Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Exp Med. Sep 20, 2025; 15(3): 105208
Published online Sep 20, 2025. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v15.i3.105208
Published online Sep 20, 2025. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v15.i3.105208
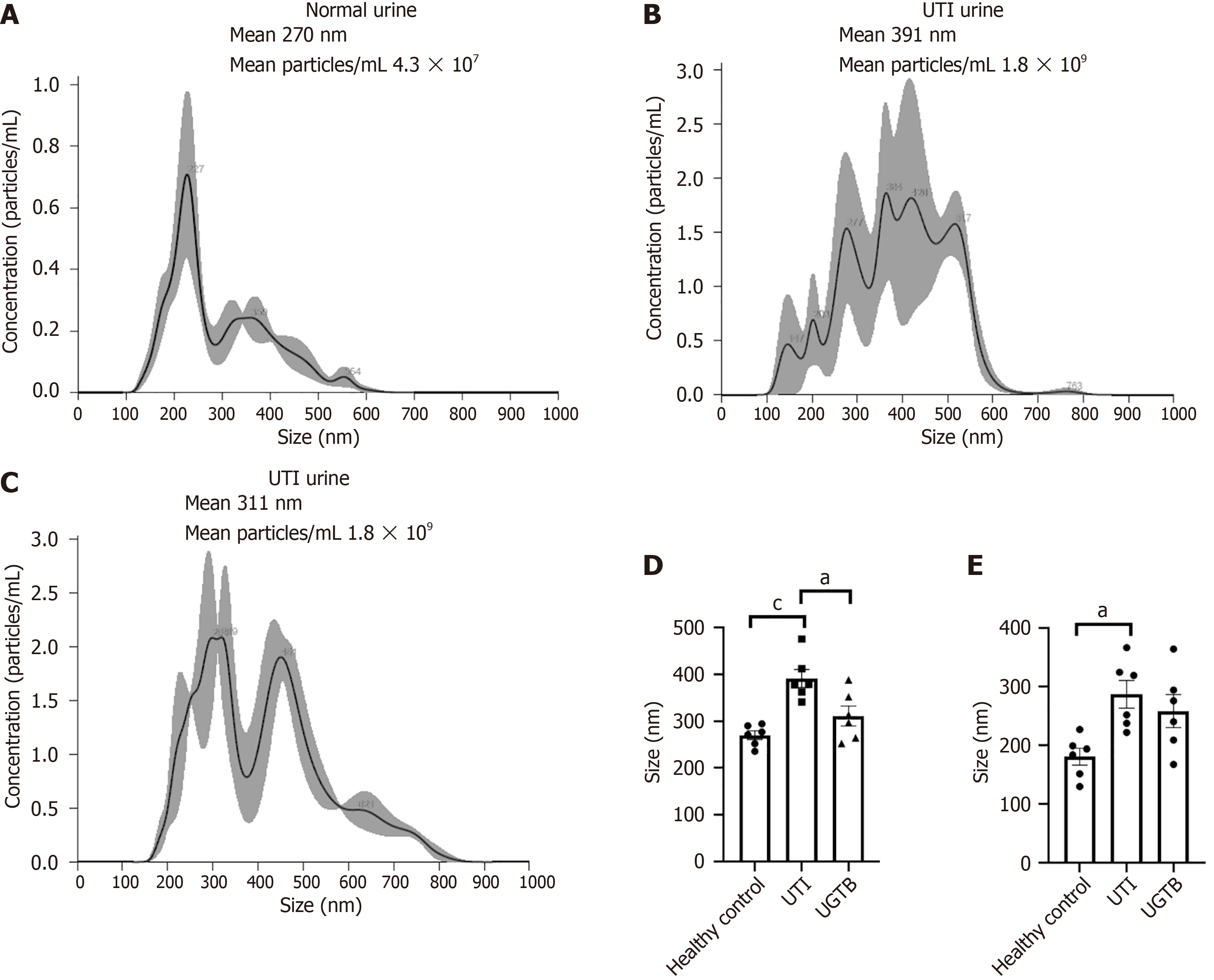
Figure 1 Urinary extracellular vesicles characterization representative nanoparticle tracking analysis plots of urinary extracellular vesicles showing mean size and mean exosome concentration (particles/mL)/size in pellet.
aP value < 0.05; cP value < 0.001. Statistical significance calculated using one-way analysis of variance test (n = 6/group). A: Normal urine; B: Urinary tract infections urine; C: Urogenital tuberculosis urine; D: Histogram depicting the nanoparticle tracking analysis mean; E: Histogram depicting the nanoparticle tracking analysis mode. UTI: Urinary tract infections; UGTB: Urogenital tuberculosis.
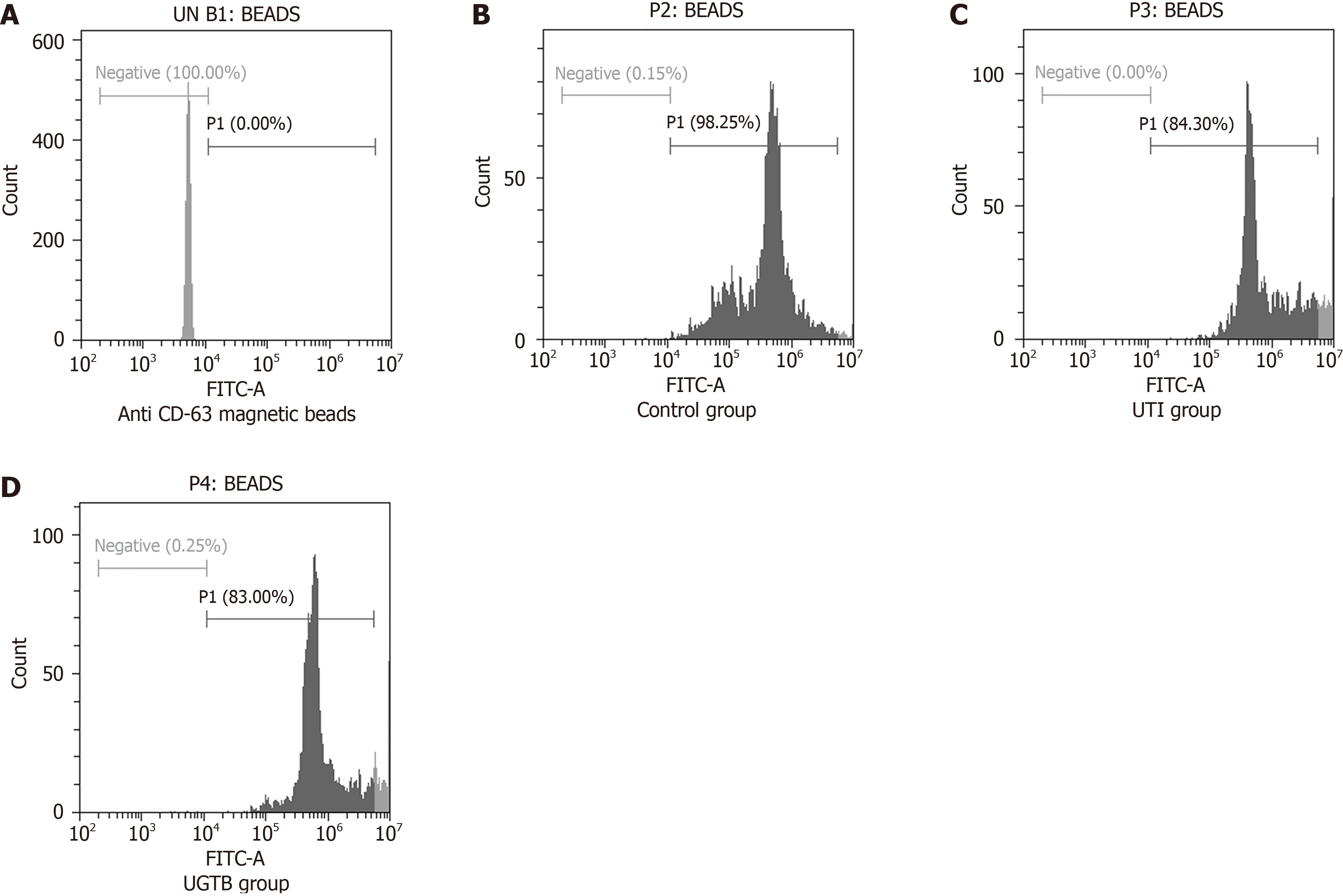
Figure 2 Urinary extracellular vesicles characterization using flow cytometry histogram depicting the expression of CD63 on the surface of urinary extracellular vesicles samples of the three study groups (n = 3/group).
Samples urinary extracellular vesicle (uEV) 1, uEV2 and uEV3, captured on anti-human CD63 magnetic beads followed by anti-CD63 primary antibody and stained with detection antibody. Grey color on histogram represents CD63 positive-extracellular vesicle population. A: Unstained anti-human CD63 magnetic beads; B: Control; C: Urinary tract infections group; D: Urogenital tuberculosis group. FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate; UTI: Urinary tract infections; UGTB: Urogenital tuberculosis.
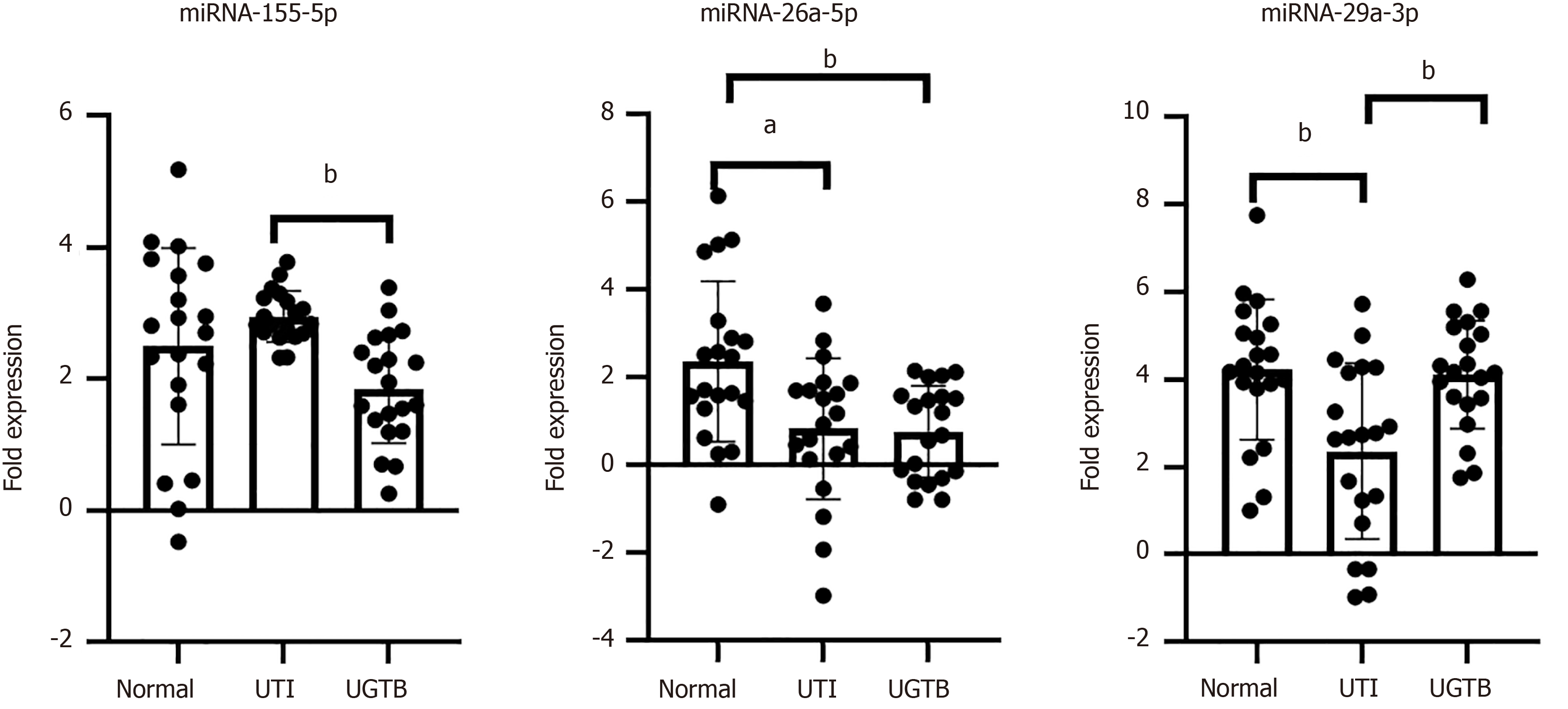
Figure 3 MicroRNAs expression in the three study groups Histogram depicting the expression of microRNA-155-5p, microRNA-26a-5p and microRNA-29a-3p amongst the three groups (n = 20/group).
aP value < 0.05; bP value < 0.01. Statistical significance calculated using one-way analysis of variance for microRNA (miRNA)-155-5 and miRNA-29a-3p and Kruskal-Wallis test for miRNA-26a-5p. MiRNAs: MicroRNA; UTI: Urinary tract infections; UGTB: Urogenital tuberculosis.
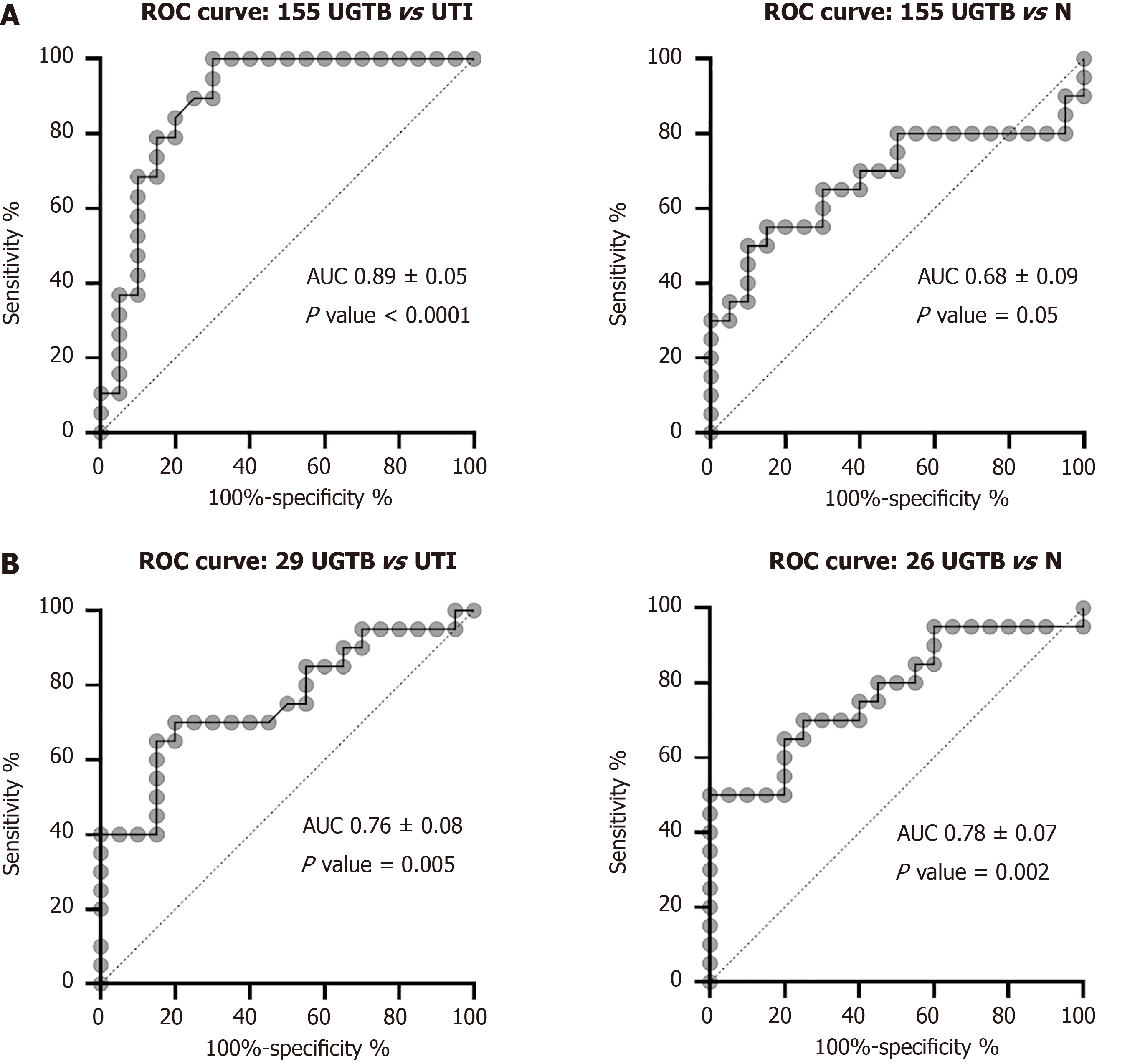
Figure 4 Receivers operating characteristic curve analysis for microRNAs expression.
A: Receivers operating characteristic curve of microRNA (miRNA)-155-5p to differentiate urogenital tuberculosis from urinary tract infection as well as from healthy controls cases, with a likely hood ratio of 5 (P < 0.0001) and 2 (P = 0.05), respectively; B: Receivers operating characteristic curve of miRNA-29a-3p and miRNA-26a-5p to differentiate urogenital tuberculosis from urinary tract infection and healthy control cases, respectively with optimal sensitivity and specificity with a likelihood ratio of more than 2. ROC: Receivers operating characteristic; N: Controls; AUC: Area under curve; UTI: Urinary tract infections; UGTB: Urogenital tuberculosis.
- Citation: Das P, Chaudhary DK, Mishra R, Tiwari S. Evaluation of urinary extracellular vesicles and microRNAs to diagnose urogenital tuberculosis. World J Exp Med 2025; 15(3): 105208
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-315X/full/v15/i3/105208.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v15.i3.105208