Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 26, 2025; 13(24): 107535
Published online Aug 26, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i24.107535
Published online Aug 26, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i24.107535
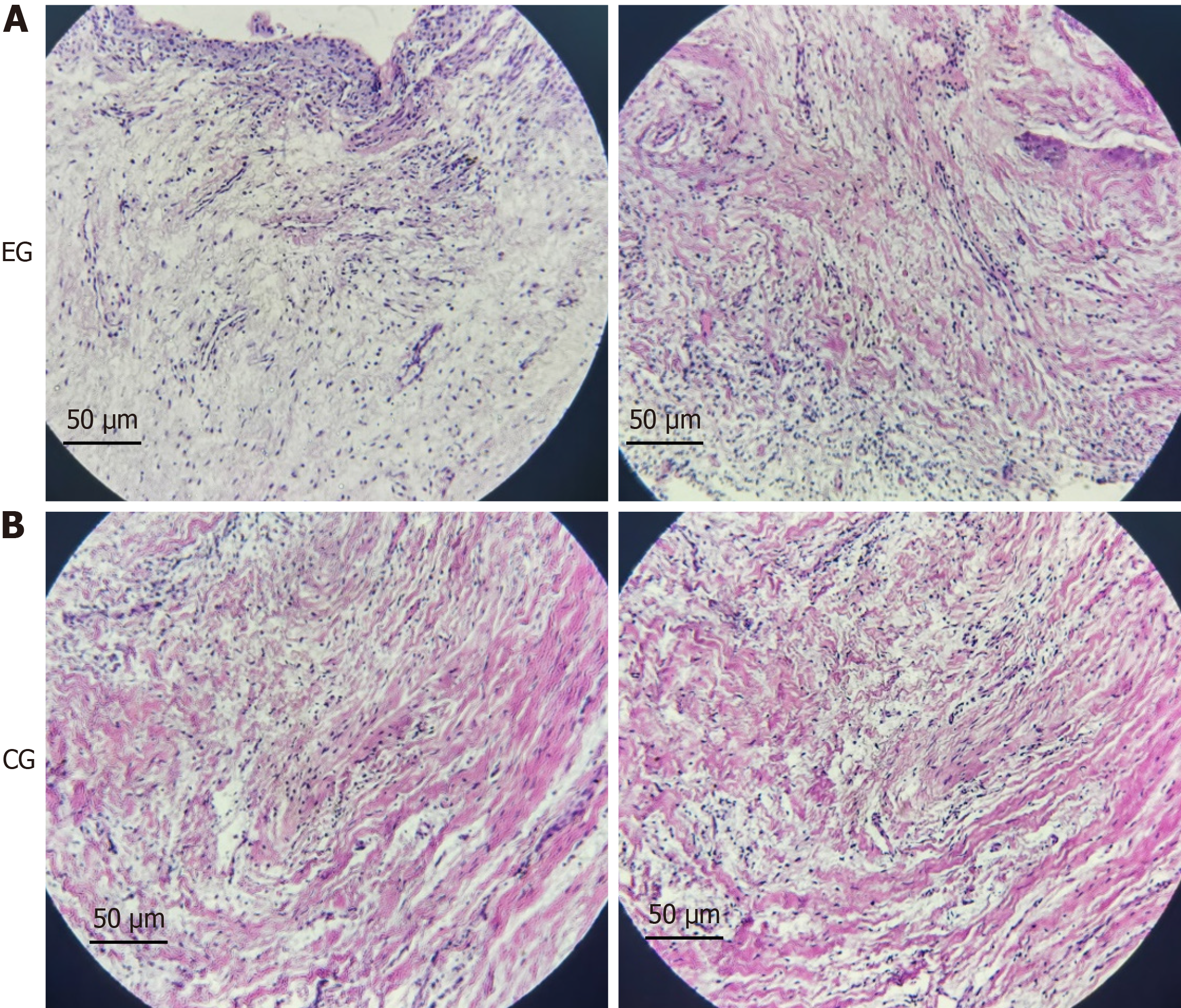
Figure 1 Morphological changes in dental follicles of patients with tooth eruption disorders.
A: The hematoxylin and eosin staining results of dental follicle tissues from the two patients with tooth eruption disorder showed that the volume of dental follicle cells decreased, the nuclei were condensed, and there seemed to be cellular fibrosis; B: The result of hematoxylin and eosin staining of normal dental follicle tissue in the control group (×200).
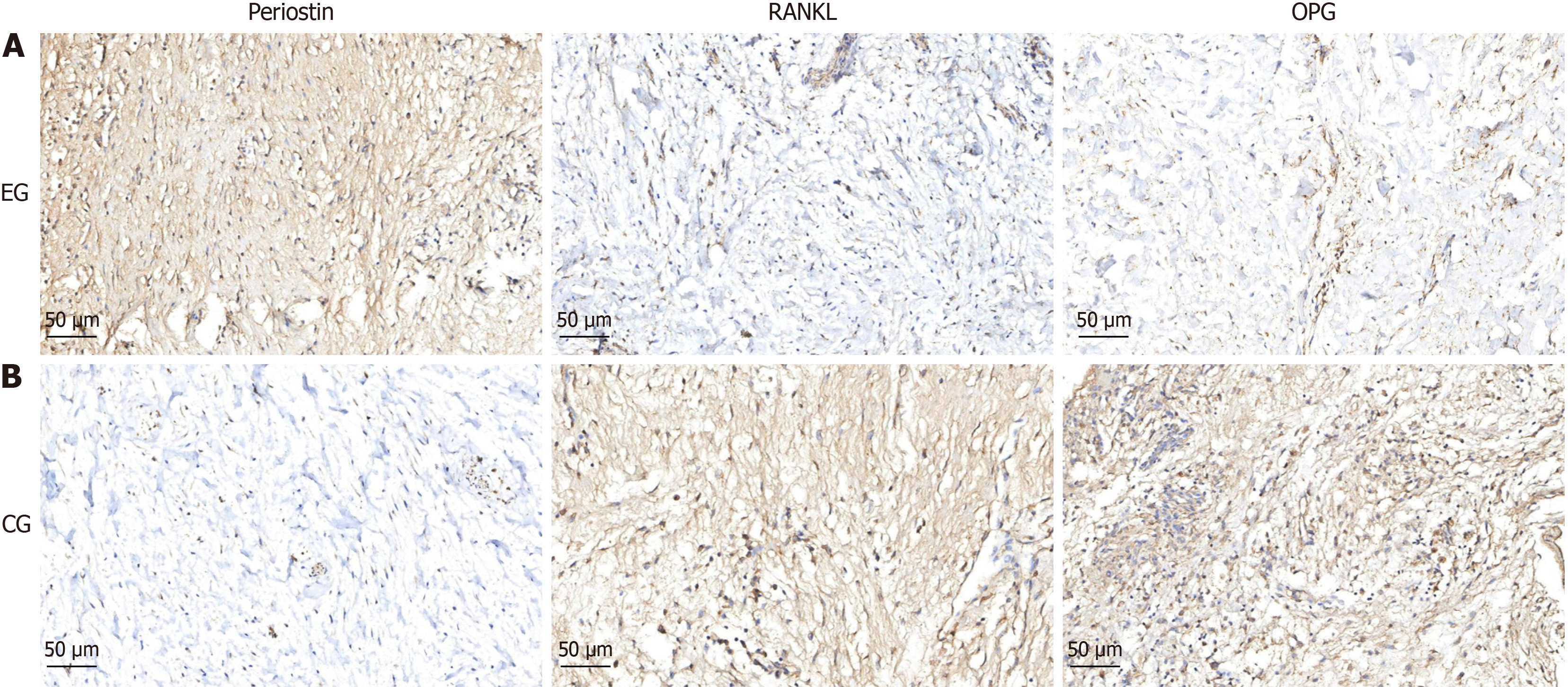
Figure 2 Detection of relevant proteins in dental follicle tissue.
A: Immunohistochemical staining results of dental follicle tissue from two patients with tooth eruption disorders. The expression of periostin protein increases, while the expression of nuclear factor kappa B ligand and osteoprotegerin protein decreases, and the ratio of nuclear factor kappa B ligand/osteoprotegerin decreases; B: Immunohistochemical results of normal dental follicle tissue in the control group (×200).
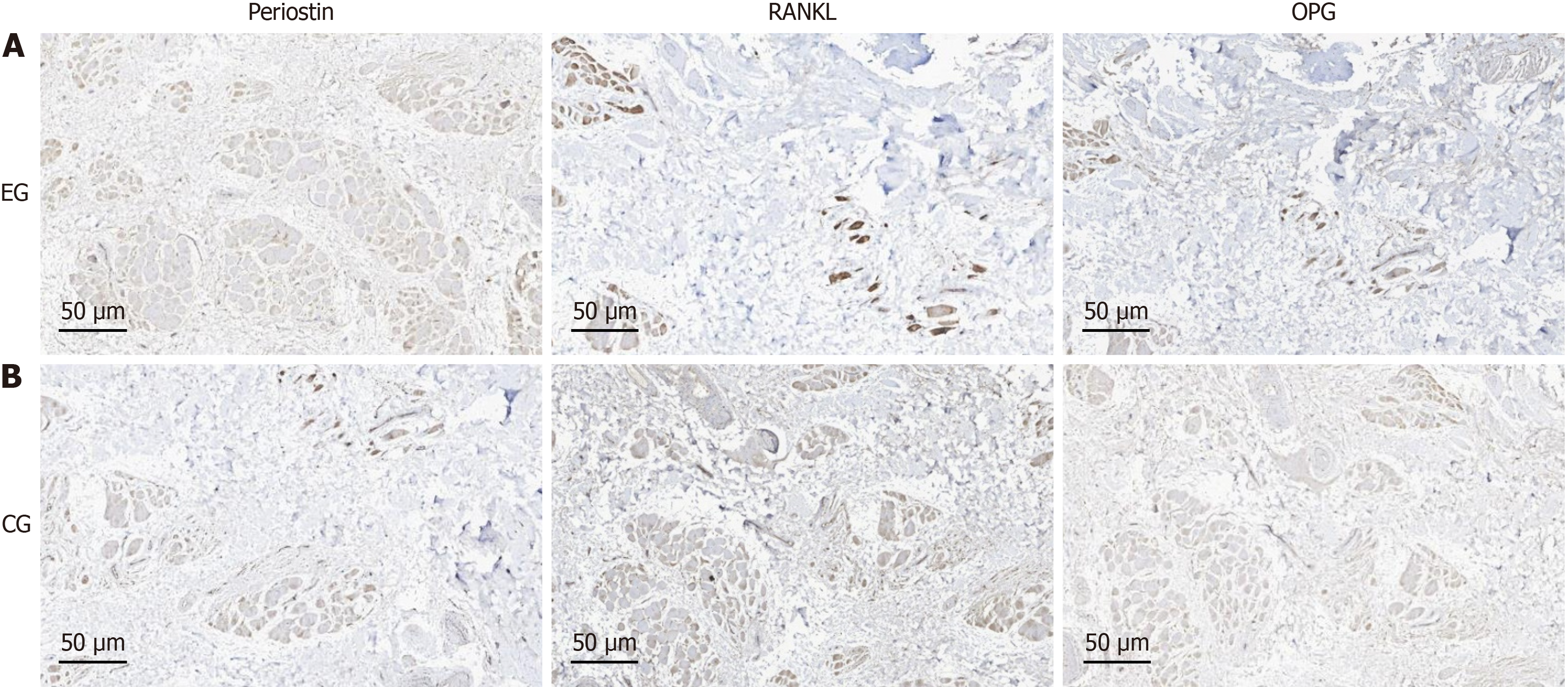
Figure 3 Detection of relevant proteins in alveolar bone tissue.
A: Immunohistochemical staining results of alveolar bone tissue from two patients with tooth eruption disorders. The expression of periostin protein increases, while the expression of nuclear factor kappa B ligand and osteoprotegerin protein decreases, and the ratio of nuclear factor kappa B ligand/osteoprotegerin decreases; B: Immunohistochemical results of normal alveolar bone tissue in the control group (×200).
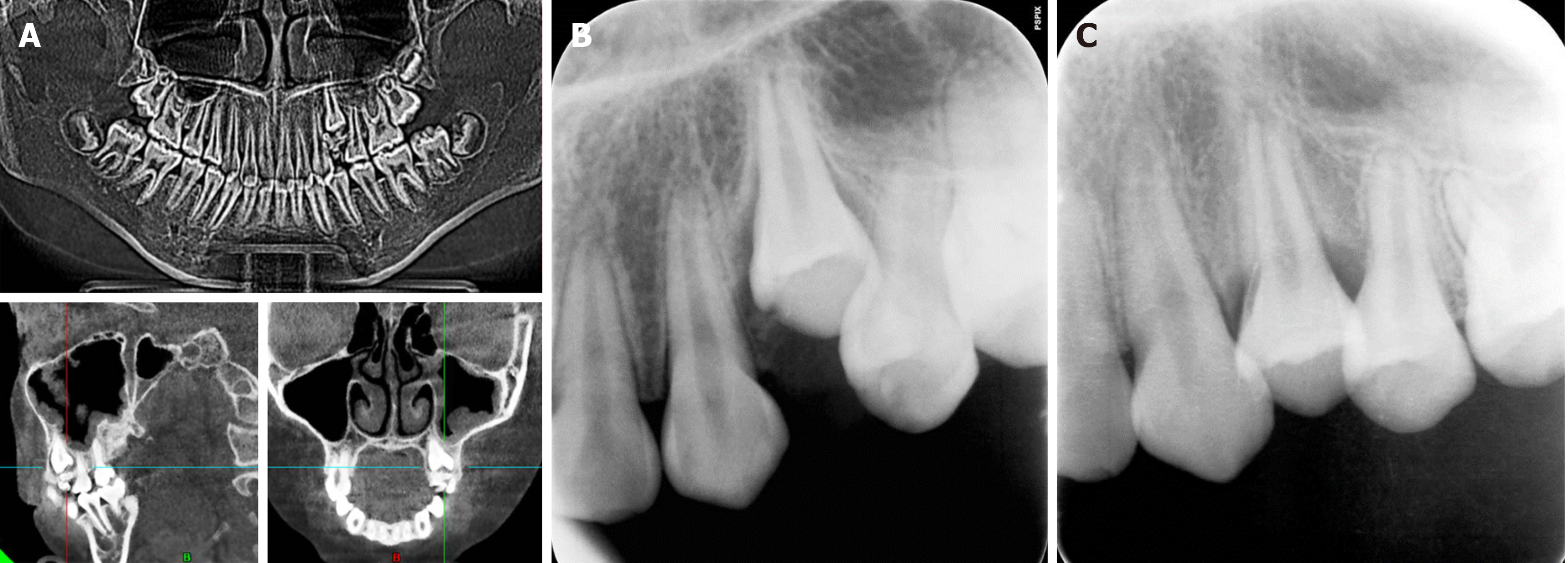
Figure 4 Imaging examination of the patient with single tooth eruption disorder.
A: Preoperative observation of tooth 24 coronal odontoma; B: First eruption of teeth observed one month after surgery; C: Three months after surgery, most of the teeth have already erupted.
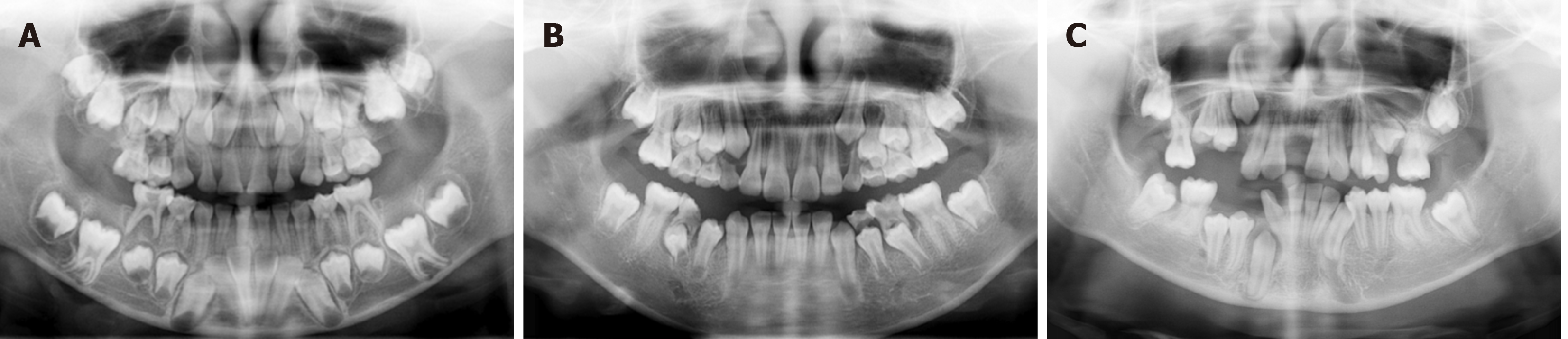
Figure 5 Imaging examination of the patient with full mouth permanent tooth eruption disorder.
A: The number of permanent tooth embryos was normal, the root of teeth 16, 26, 36, 46 were curve, root development of teeth 12-22, 32-42 was basically complete, and no obvious abnormalities were observed in alveolar bone; B: His twin sister showed no abnormality in primary and permanent teeth replacement; C: Remove crown resistance for 2 year, the panoramic radiograph examination showed that all permanent teeth have basically erupted.
- Citation: Cai J, Qin H. Mechanism analysis of periostin in osteoclasts differentiation of dental follicle: Two case reports. World J Clin Cases 2025; 13(24): 107535
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v13/i24/107535.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v13.i24.107535