Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 6, 2020; 8(7): 1257-1264
Published online Apr 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i7.1257
Published online Apr 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i7.1257
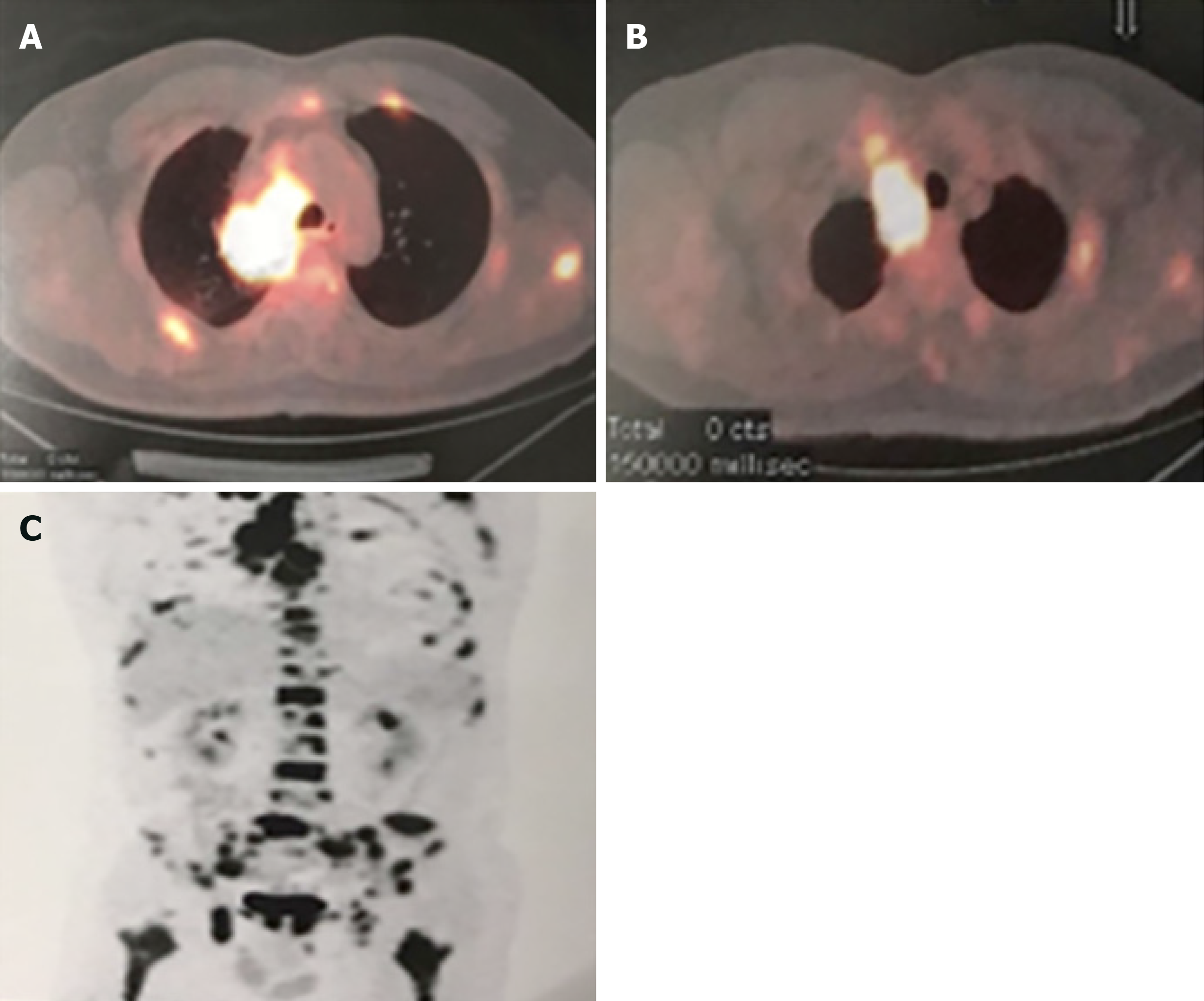
Figure 1 Computed tomography and nuclear medicine imaging.
A: Positron emission tomography-computed tomography scan of the chest revealed the presence of a mass (4.2 cm × 3.5 cm) in the right upper lobe with the maximum standardized uptake value of 18.4, indicating lung cancer; B: Chest positron emission tomography-computed tomography scan showed soft tissue thickening in the right superior lobar bronchus and right lower lobar bronchus in the dorsal segment. The maximum standardized uptake value was 11.5, indicating a malignancy; C: Multiple bone metastases illustrated through nuclear medicine imaging.
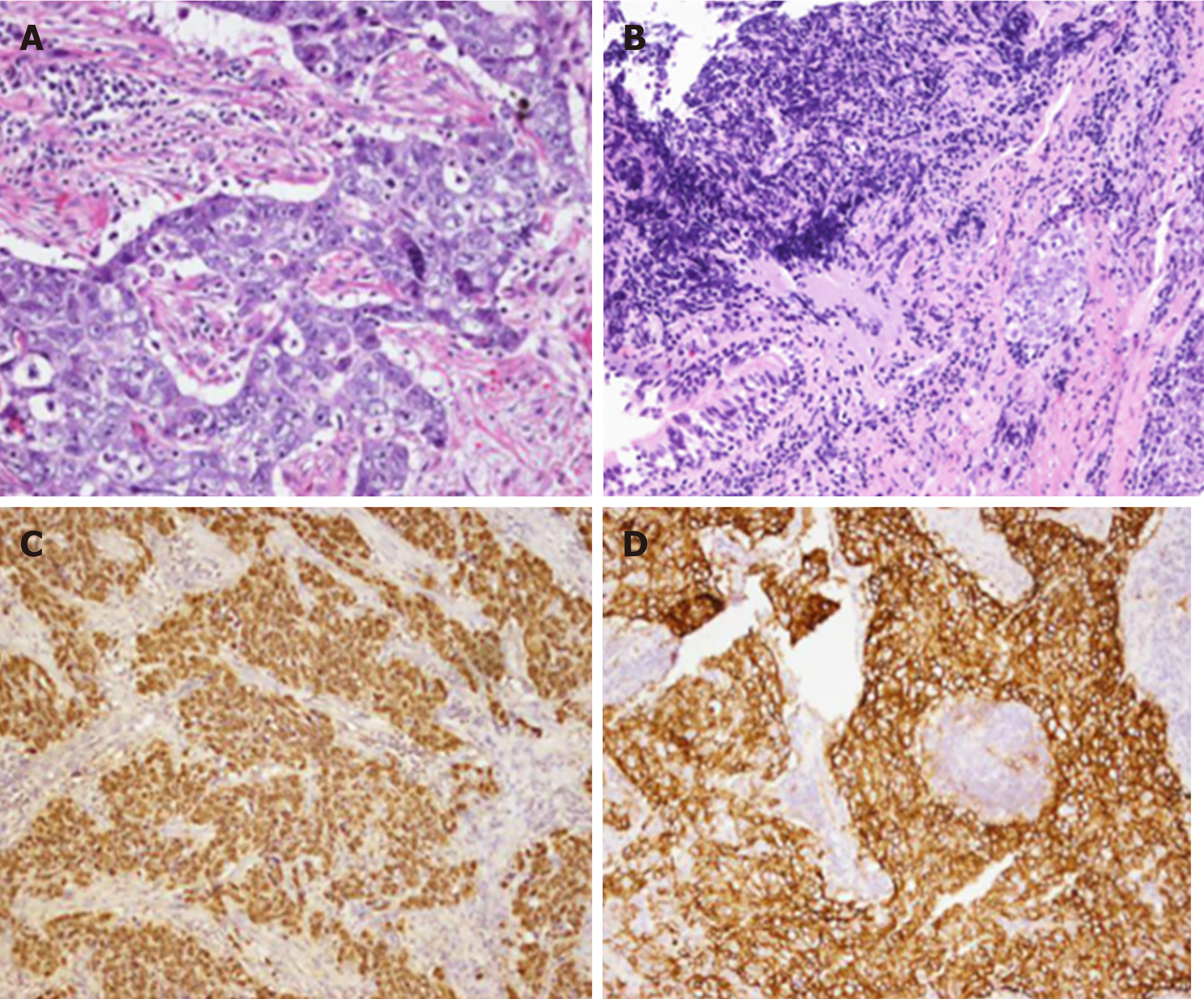
Figure 2 Histological findings.
A: Cervical lymph node biopsy (HE staining, ×200); B: Bronchoscopy biopsy (HE staining, ×200). The tumor cells were large with vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli; C: Positive immunohistochemical staining for encoded small nuclear RNA (×400) in the cervical lymph node; D: Positive immunohistochemical staining for CD56 (×400) in the cervical lymph node.
- Citation: Yang L, Liang H, Liu L, Guo L, Ying JM, Shi SS, Hu XS. CD56+ lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the lung: A case report and literature review. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(7): 1257-1264
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i7/1257.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i7.1257