Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 6, 2019; 7(23): 4044-4051
Published online Dec 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.4044
Published online Dec 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.4044
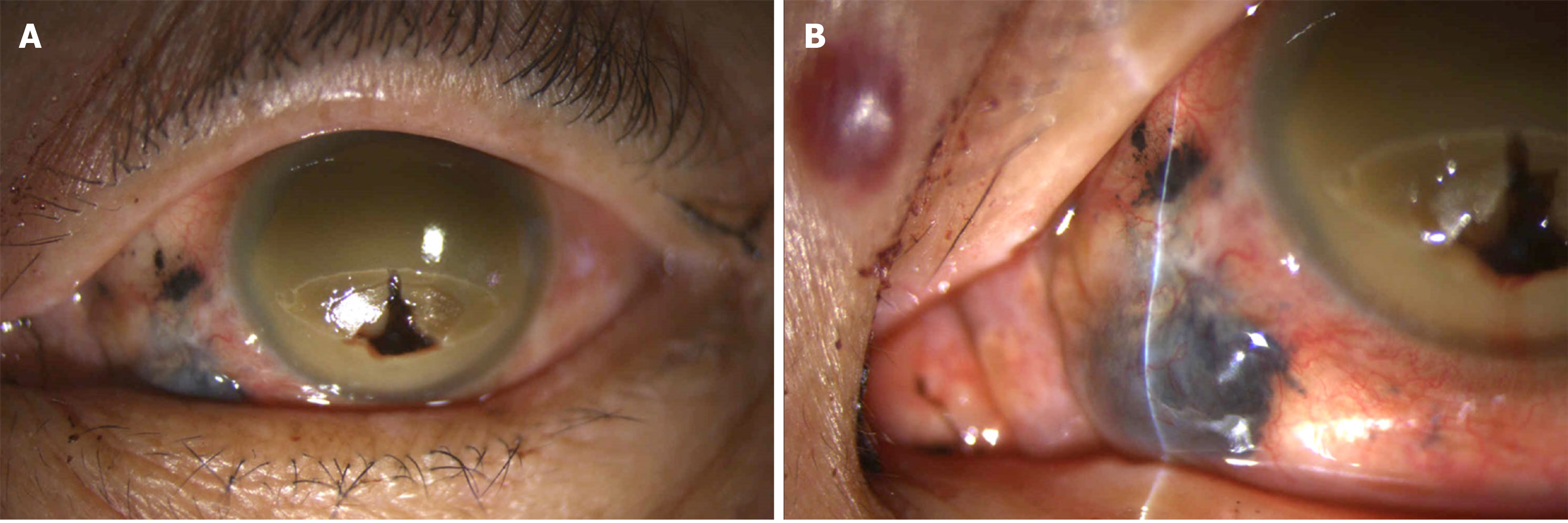
Figure 1 External view of the left eye.
A: Gross view of the left eyeball. Prolapsed uveal tissue throughout the perforated corneal zone was noted (×10); B: A 4 mm × 4 mm fixed dark brown-black subconjunctival mass with dilated and tortuous sentinel vessels at the nasal lower region of the eyeball was observed (×16).
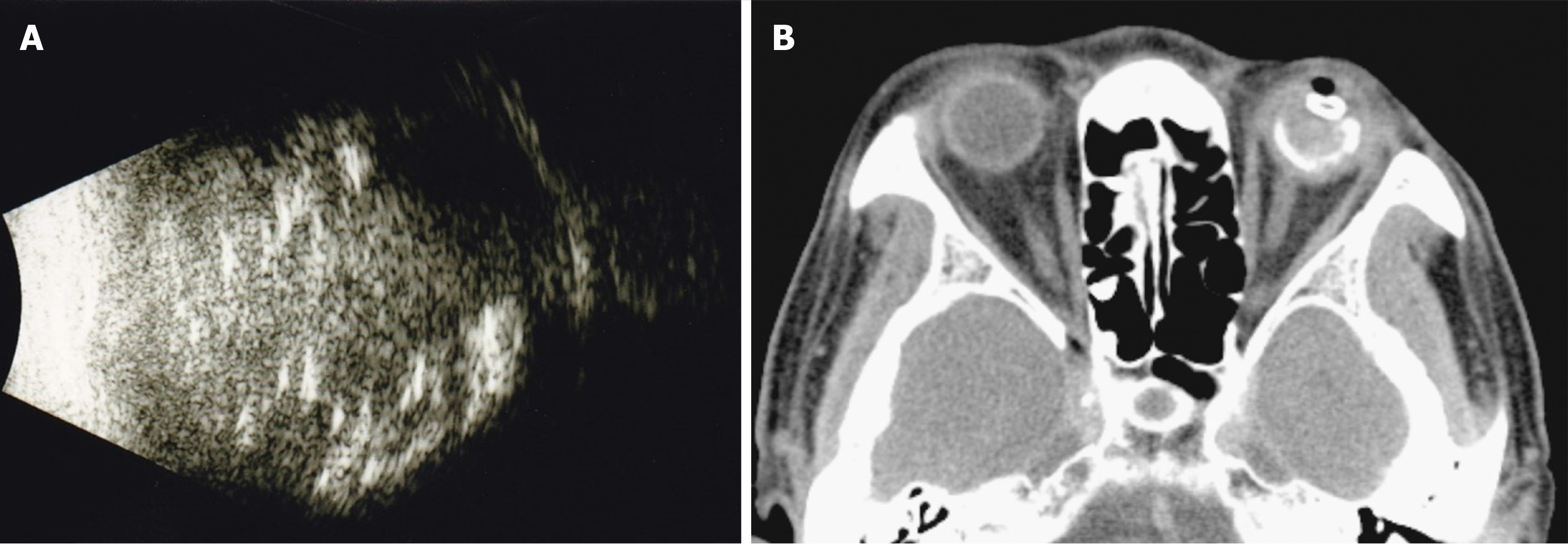
Figure 2 Initial radiological appearance of the tumor in the left eye.
A: B-scan revealed heterogenous echogenicity throughout the left eyeball; B: Computed tomography scan of the orbit showed a high-density lesion within the left eye without orbital extension.
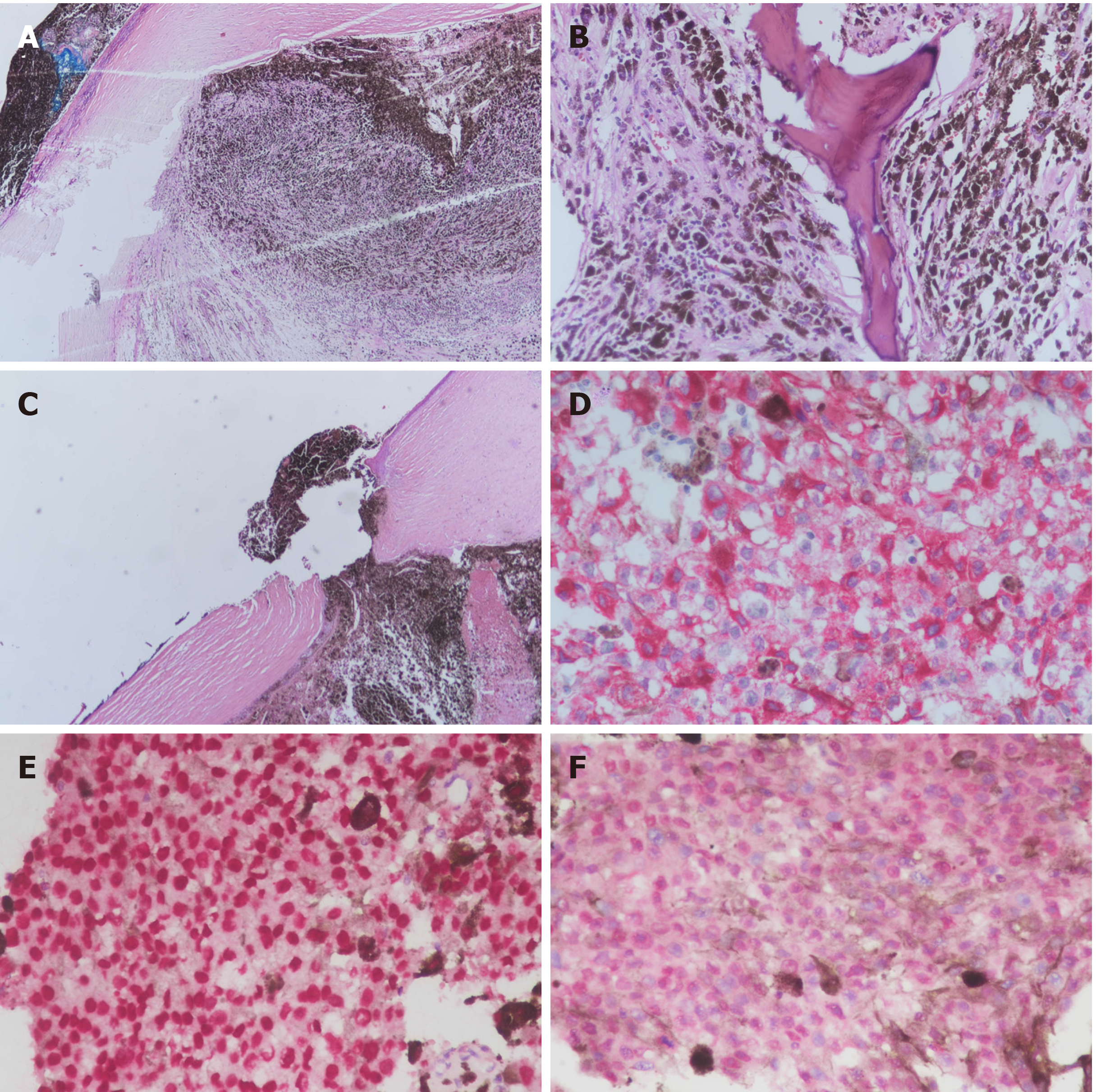
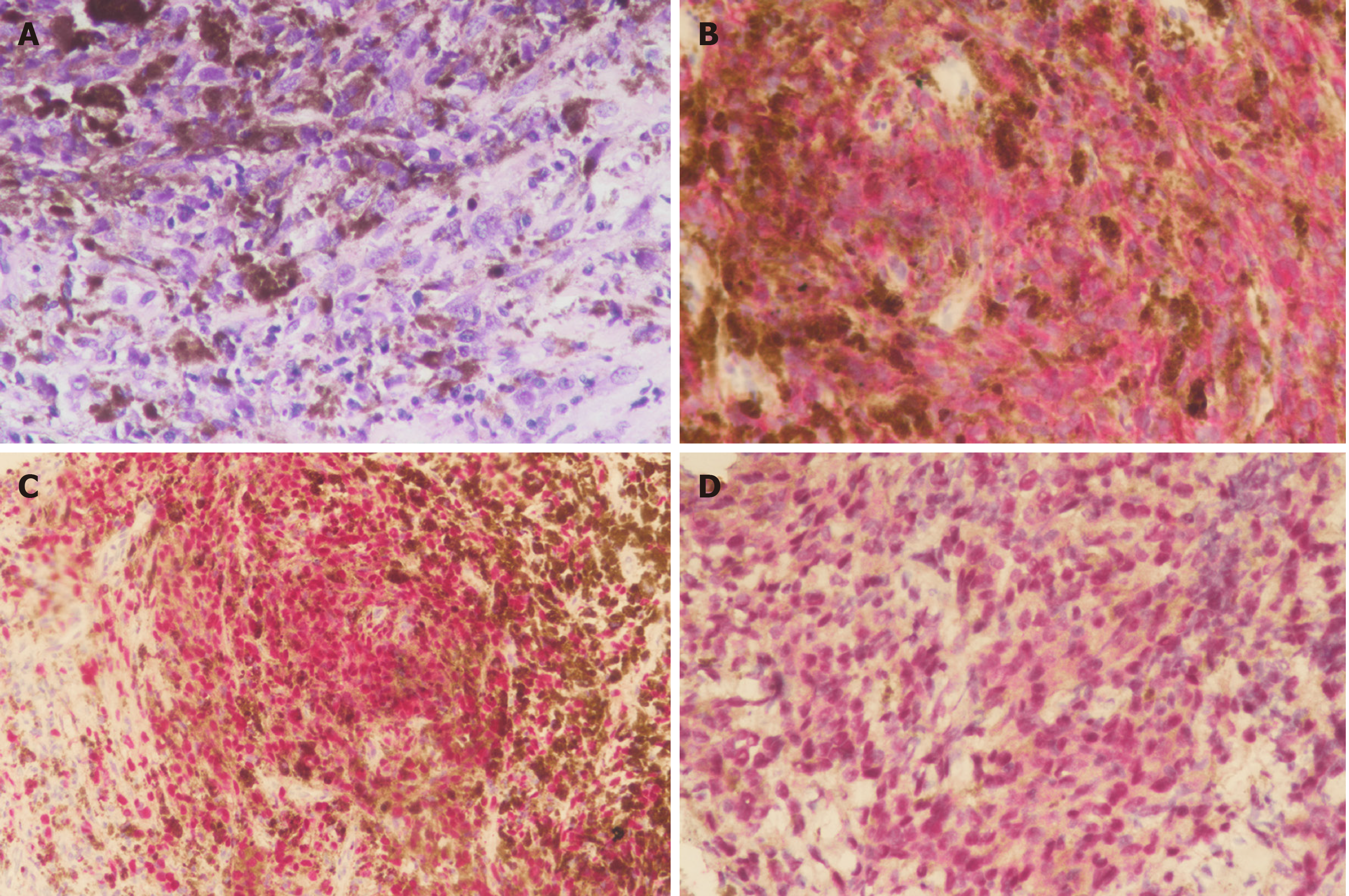
Figure 3 Histological findings of the resected tumor specimens.
A: Tumor cells occupied the entire eyeball (×40); B: Ossification was noted in the tumor (×200); C: Uveal tissue was confined in the region of the perforated cornea. Intact cornea layers and no corneal thinning or corneal ulcer was noted (×40); D: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) revealed diffusely positive melanin-A immunostaining in the cytoplasm of primary tumor cells (Red chromogen, ×400); E: IHC revealed diffusely positive SOX-10 immunostaining in the nuclei of primary tumor cells (Red chromogen, ×400); F: Primary epithelioid tumor cells showed strong nuclear labeling for BAP1 expression (Red chromogen, ×400).
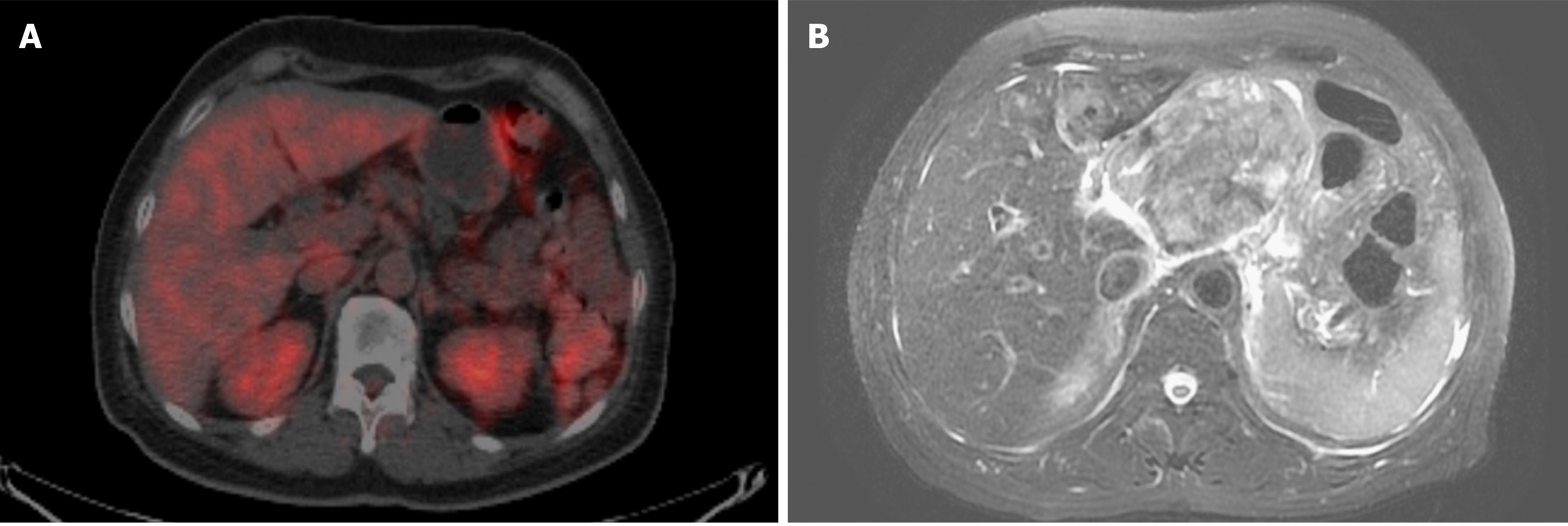
Figure 4 Images from abdominal positron emission tomography-computed tomography scans and magnetic resonance imaging.
A: positron emission tomography-computed tomography scan at initial presentation revealed no definite Fluorodeoxyglucose-avid tumor in the abdomen; B: Magnetic resonance imaging of the abdomen at 1.5 years after enucleation revealed a large mass at the upper abdomen abutting the pancreatic neck and body with a maximal diameter of at least 9.5 cm.
Figure 5 Histological findings of the fine needle aspiration specimens.
A: Specimen from the fine needle aspiration of liver tumor showed sheets of epithelioid and spindle neoplastic cells arranged in a solid pattern with occasional prominent nucleoli and eosinophilic cytoplasm that exhibited stromal reaction and abundant melanin pigment (×400); B: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) revealed diffusely positive melanin-A immunostaining in the cytoplasm of metastatic neoplastic cells (Red chromogen, ×400); C: IHC revealed diffusely positive SOX-10 immunostaining in the nuclei of metastatic neoplastic cells (Red chromogen, ×400); D: The epithelioid metastatic tumor cells showed strong nuclear labeling for BAP1 expression (Red chromogen, ×400).
- Citation: Wang TW, Liu HW, Bee YS. Distant metastasis in choroidal melanoma with spontaneous corneal perforation and intratumoral calcification: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(23): 4044-4051
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i23/4044.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.4044