Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Aug 19, 2025; 15(8): 107696
Published online Aug 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i8.107696
Published online Aug 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i8.107696
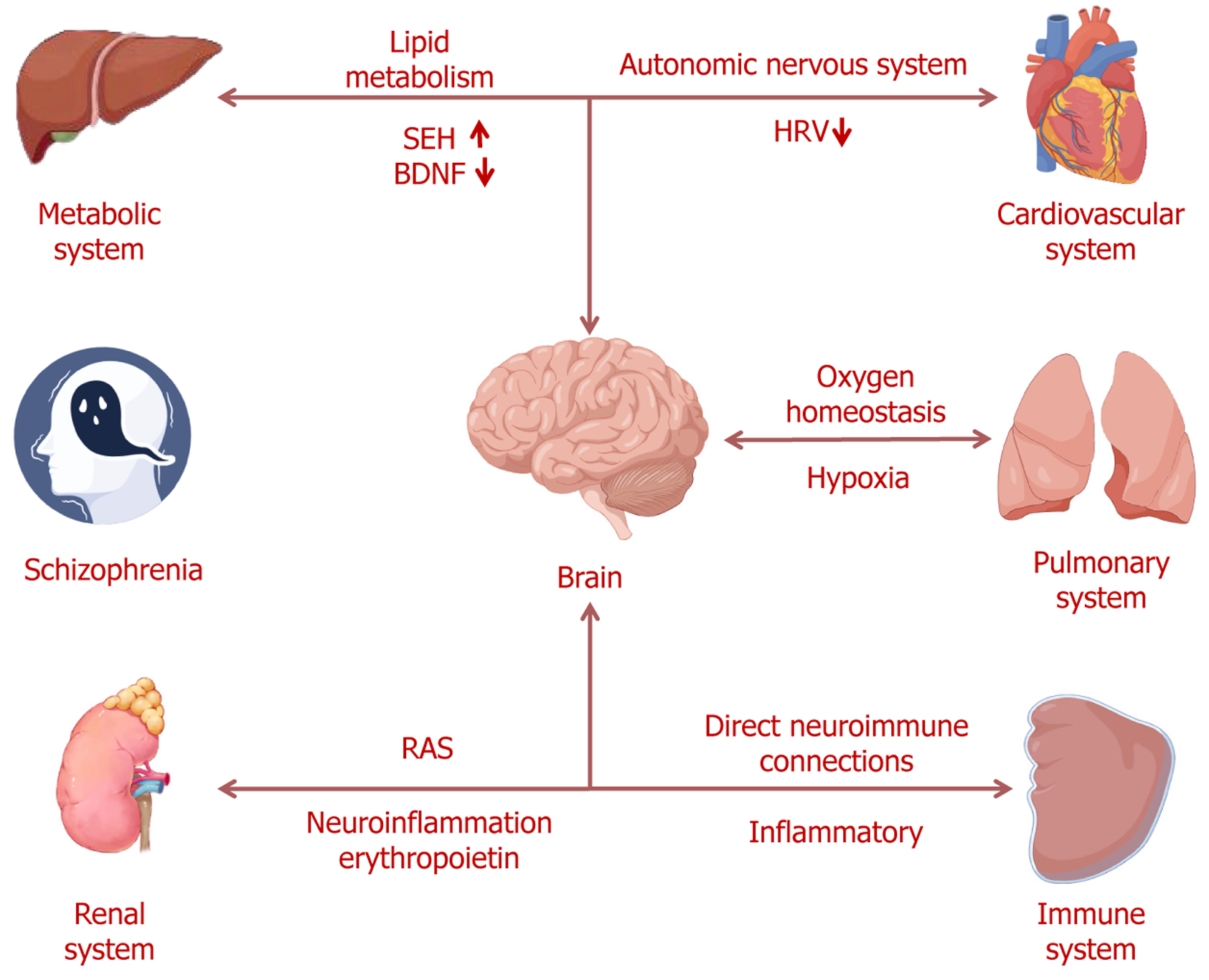
Figure 1 Dynamic interactions between the brain and other organs in schizophrenia.
Cardiovascular system: Connected to the brain via the autonomic nervous system. Reduced heart rate variability indicates dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system in schizophrenia. Pulmonary system: Interacts with the brain through oxygen homeostasis. Hypoxia can affect neurodevelopment and contribute to schizophrenia’s pathophysiology. Metabolic system: In schizophrenia, increased soluble epoxide hydrolase expression and decreased brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels may affect brain function through the brain-liver axis and lipid metabolism. Renal system: In schizophrenia, the renal system interacts with the brain via the renin-angiotensin system and is associated with neuroinflammation and erythropoietin. SEH: Soluble epoxide hydrolase; BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; HRV: Heart rate variability; RAS: Renin-angiotensin system.
- Citation: Lin J, Feng ST, Wu ZY, Dong LR, Yin DQ, Zhu H, Jia HX, Ning YZ. Interaction between the brain and multiple organ systems in schizophrenia. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(8): 107696
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i8/107696.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i8.107696