Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Ophthalmol. Aug 12, 2016; 6(3): 20-27
Published online Aug 12, 2016. doi: 10.5318/wjo.v6.i3.20
Published online Aug 12, 2016. doi: 10.5318/wjo.v6.i3.20
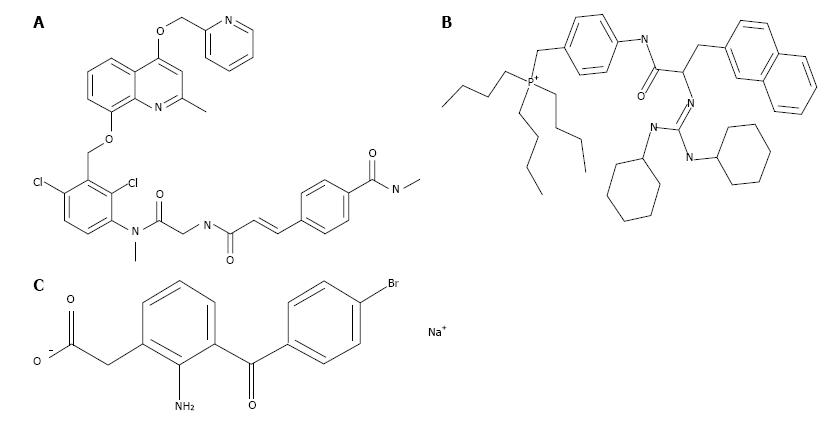
Figure 1 Structures of compounds used in the current studies.
BK: Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg; Met-Lys-BK: Met-Lys-Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg; RMP-7: H-Arg-Pro-Hyp-Gly-Thi-Ser-Pro-4-Me-Tyrψ(CH2NH)-Arg-OH; Des-Arg9-BK: Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe. A: FR-190997. HOE-140: H-D-Arg-Arg-Pro-Hyp-Gly-Thi-Ser-D-Tic-Oic-Arg-OH (peptide B2-receptor antagonist); D: D configuration of amino acid; D-BT: (3S)[amino]-5-(carbonylmethyl)-2,3-dihydro-1,5-benzothiazepin-4(5H)-one; Hyp: Trans-4-Hydroxy-L-proline; Igl: α-(2-Indanyl)glycine; Oic: Octahydroindole-2-carboxylic acid; Thi: O-(2-thienyl)-alanine; Tic: L-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carbonyl; TFA: Trifluoroacetic acid; B: WIN-64338 (non-peptide B2-receptor antagonist); C: Bromfenac sodium (cyclooxygenase inhibitor; prostaglandin synthase inhibitor).
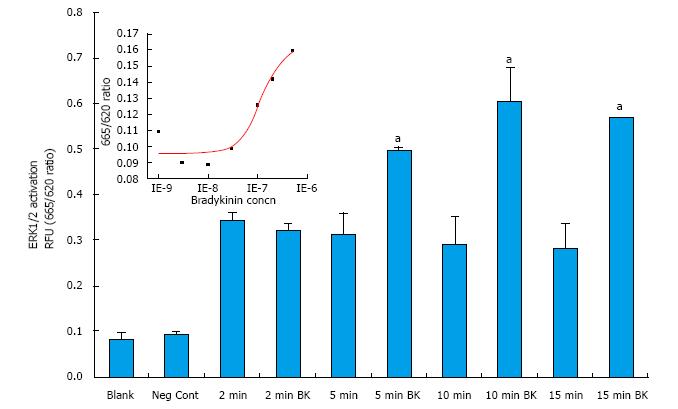
Figure 2 Time-course of bradykinin activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 in cultured primary human ciliary muscle cells.
Serum-deprived h-CM cells were incubated with either vehicle as control or with BK (100 nmol/L) for different time periods. At the end of incubation, cell lysates were analyzed for phosphorylated ERK1/2 as described in the Methods section. Data shown are blank (with nothing added), negative control (just vehicle added), followed by time control and with BK over 2-15 min. The BK-stimulated response was compared with its respective vehicle control at the same time of study. Statistical significances were determined by Student’s t-test with P < 0.05 being the minimally acceptable level of significance. Data are mean ± SEMs from 3 experiments. Differs from control at aP < 0.05 by Student’s t-test. The inset depicts a concentration-response curve for ERK1/2 activation by different concentrations of BK (1, 3, 10, 30, 100 nmol/L, etc.). ERK1/2: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2; h-CM: Human ciliary muscle; BK: Bradykinin.
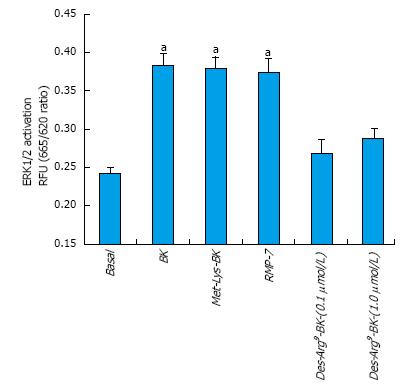
Figure 3 Effect of B2 and B1 selective agonists on extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 activation in cultured primary human ciliary muscle cells.
Serum-deprived h-CM cells were incubated for 10 min with 100 nmol/L B2 selective agonists (BK, Met-Lys-BK and RMP-7) or B1 selective agonist (Des-Arg9-BK). At the end of incubation, cell lysates were analyzed for phosphorylated ERK1/2 using Cellul’erk kit from CisBio. Differs from base-line control, aP < 0.05 by Student’s t-test. ERK1/2: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2; h-CM: Human ciliary muscle; BK: Bradykinin.
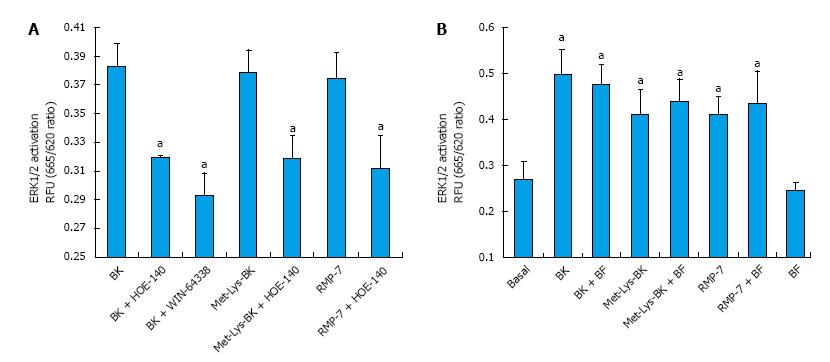
Figure 4 Extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 activation in cultured primary human ciliary muscle cells.
Effects of two B2-receptor antagonists on kinin-induced ERK1/2 activation by three BK agonists are shown in (A). Effect of bromfenac on kinin-mediated ERK1/2 activation are shown in (B). Serum-deprived h-CM cells were incubated for 10 min with 100 nmol/L B2 selective agonists BK, Met-Lys-BK and RMP-7. In experiments with antagonists or bromfenac, cells were pretreated with 100 nmol/L B2 receptor antagonist HOE-140 or WIN-64338 or bromfenac (1 μmol/L) for 15 min prior to addition of BK agonists. At the end of incubation, cell lysates were analyzed for phosphorylated ERK1/2 using Cellul’erk kit from CisBio. Significantly different than basal responses, aP < 0.05 by Student’s t-test. BK: Bradykinin; ERK1/2: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2; h-CM: Human ciliary muscle; BF: Bromfenac.
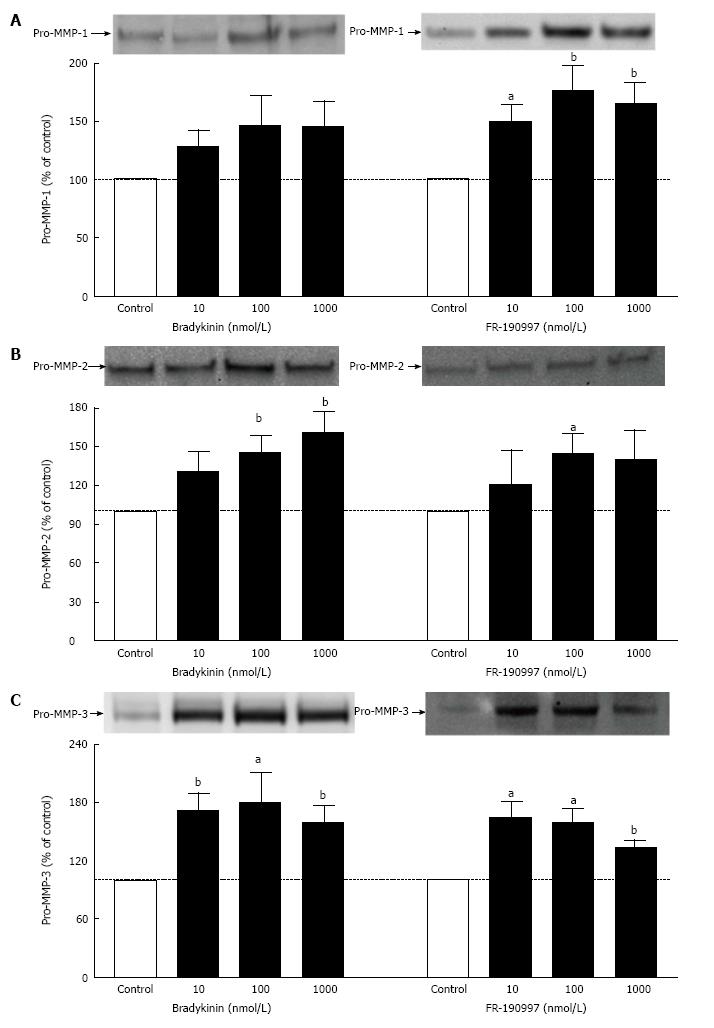
Figure 5 Effect of Bradykinin and FR-190997 on pro-matrix metalloproteinases generation in human ciliary muscle cells.
The levels of pro-MMPs produced by h-CM cells following exposure to different concentrations of either BK or FR-190997 for 6 h were determined as described in the methods section. Results shown are mean ± SEM from n = 8 for pro-MMP-1 (A); n = 6-8 for pro-MMP-2 (B); n = 4-8 for pro-MMP-3 (C). aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01 relative to base-line controls by Student’s t-test. BK: Bradykinin; h-CM: Human ciliary muscle; pro-MMPs: Pro-matrix metalloproteinases.
- Citation: Sharif NA, Patil R, Li L, Husain S. Human ciliary muscle cell responses to kinins: Activation of ERK1/2 and pro-matrix metalloproteinases secretion. World J Ophthalmol 2016; 6(3): 20-27
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-6239/full/v6/i3/20.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5318/wjo.v6.i3.20