Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 16, 2023; 11(29): 7061-7074
Published online Oct 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i29.7061
Published online Oct 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i29.7061
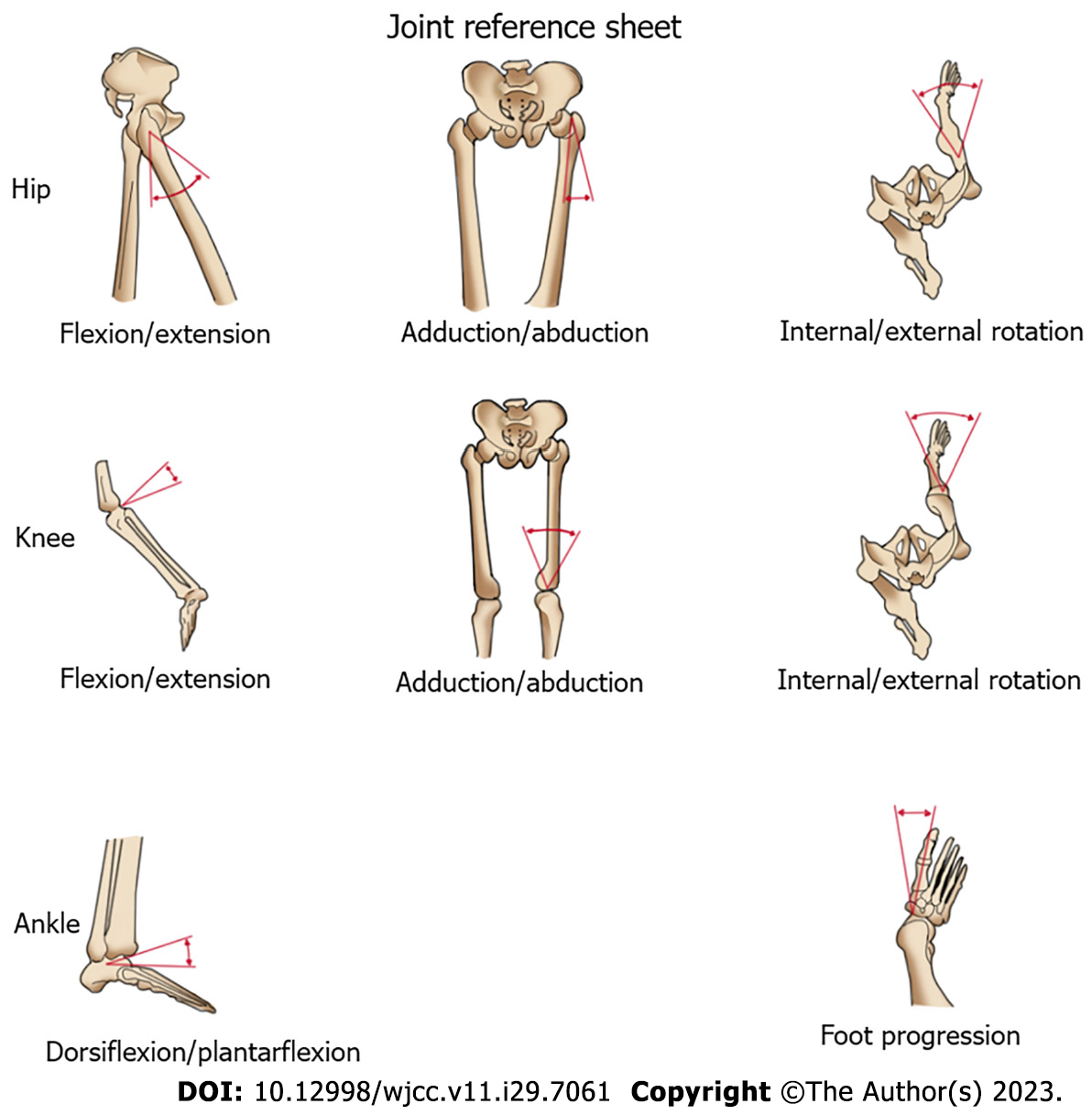
Figure 1 Illustrations of the hip, knee, and ankle joint movements in different planes.
Figure 2 Joint angle, moment and power of hip.
A: Angle of hip flexion and extension movements in males and females, with the horizontal axis representing a complete gait cycle and the vertical axis representing the angles of flexion and extension. Positive values indicated flexion, whereas negative values indicated extension. Statistical Parametric Mapping compared the differences between males and females throughout the complete gait cycle, and differences with P < 0.05 were considered statistically significant; B: Angle of hip adduction and abduction movements in males and females, with the horizontal axis representing a complete gait cycle and the vertical axis representing the angles of adduction and abduction. Positive values indicated adduction, whereas negative values indicated abduction; C: Angle of hip internal and external rotation movements for males and females, with the horizontal axis representing a complete gait cycle and the vertical axis representing the angles of internal and external rotation. Positive values indicated internal rotation, whereas negative values indicated external rotation; D: Flexor and extensor moments of the hip joint for males and females, with the horizontal axis representing a complete gait cycle and the vertical axis representing the magnitude of the moment. Positive values represented the extensor moment, whereas negative values represented the flexor moment; E: Abductor and adductor moments of the hip joint for males and females, with the horizontal axis representing a complete gait cycle and the vertical axis representing the magnitude of the moment. Positive values represent abductor moments, whereas negative values represent adductor moments; F: Hip power in males and females, with the horizontal axis representing a complete gait cycle and the vertical axis representing the magnitude of power. Positive values represent power generation whereas negative values represent power absorption. SPM: Statistical parametric mapping.
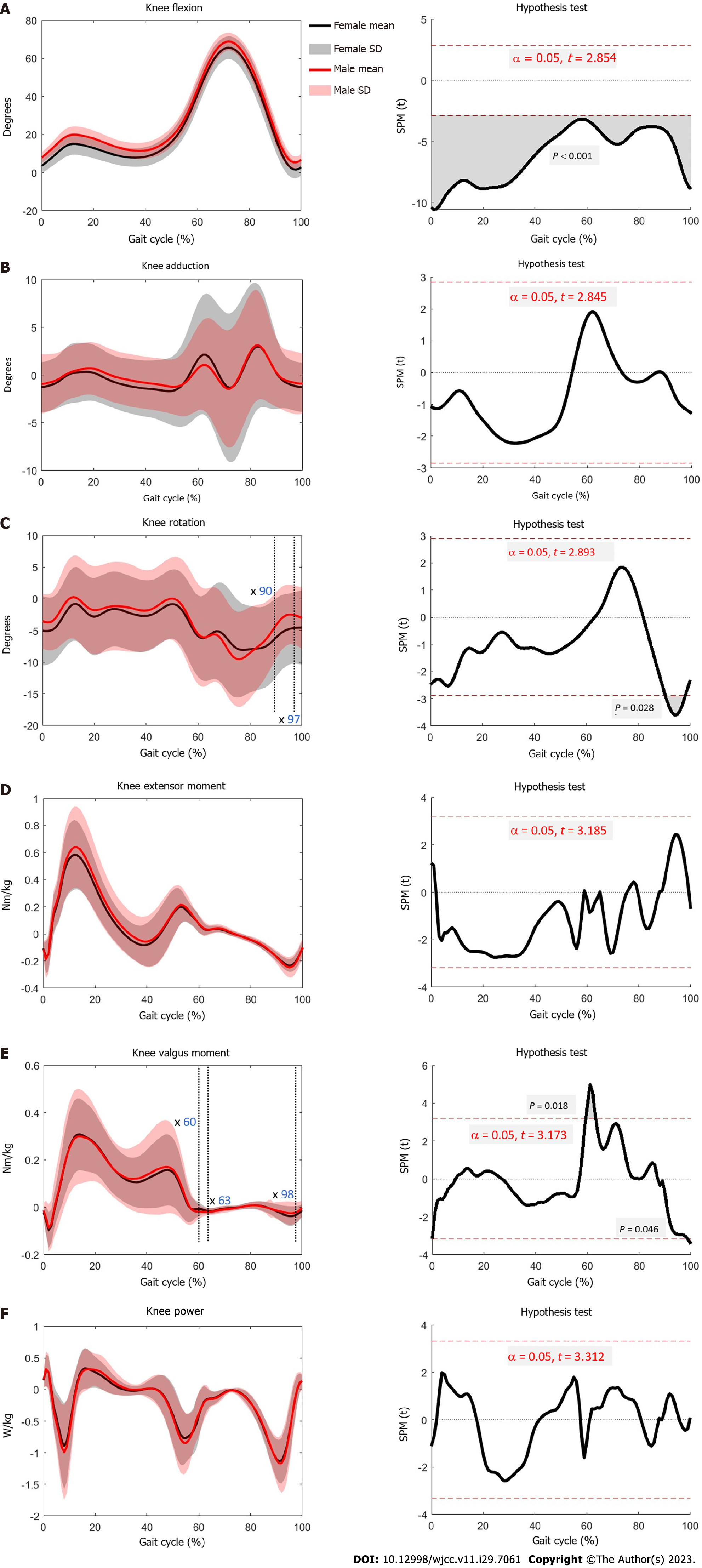
Figure 3 Joint angle, moment and power of knee.
A: Angle of knee flexion and extension movements in males and females, with the horizontal axis representing a complete gait cycle and the vertical axis representing the angles of flexion and extension. Positive values indicated flexion, whereas negative values indicated extension. Statistical Parametric Mapping compared the differences between males and females throughout the complete gait cycle, and differences with P < 0.05 were considered statistically significant; B: Angle of knee adduction and abduction movements for males and females, with the horizontal axis representing a complete gait cycle, and the vertical axis representing the angles of adduction and abduction. Positive values indicate adduction, whereas negative values indicate abduction; C: Angle of knee internal and external rotation movements for males and females, with the horizontal axis representing a complete gait cycle, and the vertical axis representing the angles of internal and external rotation. Positive values indicate internal rotation, whereas negative values indicate external rotation; D: Flexor and extensor moments of the knee joint for males and females, with the horizontal axis representing a complete gait cycle, and the vertical axis representing the magnitude of the moment. Positive values represent extensor moment, whereas negative values represented the flexor moment; E: Valgus and varus moments of the knee joint for males and females, with the horizontal axis representing a complete gait cycle, and the vertical axis representing the magnitude of the moment. Positive values represent valgus moment, whereas negative values represent varus moment; F: Knee power in males and females, with the horizontal axis representing a complete gait cycle, and the vertical axis representing the magnitude of power. Positive values represent power generation, whereas negative values represent power absorption. SPM: Statistical parametric mapping.
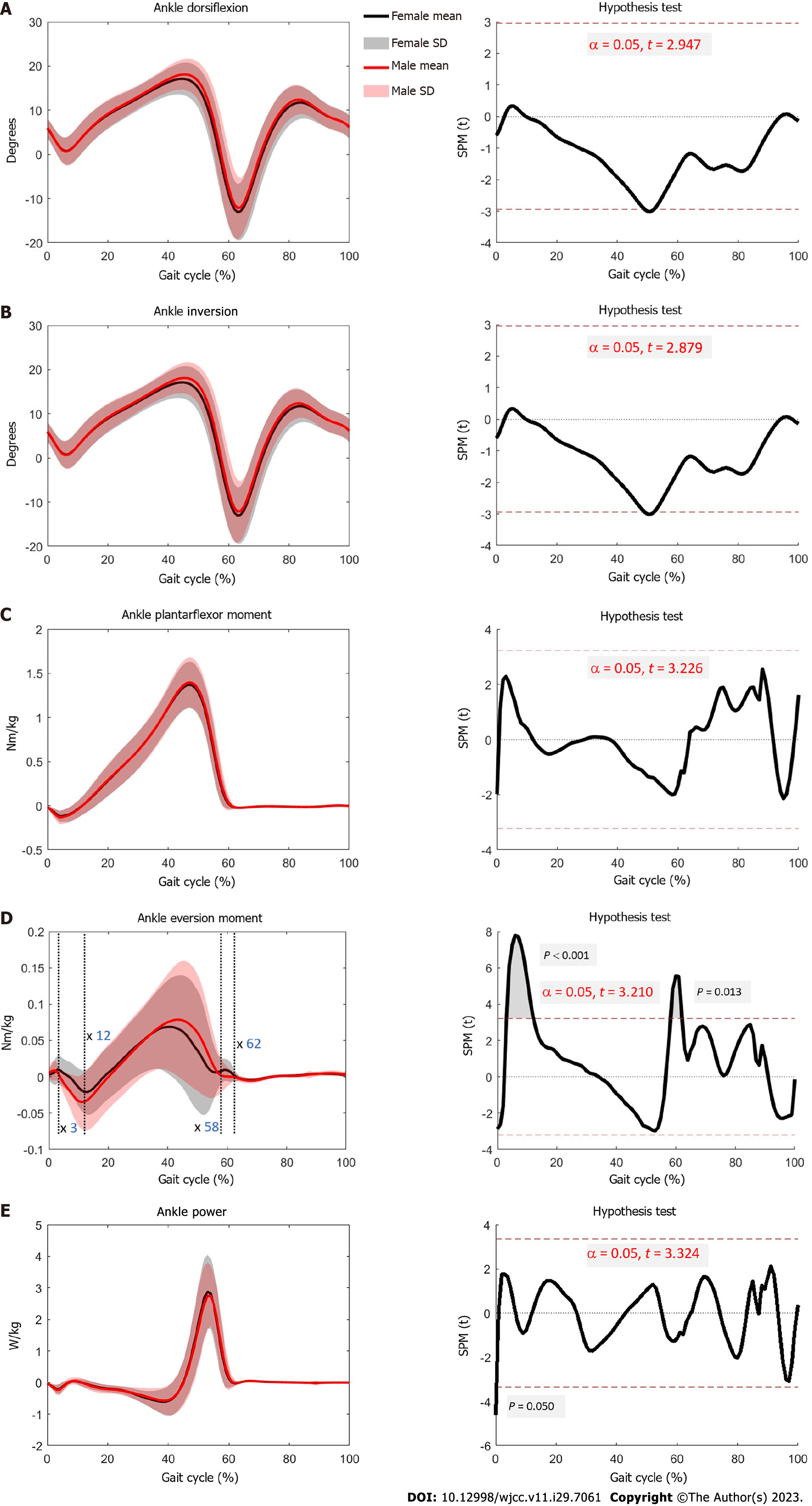
Figure 4 Joint angle, moment and power of ankle.
A: Angle of ankle dorsiflexion and plantarflexion movements for males and females, with the horizontal axis representing a complete gait cycle, and the vertical axis representing the angles of dorsiflexion and plantarflexion. Positive values indicate dorsiflexion, whereas negative values indicate plantarflexion. Statistical Parametric Mapping compared the differences between males and females throughout a complete gait cycle, and differences with P < 0.05 were considered statistically significant; B: Angle of ankle inversion and eversion movements for males and females, with the horizontal axis representing a complete gait cycle, and the vertical axis representing the angles of inversion and eversion. Positive values indicate inversion, while negative values indicate eversion; C: Plantarflexor and dorsiflexor moments of the ankle joint for males and females, with the horizontal axis representing a complete gait cycle, and the vertical axis representing the magnitude of the moment. Positive values represent plantarflexor moment, whereas negative values represent dorsiflexor moment; D: Eversion and inversion moment of the ankle joint for males and females, with the horizontal axis representing a complete gait cycle, and the vertical axis representing the magnitude of the moment. Positive values represent eversion moment, whereas negative values represent inversion moment; E: Ankle power for males and females, with the horizontal axis representing a complete gait cycle, and the vertical axis representing the magnitude of power. Positive values represent power generation, whereas negative values represent power absorption. SPM: Statistical parametric mapping.
- Citation: Yu JS, Zhuang C, Guo WX, Chen JJ, Wu XK, Xie W, Zhou X, Su H, Chen YX, Wang LK, Li WK, Tian K, Zhuang RJ. Reference values of gait parameters in healthy Chinese university students: A cross-sectional observational study. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(29): 7061-7074
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i29/7061.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i29.7061