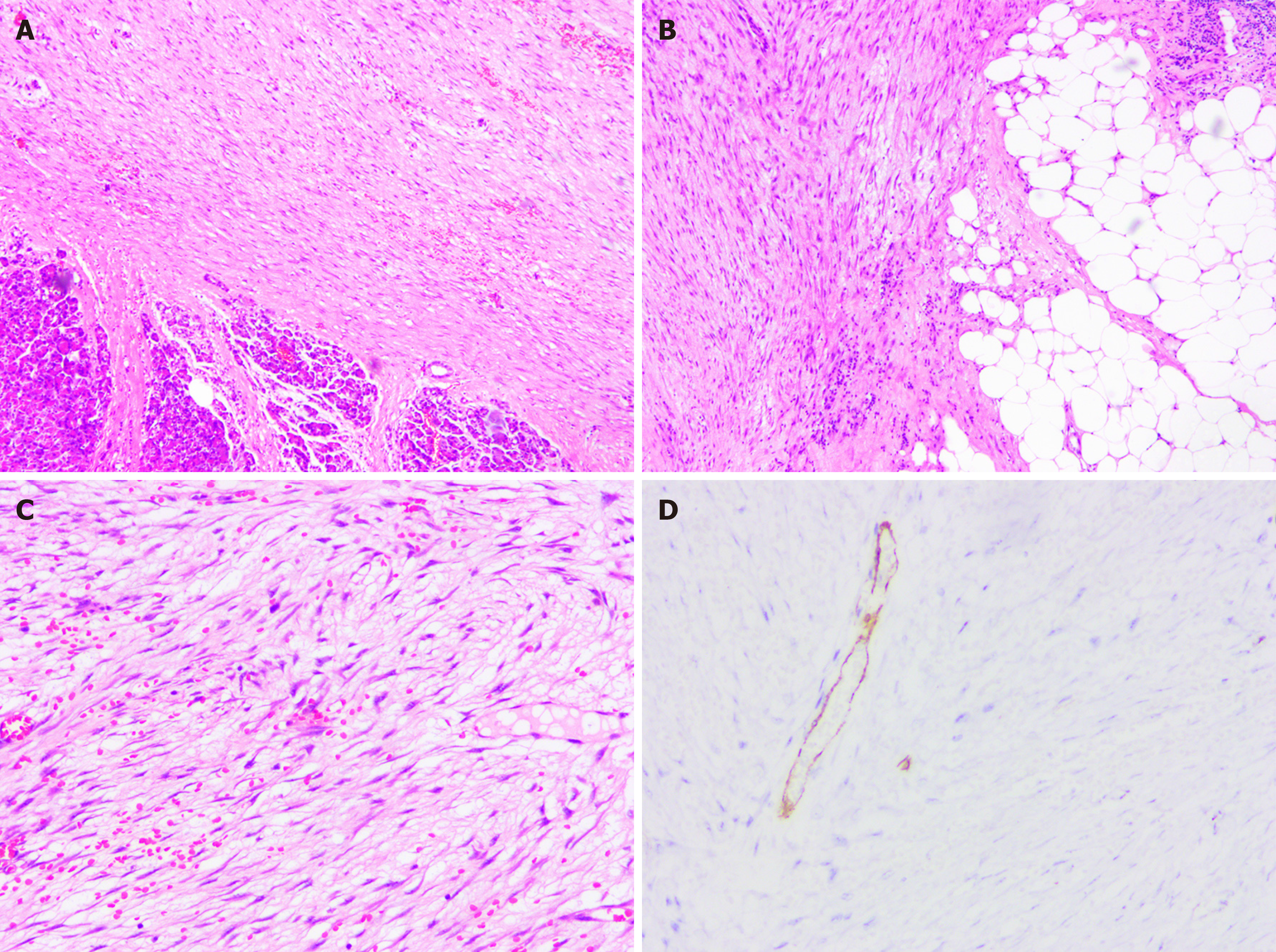
A detailed postoperative histopathological examination revealed that the carcinoma cells stained positively for desmin, vimentin, CD34, CD31, BCL2 and β-catenin and negatively for S-100, Pan-CK (AE1/AE3), caldesmon, DOG1, CD117, smooth muscle actin and P53.
A diagnosis of pancreatic neck IMT was determined on the basis of the histopathological results (Figure 2).
The patient with pancreatic IMT underwent enucleation of the pancreatic mass after multidisciplinary team discussion. During the laparotomy, a hard protruding mass with a size of 2.3 cm × 1.5 cm was observed on the pancreatic neck and subsequently enucleated. The entire mass was fleshy with a grayish-white cut surface and was confirmed with the intraoperative frozen section to be an IMT.
The postoperative recovery was uneventful, and the patient was discharged on postoperative day 11 (Figure 3). No adjuvant treatment was administered, and no obvious signs of metastasis or recurrence in the next 10 mo of follow-up were observed.
IMT, first reported in the lungs[8,9], is a special type of disease that is often termed differently in primary research, including designations such as plasma cell granuloma, plasma cell pseudotumor, inflammatory pseudotumor, inflammatory fibroxanthoma and histiocytoma[10]. IMTs can occur almost anywhere in the body, including the lungs, liver, bladder, mesentery and neck[11-13]. However, an IMT arising from the pancreas is extremely rare. A complete search of the literature from 1900 to 2020 using the PubMed database with the search terms “inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor,” “IMT,” “pancreas” and “pancreatic” was performed, and only 29 reported cases were discovered. A brief literature review of reported cases with pancreatic IMT was conducted to better understand pancreatic IMT, as summarized in Table 1[5,10,14-34]. Of these patients, 20 were male (20/29, 69%), and 9 were female (9/29, 31%), with an obvious male predilection. The tumor diameter for all reported cases ranged from 1.5 to 15.0 cm. Most tumors occurred in the pancreatic head (21/29 patients), followed by the pancreatic tail (4/29 patients) and pancreatic body (3/29 patients), suggesting that pancreatic IMT was more common in the pancreatic head.
| Cases | Sex | Age in yr | Location | Diameter in cm | Symptoms | Treatment | Follow-up | Ref. |
| 1 | M | 70 | PT | 3.8 | Asymptomatic | DP + splenectomy | Disease-free at 10 mo | Pungpapong et al[29], 2004 |
| 2 | M | 62 | PH | 3 | Jaundice | PD | Disease-free at 6 yr | Wreesmann et al[14], 2001 |
| 3 | M | 56 | PH | no | Jaundice | PD | Disease-free at 5 yr | Wreesmann et al[14], 2001 |
| 4 | M | 50 | PH | 5 | Jaundice, abdominal pain | PD | Disease-free at 4 yr | Wreesmann et al[14], 2001 |
| 5 | F | 57 | PH | Not available | Jaundice | PD | Disease-free at 3 yr | Wreesmann et al[14], 2001 |
| 6 | M | 45 | PH | Not available | Jaundice | PD | Disease-free at 10 yr | Wreesmann et al[14], 2001 |
| 7 | F | 32 | PH | 3 | Abdominal pain | PD | Disease-free at 12 yr | Wreesmann et al[14], 2001 |
| 8 | F | 42 | PB | 7 | Abdominal pain, weight loss | DP | Disease-free at 6 mo | Kroft et al[15], 1998 |
| 9 | F | 8 | PBT | 10.7 | Abdominal mass | DP | Disease-free at 2 yr | Shankar et al[16], 1998 |
| 10 | M | 35 | PH | 5 × 4 × 3 | Abdominal pain, weight loss | PD | Lung metastasis at 6 yr | Walsh et al[17], 1998 |
| 11 | M | 55 | PH | 1.5 | Asymptomatic | PD | Disease-free at 28 mo | Yamamoto et al[10], 2002 |
| 12 | M | 69 | PBT | Not available | Abdominal pain | DP + splenectomy + colon splenic flexure | Died after 7 mo of hospitalization due to sepsis | Esposito et al[18], 2004 |
| 13 | M | 65 | PB | 2 | Asymptomatic | DP + splenectomy | Disease-free at 3 yr | Dulundu et al[19], 2007 |
| 14 | M | 56 | PT | 5 × 7 | Melena | DP + splenectomy | Disease-free at 18 mo | Sim et al[30], 2008 |
| 15 | F | 13 | PH | 3 | Vomiting, weight loss | PD | Disease-free at 7 yr | Dagash et al[20], 2009 |
| 16 | M | 10 | PH | 2.2 | Abdominal pain, anepithymia | Prednisolone, cefuroxime | Disease-free at 6 yr | Dagash et al[20], 2009 |
| 17 | M | 19 | PT | 8.2 × 6.5 × 6.0 | Abdominal pain | DP + splenectomy | Disease-free at 6 yr | Hassan et al[22], 2010 |
| 18 | M | 44 | PH | 6 × 4 | Abdominal pain, vomiting | PD | Disease-free at 1 yr | Schütte et al[23], 2010 |
| 19 | M | 65 | PH | Not available | Abdominal pain | PD | Not available | Lacoste et al[25], 2012 |
| 20 | M | 0.5 | PH | 4 | Jaundice | PD | Disease-free at 3.5 yr | Tomazic et al[31], 2015 |
| 21 | F | 32 | PH | 4.8 × 3.2 | Abdominal pain | PD | Disease-free at 2.5 yr | Panda et al[26], 2015 |
| 22 | M | 46 | PH | 8 × 6 × 5 | Jaundice | PD | Not available | Battal et al[27], 2016 |
| 23 | M | 69 | PH | 4 × 3 | Vomiting, anepithymia | PD | Disease-free at 3 yr | Ding et al[21], 2016 |
| 24 | M | 15 | PH | 5 × 5 × 4.3 | Abdominal pain, fever | PD | Not available | Liu et al[24], 2017 |
| 25 | M | 1 | PH | 4 × 3 | Asymptomatic | PD | Not available | Berhe et al[34], 2019 |
| 26 | F | 82 | PH | 5 | Abdominal pain | None | Disease-free at 9 mouths | Matsubayashi et al[28], 2019 |
| 27 | M | 61 | PT | 15 × 13 × 7 | Abdominal pain | DP + left surrenalectomy + left hemicolectomy + splenectomy | Disease-free at 8 mo | İflazoğlu et al[5], 2020 |
| 28 | F | 11 | PH | 3.4 | Abdominal pain, weight loss | PD | Not available | Mcclain et al[32], 2000 |
| 29 | F | 13 | PH | 2.5 | Abdominal pain | PD | Disease-free at 4 yr | Zanchi et al[33], 2015 |
| 30 | F | 66 | PN | 2.3 × 1.5 | Asymptomatic | Enucleation | Disease-free at 9 mo | Current |
Pancreatic IMT can occur at all ages but shows a preference for children and young adults[35]. All reported cases range from 6 mo to 82 years (mean age: 42 years). As described previously, the clinical presentation of pancreatic IMT varies depending on its anatomic location and can range from asymptomatic to hemorrhagic shock due to rupture of the spleen[19,22]. Nonetheless, almost all pancreatic IMTs have similar nonspecific symptoms, such as abdominal discomfort, abdominal distension, abdominal pain, general fatigue and weight loss. Obstructive jaundice may be noted in typical patients with a pancreatic head IMT. The tumor can also obstruct the pancreatic duct and induce chronic pancreatitis with abdominal discomfort, diarrhea and indigestion[23]. An IMT arising from the pancreatic tail can also obstruct blood vessels of the spleen, resulting in rupture of the spleen with severe abdominal pain and hemorrhagic shock[22]. However, the IMT of our patient arose from the neck of the pancreas, and she had no special symptoms.
The preoperative laboratory findings were nonspecific for the diagnosis of pancreatic IMT. Only a few patients with a solitary mass occurring in the head of the pancreas may have elevated total serum bilirubin, amylase and carbohydrate antigen 19-9 due to obstruction of the bile duct or pancreatic duct[26]. Moreover, the radiological features are often deceptive. Ultrasound, CT and magnetic resonance imaging examinations showed mass lesions mimicking pancreatic cancer or pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Similar to that of other malignant tumors, whole-body 18F-FDG positron emission tomography/CT also showed an elevated SUVmax[36], which can distinguish IMTs from non-neoplastic lesions, such as pancreatic pseudocysts and swollen lymph nodes. In addition, whole-body 18F-FDG positron emission tomography /CT is the best tool to detect tumor recurrence or distant metastasis. Even standard intraoperative frozen pathology may not provide definitive information to distinguish pancreatic IMTs from pancreatic inflammatory pseudotumors.
The definitive diagnosis of IMTs relies on histological evaluations and immunohistochemical tests[37]. The histological features of IMTs are spindle-shaped cells accompanied by varying degrees of inflammatory cells[38,39]. Coffin et al[37] suggested that clonal cytogenetic abnormalities involving the anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene on the short arm of chromosome 2 at 2p23 occur in approximately 50% of IMTs[37]. This can be a useful test for a definitive clinicopathologic diagnosis. In addition, most extrapulmonary IMTs display immunohistochemical reactivity for spinal muscular atrophy, desmin, the tissue cell marker CD68 and the vascular marker CD34[40].
To date, no standard consensus regarding the treatment of pancreatic IMT has been reached. However, surgical resection of the lesion is recommended as the primary therapeutic option for pancreatic IMT. The surgical approach is related to the location of the lesion on the pancreas. For pancreatic head IMTs, pancreaticoduodenectomy is recommended, while distal pancreatectomy is recommended for pancreatic body or tail IMTs. Pancreatic IMTs often invade surrounding organs such as the colon, duodenum and stomach. However, these theories are not widely accepted for such low-grade malignant lesions. Whether radical surgery is necessary requires a large number of further clinical studies.
Radiation therapy, chemotherapy and high-dose steroid therapy have also been used in patients with incomplete resection, impossible resection or malignant disease status postsurgical resection[20,28,41]. Spontaneous regression of pancreatic IMTs has been reported infrequently[28]. Given that our patient was an elderly and infirm female with pancreatic neck IMT only, multidisciplinary team discussion suggested that enucleation would be a more beneficial therapeutic option. No adjuvant treatment was administered following the enucleation of the pancreatic IMT. The patient remained symptom-free and healthy without tumor recurrence or metastasis 10 mo after surgery. Although only one patient with IMT has been reported to have undergone enucleation, such operative procedures could be considered in the future. More cases are required to explore the surgical treatment of pancreatic IMTs.
Pancreatic IMT is regarded as a low-grade malignancy with a generally favorable prognosis. However, a close and long-term follow-up after surgery must be carried out due to its potential for malignancy, distant metastasis and recurrence.
This paper reports a rare case of IMT of the pancreatic neck managed with enucleation treatment to confirm whether radical surgery could be avoided. This is the first reported case in which enucleation usage resulted in a favorable prognosis of pancreatic IMT. Surgical resection may be the preferred treatment and may provide a better prognosis. However, using enucleation as a surgical measure for treating patients with IMT may also yield a good prognosis.
The authors would like to thank the support of the Department of Radiology at Shulan (Hangzhou) Hospital Affiliated to Zhejiang Shuren University Shulan International Medical College.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Specialty type: Medicine, research and experimental
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C, C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Cianci P, Tomažič A S-Editor: Fan JR L-Editor: Filipodia P-Editor: Xing YX
| 1. | Panagiotopoulos N, Patrini D, Gvinianidze L, Woo WL, Borg E, Lawrence D. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour of the lung: a reactive lesion or a true neoplasm? J Thorac Dis. 2015;7:908-911. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Travis WD. The 2015 WHO classification of lung tumors. Pathologe. 2014;35 Suppl 2:188. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 68] [Cited by in RCA: 86] [Article Influence: 8.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Gao F, Zhong R, Li GH, Zhang WD. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging findings of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors of the head and neck. Acta Radiol. 2014;55:434-440. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Thavamani A, Mandelia C, Anderson PM, Radhakrishnan K. Pediatric Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Liver: A Rare Cause of Portal Hypertension. ACG Case Rep J. 2019;6:1-4. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | İflazoğlu N, Kaplan Kozan S, Biri T, Ünlü S, Gökçe H, Doğan S, Gökçe ON. Pancreatic inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor presenting with extracolonic obstruction. Turk J Surg. 2020;36:233-237. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Palanisamy S, Chittawadagi B, Dey S, Sabnis SC, Nalankilli VP, Subbiah R, Chinnusamy P. Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of Colon Mimicking Advanced Malignancy: Report of Two Cases with Review of Literature. Indian J Surg. 2020;82:1280-1283. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | An N, Luo Y, Wang J, Wang XL, Man GD, Song YD. [Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of thyroid: a case report]. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018;53:148-149. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Coffin CM, Humphrey PA, Dehner LP. Extrapulmonary inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor: a clinical and pathological survey. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1998;15:85-101. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Zhao HD, Wu T, Wang JQ, Zhang WD, He XL, Bao GQ, Li Y, Gong L, Wang Q. Primary inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the breast with rapid recurrence and metastasis: A case report. Oncol Lett. 2013;5:97-100. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Yamamoto H, Watanabe K, Nagata M, Tasaki K, Honda I, Watanabe S, Soda H, Takenouti T. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) of the pancreas. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2002;9:116-119. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Alabbas Z, Issa M, Omran A, Issa R. Mesenteric inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor as a rare cause of small intestinal intussusception. J Surg Case Rep. 2020;2020:rjaa322. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Zhao J, Han D, Gao M, Liu M, Feng C, Chen G, Gu Y, Jiang Y. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the neck with thyroid invasion: a case report and literature review. Gland Surg. 2020;9:1042-1047. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Inamdar AA, Pulinthanathu R. Malignant transformation of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of urinary bladder: A rare case scenario. Bladder (San Franc). 2019;6:e39. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Wreesmann V, van Eijck CH, Naus DC, van Velthuysen ML, Jeekel J, Mooi WJ. Inflammatory pseudotumour (inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour) of the pancreas: a report of six cases associated with obliterative phlebitis. Histopathology. 2001;38:105-110. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 45] [Cited by in RCA: 46] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Kroft SH, Stryker SJ, Winter JN, Ergun G, Rao MS. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the pancreas. Int J Pancreatol. 1995;18:277-283. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Shankar KR, Losty PD, Khine MM, Lamont GL, McDowell HP. Pancreatic inflammatory tumour: a rare entity in childhood. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1998;43:422-423. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 43] [Cited by in RCA: 41] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Walsh SV, Evangelista F, Khettry U. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the pancreaticobiliary region: morphologic and immunocytochemical study of three cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;22:412-418. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 44] [Cited by in RCA: 47] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Esposito I, Bergmann F, Penzel R, di Mola FF, Shrikhande S, Büchler MW, Friess H, Otto HF. Oligoclonal T-cell populations in an inflammatory pseudotumor of the pancreas possibly related to autoimmune pancreatitis: an immunohistochemical and molecular analysis. Virchows Arch. 2004;444:119-126. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Dulundu E, Sugawara Y, Makuuchi M. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the pancreas--a case report. Biosci Trends. 2007;1:167-169. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Dagash H, Koh C, Cohen M, Sprigg A, Walker J. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the pancreas: a case report of 2 pediatric cases--steroids or surgery? J Pediatr Surg. 2009;44:1839-1841. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Ding D, Bu X, Tian F. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor in the head of the pancreas with anorexia and vomiting in a 69-year-old man: A case report. Oncol Lett. 2016;12:1546-1550. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Hassan KS, Cohen HI, Hassan FK, Hassan SK. Unusual case of pancreatic inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor associated with spontaneous splenic rupture. World J Emerg Surg. 2010;5:28. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Schütte K, Kandulski A, Kuester D, Meyer F, Wieners G, Schulz HU, Malfertheiner P. Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Pancreatic Head: An Unusual Cause of Recurrent Acute Pancreatitis - Case Presentation of a Palliative Approach after Failed Resection and Review of the Literature. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2010;4:443-451. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Liu HK, Lin YC, Yeh ML, Chen YS, Su YT, Tsai CC. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors of the pancreas in children: A case report and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96:e5870. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Lacoste L, Galant C, Gigot JF, Lacoste B, Annet L. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the pancreatic head. JBR-BTR. 2012;95:267-269. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Panda D, Mukhopadhyay D, Datta C, Chattopadhyay BK, Chatterjee U, Shinde R. Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor Arising in the Pancreatic Head: a Rare Case Report. Indian J Surg. 2015;77:538-540. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Battal M, Kartal K, Tuncel D, Bostanci O. Inflammatory myofibroblastic pancreas tumor: a case report. Clin Case Rep. 2016;4:1122-1124. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Matsubayashi H, Uesaka K, Sasaki K, Shimada S, Takada K, Ishiwatari H, Ono H. A Pancreatic Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor with Spontaneous Remission: A Case Report with a Literature Review. Diagnostics (Basel). 2019;9. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Pungpapong S, Geiger XJ, Raimondo M. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor presenting as a pancreatic mass: a case report and review of the literature. JOP. 2004;5:360-367. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Sim A, Lee MW, Nguyen GK. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour of the pancreas. Can J Surg. 2008;51:E23-E24. [PubMed] |
| 31. | Tomazic A, Gvardijancic D, Maucec J, Homan M. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the pancreatic head - a case report of a 6 mo old child and review of the literature. Radiol Oncol. 2015;49:265-270. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Mcclain MB, Burton EM, Day DS. Pancreatic pseudotumor in an 11-year-old child: imaging findings. Pediatr Radiol. 2000;30:610-613. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Zanchi C, Giurici N, Martelossi S, Cheli M, Sonzogni A, Alberti D. Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Pancreatic Head: Recurrent Cholangitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015;61:e28-e29. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Berhe S, Goldstein S, Thompson E, Hackam D, Rhee DS, Nasr IW. Challenges in Diagnosis and Management of Pancreatic Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumors in Children. Pancreas. 2019;48:e27-e29. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Nonaka D, Birbe R, Rosai J. So-called inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour: a proliferative lesion of fibroblastic reticulum cells? Histopathology. 2005;46:604-613. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 53] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Manning MA, Paal EE, Srivastava A, Mortele KJ. Nonepithelial Neoplasms of the Pancreas, Part 2: Malignant Tumors and Tumors of Uncertain Malignant Potential From the Radiologic Pathology Archives. Radiographics. 2018;38:1047-1072. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Coffin CM, Hornick JL, Fletcher CD. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor: comparison of clinicopathologic, histologic, and immunohistochemical features including ALK expression in atypical and aggressive cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31:509-520. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 627] [Cited by in RCA: 624] [Article Influence: 34.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Coindre JM. [New WHO classification of tumours of soft tissue and bone]. Ann Pathol. 2012;32:S115-S116. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 31] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Coffin CM, Watterson J, Priest JR, Dehner LP. Extrapulmonary inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (inflammatory pseudotumor). A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 84 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995;19:859-872. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1100] [Cited by in RCA: 1030] [Article Influence: 34.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 40. | Ong HS, Ji T, Zhang CP, Li J, Wang LZ, Li RR, Sun J, Ma CY. Head and neck inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT): evaluation of clinicopathologic and prognostic features. Oral Oncol. 2012;48:141-148. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 51] [Cited by in RCA: 53] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 41. | Som PM, Brandwein MS, Maldjian C, Reino AJ, Lawson W. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the maxillary sinus: CT and MR findings in six cases. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994;163:689-692. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 67] [Cited by in RCA: 70] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |