Published online Jul 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i19.6507
Peer-review started: August 8, 2021
First decision: November 6, 2021
Revised: November 15, 2021
Accepted: May 5, 2022
Article in press: May 5, 2022
Published online: July 6, 2022
Processing time: 320 Days and 3.9 Hours
In driver gene-negative non-small cell lung cancer patients who relapse following radical resection, combination chemotherapy using bevacizumab and platinum-based dual drugs is known to increase both progression-free and overall survival. Treatment initially includes bevacizumab, and if patients are able to tolerate it, bevacizumab can continue to be utilized until disease progression. Bevacizumab is a recombinant humanized monoclonal neutralizing antibody that acts against vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Various anti-VEGF monoclonal antibodies, such as bevacizumab, can increase the risk of arterial thromboembolism. Current data indicate that VEGF-targeted treatment does not significantly increase the risk of venous thromboembolism events, except for bevacizumab.
A 55-year-old man underwent radical resection for cancer of the right lung. Six months following surgery, multiple metastases were observed in his left lung. Subsequently, six cycles of bevacizumab combined with pemetrexed/carboplatin chemotherapy was given. Efficacy evaluation continued to be partial relief according to RECIST 1.1 standards, and no noticeable adverse reactions were noted. After three cycles of maintenance therapy using a combination of bevacizumab and pemetrexed, the patient developed dizziness and dyspnea. The patient was diagnosed with acute cerebral infarction and pulmonary embolism following head magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography (CT) angiography, and chest enhanced CT. Although the patient received low-molecular-weight heparin anticoagulation and other treatment, the patient eventually died of respiratory failure 1 mo later. This case report may offer some insight into fatal arteriovenous embolism, which has not been previously reported.
Bevacizumab combined with chemotherapy may also increase the risk of arteriovenous thromboembolism. Accordingly, patients who receive angiogenesis inhibitor therapy should be carefully selected. Furthermore, close monitoring and timely intervention are necessary in order to reduce the risk of such toxicities.
Core Tip: This report describes a middle-aged man with postoperative recurrence of non-small cell lung cancer who developed cerebral infarction and pulmonary embolism 6 mo after treatment with bevacizumab, which was given in combination with chemotherapy. Concurrent arteriovenous thrombosis is rarely reported in the literature. Bevacizumab in conjunction with chemotherapy may increase the risk of arteriovenous thromboembolism. As a result, patients who undergo treatment with angiogenesis inhibitors should be carefully selected, and close monitoring and timely interventions (such as low-molecular-weight heparin prophylactic anticoagulant therapy) are necessary in order to reduce the risk of arterial thromboembolism and venous thromboembolism.
- Citation: Kong Y, Xu XC, Hong L. Arteriovenous thrombotic events in a patient with advanced lung cancer following bevacizumab plus chemotherapy: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(19): 6507-6513
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i19/6507.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i19.6507
Bevacizumab is a monoclonal antibody that acts against vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). A wide range of drugs targeting the VEGF signaling pathway may be used in the treatment of various solid tumors; however, a plethora of toxic effects have increasingly been discovered, which have been shown to be fatal in a small number of cases[1,2]. The increased incidence of potentially fatal arterial thromboembolism (ATE), including transient ischemic attack, stroke, angina pectoris, and myocardial infarction, has been initially reported in advanced colorectal cancer treated with a chemotherapy regimen containing bevacizumab, with the incidence of severe ATE being 4%-5%[3]. Some studies have revealed that bevacizumab can increase the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in patients with cancer; however, inconsistent conclusions have been reported. Two meta-analyses conducted at the patient level have shown that, compared to patients solely receiving chemotherapy, the risk of VTE did not increase in patients who received bevacizumab plus chemotherapy[4]. Here, we describe a 55-year-old man who suffered from arteriovenous thrombosis after receiving bevacizumab in conjunction with intravenous chemotherapy.
A 55-year-old man presented to our department with hemoptysis.
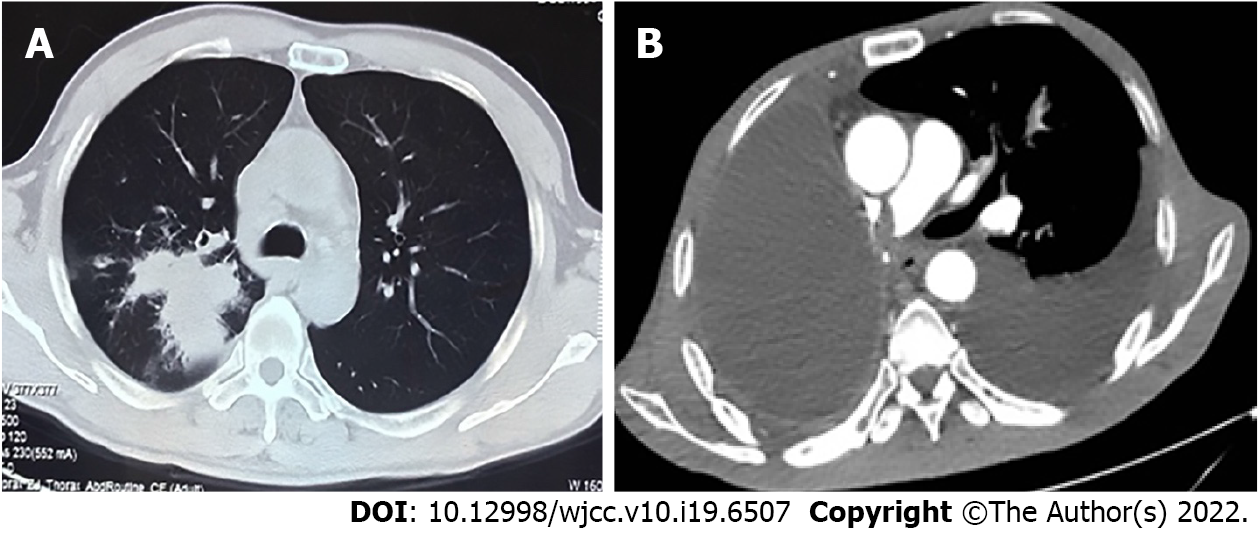
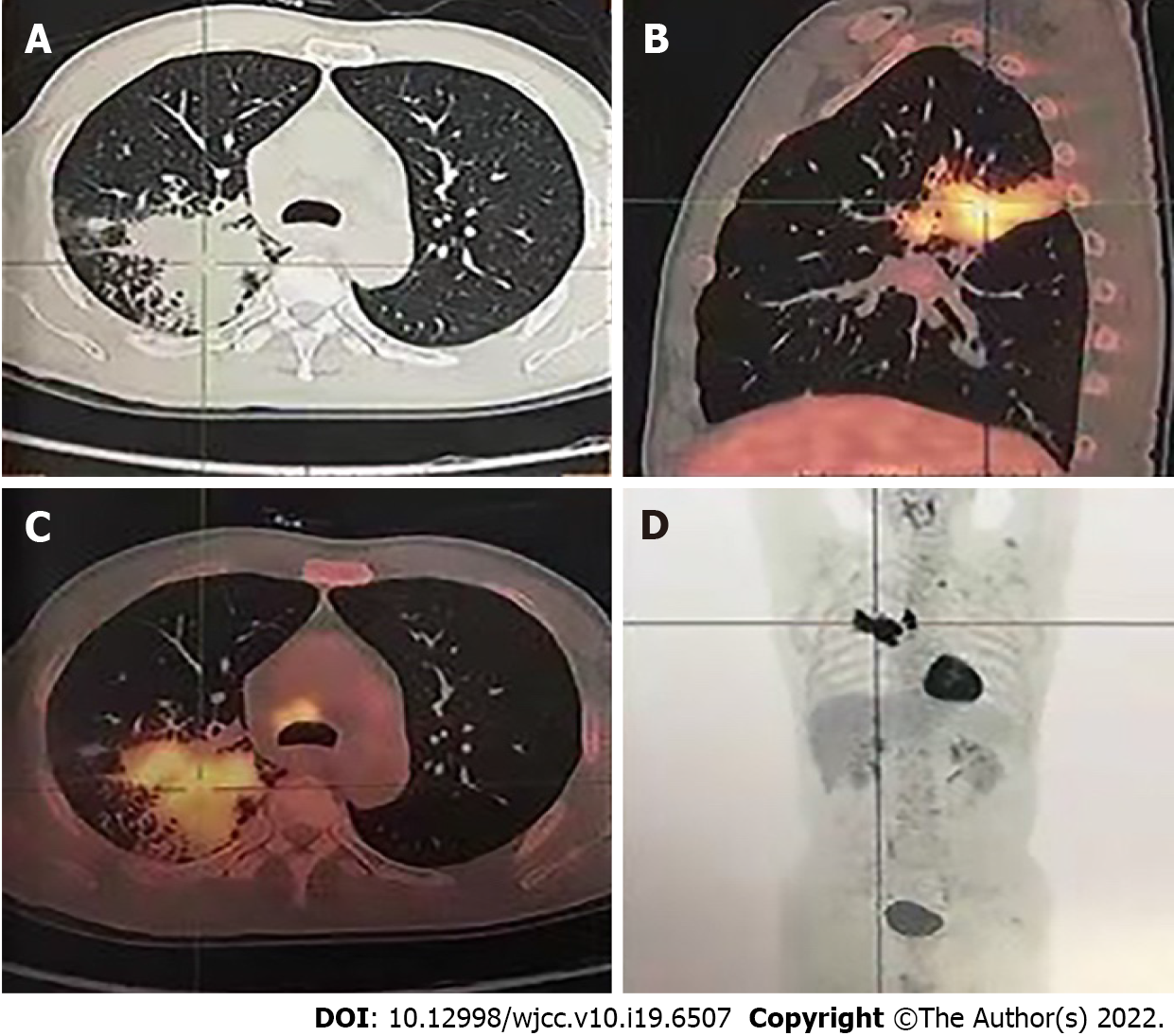
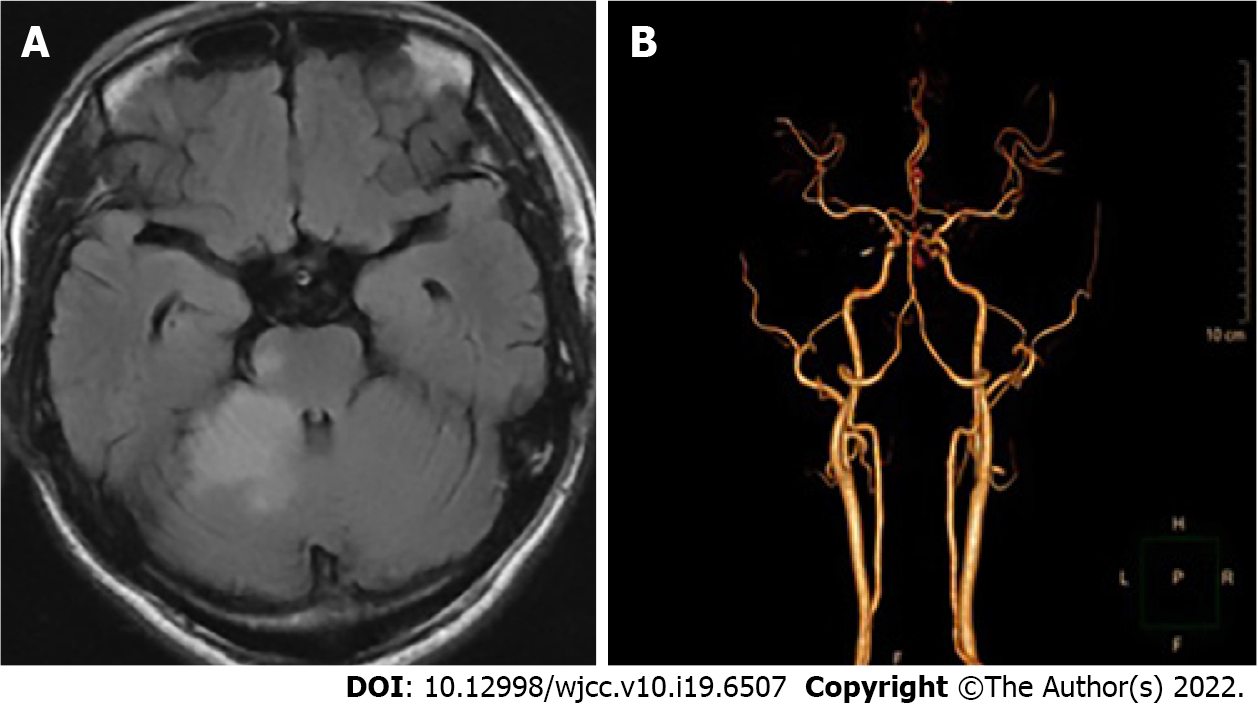
The patient’s chest computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography-CT demonstrated consolidation and thick-walled voids in the posterior and dorsal lobes of the right lung (Figures 1 and 2). Ultrasound bronchoscopy revealed the presence of adenocarcinoma. The patient then underwent radical resection for right lung cancer, after which postoperative pathology revealed central invasive adenocarcinoma (pT4N1M0, IIIA). Moreover, genetic testing revealed the following: Epidermal growth factor receptor (-), anaplastic lymphoma kinase (-), ROS1 (-), Kirsten rat sarcoma/murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1 (-), and programmed death 1 (-). Adjuvant chemotherapy was not provided following surgery in light of the patient’s poor physical condition. Six months postoperatively, the patient’s condition worsened, and chest enhanced CT demonstrated enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes, diffuse nodules in the left lung, and left pleural effusion. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial lung biopsy was difficult to obtain and was not performed due to the presence of diffuse small lesions within the left lung. The patient subsequently received regimen chemotherapy with bevacizumab 400 mg d1 + pemetrexed 750 mg d1 + carboplatin 500 mg d1, q3w for six cycles. The curative effect was evaluated as partial relief during chemotherapy according to RECIST 1.1 standards. The patient had no chemotherapy-related adverse reactions, including nausea and vomiting, and no bone marrow suppression, increased blood pressure, proteinuria, or bleeding. Bevacizumab 400 mg d1 + pemetrexed 750 mg d1, q3w was then maintained for three cycles. Afterward, the patient developed dizziness with nausea and vomiting, for which magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the head displayed acute cerebral infarction in the right lateral ventricle (Figure 3A), and CT angiography (CTA) of the head demonstrated local occlusion of the right superior cerebellar artery following bevacizumab combined with chemotherapy (Figure 3B). In addition, the patient experienced symptoms, such as progressive dyspnea and decreased blood oxygen saturation. D-dimer increased 10-fold, and other blood coagulation function indexes were within normal range. Routine blood tests and C-reactive protein and procalcitonin levels were also within normal range. Chest enhanced CT revealed a filling defect of the right pulmonary artery (Figure 1), after which pulmonary embolism was diagnosed.
The patient had no history of hypertension, cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease, and chronic kidney disease. He was a smoker for 30 years.
There was no family history of lung cancer.
There were no breath sounds in his right lung and low breath sounds in his left lung. His heart examination showed no significant abnormality.
Routine blood tests and C-reactive protein and procalcitonin levels were within normal range. D-dimer increased 10-fold, and other blood coagulation function indexes were within normal range.
MRI of the head displayed acute cerebral infarction in the right lateral ventricle (Figure 3A). CTA of the head demonstrated local occlusion of the right superior cerebellar artery following bevacizumab combined with chemotherapy (Figure 3B). Chest enhanced CT revealed a filling defect of the right pulmonary artery (Figure 1). Electrocardiogram (ECG) and color Doppler echocardiography showed no obvious abnormalities.
Cerebral infarction and pulmonary embolism.
The patient developed distant metastatic disease and was unable to be cured; therefore, systemic treatment was the goal in his palliative care plan. Accordingly, treatment with bevacizumab was terminated, and aspirin (100 mg/d) + clopidogrel bisulfate tablets (75 mg/d) + atorvastatin (20 mg/d) + low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) (4100 IU/12 h) anticoagulation were provided. In addition, diuresis, drainage of pleural fluid, and non-invasive ventilator therapy were performed.
The patient died of respiratory failure 1 mo later.
Patients suffering from lung cancer are known to have the highest incidence of cerebral infarction among all existing cancer types. Previous studies have shown that cancer-related cerebral infarction may give rise to unique clinical manifestations, including increased D-dimer levels and multiple cerebral infarctions distributed in the blood supply area of various arteries in the brain[5]. Its patho
A variety of anti-angiogenic drugs, such as bevacizumab, are known to be associated with an increased risk of ATE[7]. However, it remains unclear whether these patients have an increased risk of VTE due to inconsistent research data. Patients receiving angiogenesis inhibitors have an increased risk of thromboembolism, but its pathophysiology remains unclear[8]. The common hypothesis posits that tumor-associated endothelial cells are disturbed, which then transforms the endothelium from a natural anticoagulant state to a pro-thrombotic state. Afterward, systemic coagulation is activated, where such cancer patients are more prone to thromboembolism for underlying diseases. In addition, the VEGF pathway can regulate and protect endothelial cell function by inhibiting apoptosis and inflammation pathways. Endothelial dysfunction may expose phospholipids that can promote thrombosis and underlying stroma[9]. Recent studies have shown that the preventive application of antiplatelet and anticoagulant drugs can effectively reduce the incidence of thrombotic events in cancer patients[10]. Lung cancer has a higher risk of VTE compared to other malignancies[11,12]. The mechanism of lung cancer with pulmonary embolism is complicated. Adenocarcinoma, advanced lung cancer, surgery, chemotherapy, and underlying co-morbidities serve as important high-risk factors. International guidelines recommend LMWH as the first-line treatment in the management of tumor-related pulmonary embolism[13]. If patients with lung cancer and pulmonary embolism have no bleeding manifestations and are at a low risk of bleeding, novel oral anticoagulants can be considered instead of LMWH[14]. The anticoagulation time should be at least 6 mo, while anticoagulation time should be prolonged or even given long-term depending on the situation[15].
Certain lung cancer patients that are at a high risk of pulmonary embolism can benefit from preventive anticoagulation, which should be carefully evaluated in combination with the thrombosis risk assessment model and D-dimer levels. The prediction models used for VTE risk assessment of cancer patients include the Khorana score, PROTECHT score, COMPASS-CAT score, and CONKO score. These models have been developed and validated in patients with ambulatory lung cancer[16]. Khorana score is currently the most validated chemotherapy-related VTE risk assessment model, which is a reliable model based on five clinical and laboratory parameters. It is suitable for the VTE risk assessment of patients undergoing lung cancer chemotherapy and can be used to customize anticoagulant thrombosis prevention in such patients[17]. However, Khorana score may not be sensitive enough to identify high-risk lung cancer patients. Verso et al[18] have shown that PROTECHT score is more advantageous than Khorana score in distinguishing patients at high risk of VTE. Meanwhile, COMPASS-CAT score is able to accurately distinguish high-risk and low-risk VTE patients[19]. It is more sensitive in predicting the VTE risk of lung cancer patients compared to Khorana, PROTECHT, and CONKO models and may be more suitable for thrombosis prevention in lung cancer patients receiving anti-tumor therapy; however, further verification is needed.
The patient reported in this study was suffering from advanced lung cancer and benefited from treatment with bevacizumab in conjunction with chemotherapy. The patient was in good physical condition and did not have hypertension or a history of cardiovascular or cerebrovascular diseases. Risk factors for deep vein thrombosis include hospitalization, indwelling deep vein catheters, and aggressive chemotherapy. Unfortunately, fatal arteriovenous thrombosis occurred during maintenance treatment with bevacizumab. Moreover, pleural effusion of the left lung increased during maintenance therapy, indicating that the patient had disease progression at the time of these thromboembolic events. Therefore, LMWH anticoagulation, diuresis, drainage of pleural fluid, and non-invasive ventilator therapy were administered for the patient; however, the patient still developed shock and experienced a progressive decrease in blood oxygen saturation. The patient continued to suffer from uncontrollable respiratory failure and died after 1 mo.
This report is the first to discuss cerebral infarction and pulmonary embolism occurring in a patient with non-small cell lung cancer following treatment using bevacizumab combined with chemotherapy. Accordingly, the above drug combination may increase the risk of arteriovenous thromboembolism. However, its mechanism of occurrence remains unclear, and future studies are required to investigate the prevention and management of ATE and VTE associated with bevacizumab. In light of these findings, patients who receive angiogenesis inhibitor therapy should be carefully selected according to certain parameters, such as reasonable daily physical status, controlled blood pressure, and no severe cardiovascular events within 6-12 mo. Furthermore, close monitoring and timely intervention are necessary to reduce risk of toxicity.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Medicine, research and experimental
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: uz Zaman M, Pakistan; Yip D, Australia S-Editor: Wang JJ L-Editor: Wang TQ P-Editor: Wang JJ
| 1. | Ranpura V, Hapani S, Wu S. Treatment-related mortality with bevacizumab in cancer patients: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2011;305:487-494. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 358] [Cited by in RCA: 325] [Article Influence: 23.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Schutz FA, Je Y, Richards CJ, Choueiri TK. Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials for the incidence and risk of treatment-related mortality in patients with cancer treated with vascular endothelial growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:871-877. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 139] [Cited by in RCA: 150] [Article Influence: 11.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Scappaticci FA, Skillings JR, Holden SN, Gerber HP, Miller K, Kabbinavar F, Bergsland E, Ngai J, Holmgren E, Wang J, Hurwitz H. Arterial thromboembolic events in patients with metastatic carcinoma treated with chemotherapy and bevacizumab. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99:1232-1239. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 706] [Cited by in RCA: 693] [Article Influence: 38.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Tebbutt NC, Murphy F, Zannino D, Wilson K, Cummins MM, Abdi E, Strickland AH, Lowenthal RM, Marx G, Karapetis C, Shannon J, Goldstein D, Nayagam SS, Blum R, Chantrill L, Simes RJ, Price TJ; Australasian Gastro-Intestinal Trials Group. Risk of arterial thromboembolic events in patients with advanced colorectal cancer receiving bevacizumab. Ann Oncol. 2011;22:1834-1838. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 32] [Cited by in RCA: 35] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Hurwitz HI, Saltz LB, Van Cutsem E, Cassidy J, Wiedemann J, Sirzén F, Lyman GH, Rohr UP. Venous thromboembolic events with chemotherapy plus bevacizumab: a pooled analysis of patients in randomized phase II and III studies. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:1757-1764. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 163] [Cited by in RCA: 145] [Article Influence: 10.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Gon Y, Sakaguchi M, Takasugi J, Kawano T, Kanki H, Watanabe A, Oyama N, Terasaki Y, Sasaki T, Mochizuki H. Plasma D-dimer levels and ischaemic lesions in multiple vascular regions can predict occult cancer in patients with cryptogenic stroke. Eur J Neurol. 2017;24:503-508. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 54] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Mir O, Mouthon L, Alexandre J, Mallion JM, Deray G, Guillevin L, Goldwasser F. Bevacizumab-induced cardiovascular events: a consequence of cholesterol emboli syndrome? J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99:85-86. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 52] [Cited by in RCA: 39] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Zangari M, Fink LM, Elice F, Zhan F, Adcock DM, Tricot GJ. Thrombotic events in patients with cancer receiving antiangiogenesis agents. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:4865-4873. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 145] [Cited by in RCA: 144] [Article Influence: 9.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Schwarzbach CJ, Schaefer A, Ebert A, Held V, Bolognese M, Kablau M, Hennerici MG, Fatar M. Stroke and cancer: the importance of cancer-associated hypercoagulation as a possible stroke etiology. Stroke. 2012;43:3029-3034. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 167] [Cited by in RCA: 201] [Article Influence: 15.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Wharin C, Tagalakis V. Management of venous thromboembolism in cancer patients and the role of the new oral anticoagulants. Blood Rev. 2014;28:1-8. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Key NS, Khorana AA, Kuderer NM, Bohlke K, Lee AYY, Arcelus JI, Wong SL, Balaban EP, Flowers CR, Francis CW, Gates LE, Kakkar AK, Levine MN, Liebman HA, Tempero MA, Lyman GH, Falanga A. Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis and Treatment in Patients With Cancer: ASCO Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:496-520. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 562] [Cited by in RCA: 948] [Article Influence: 158.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Blom JW, Doggen CJ, Osanto S, Rosendaal FR. Malignancies, prothrombotic mutations, and the risk of venous thrombosis. JAMA. 2005;293:715-722. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1353] [Cited by in RCA: 1459] [Article Influence: 73.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Farge D, Bounameaux H, Brenner B, Cajfinger F, Debourdeau P, Khorana AA, Pabinger I, Solymoss S, Douketis J, Kakkar A. International clinical practice guidelines including guidance for direct oral anticoagulants in the treatment and prophylaxis of venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:e452-e466. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 274] [Cited by in RCA: 270] [Article Influence: 30.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Khorana AA, Noble S, Lee AYY, Soff G, Meyer G, O'Connell C, Carrier M. Role of direct oral anticoagulants in the treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism: guidance from the SSC of the ISTH. J Thromb Haemost. 2018;16:1891-1894. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 272] [Cited by in RCA: 296] [Article Influence: 42.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Streiff MB, Holmstrom B, Angelini D, Ashrani A, Bockenstedt PL, Chesney C, Fanikos J, Fenninger RB, Fogerty AE, Gao S, Goldhaber SZ, Gundabolu K, Hendrie P, Lee AI, Lee JT, Mann J, McMahon B, Millenson MM, Morton C, Ortel TL, Ozair S, Paschal R, Shattil S, Siddiqi T, Smock KJ, Soff G, Wang TF, Williams E, Zakarija A, Hammond L, Dwyer MA, Engh AM. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolic Disease, Version 2.2018. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2018;16:1289-1303. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 118] [Cited by in RCA: 153] [Article Influence: 25.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Yan AR, Samarawickrema I, Naunton M, Peterson GM, Yip D, De Rosa S, Mortazavi R. Risk Factors and Prediction Models for Venous Thromboembolism in Ambulatory Patients with Lung Cancer. Healthcare (Basel). 2021;9. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | van Es N, Ventresca M, Di Nisio M, Zhou Q, Noble S, Crowther M, Briel M, Garcia D, Lyman GH, Macbeth F, Griffiths G, Iorio A, Mbuagbaw L, Neumann I, Brozek J, Guyatt G, Streiff MB, Baldeh T, Florez ID, Gurunlu Alma O, Agnelli G, Ageno W, Marcucci M, Bozas G, Zulian G, Maraveyas A, Lebeau B, Lecumberri R, Sideras K, Loprinzi C, McBane R, Pelzer U, Riess H, Solh Z, Perry J, Kahale LA, Bossuyt PM, Klerk C, Büller HR, Akl EA, Schünemann HJ; IPDMA Heparin Use in Cancer Patients Research Group. The Khorana score for prediction of venous thromboembolism in cancer patients: An individual patient data meta-analysis. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18:1940-1951. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 54] [Cited by in RCA: 78] [Article Influence: 15.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Verso M, Agnelli G, Barni S, Gasparini G, LaBianca R. A modified Khorana risk assessment score for venous thromboembolism in cancer patients receiving chemotherapy: the Protecht score. Intern Emerg Med. 2012;7:291-292. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 231] [Cited by in RCA: 284] [Article Influence: 21.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Rupa-Matysek J, Lembicz M, Rogowska EK, Gil L, Komarnicki M, Batura-Gabryel H. Evaluation of risk factors and assessment models for predicting venous thromboembolism in lung cancer patients. Med Oncol. 2018;35:63. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 41] [Article Influence: 5.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |