Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
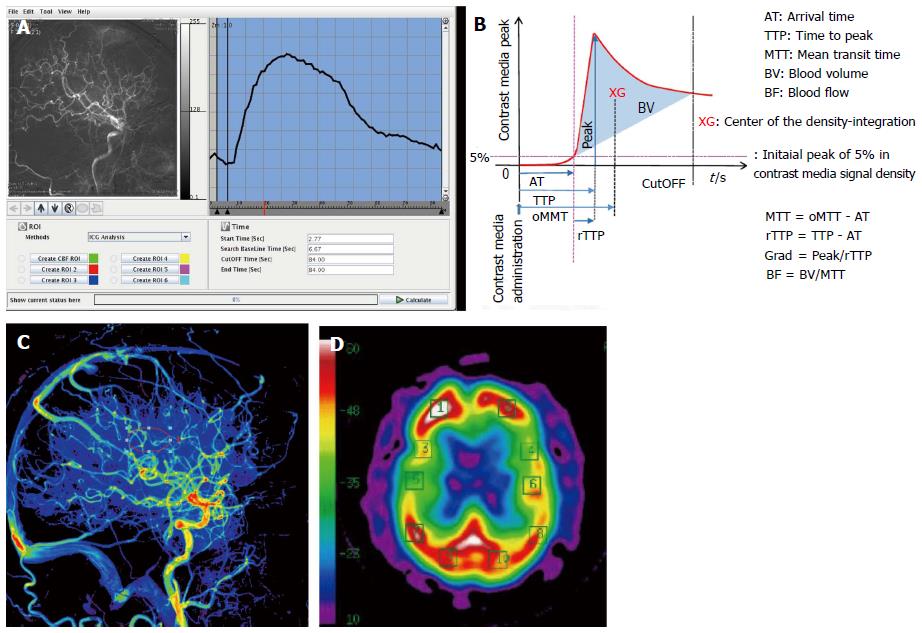
Figure 1 Digital subtraction angiography.
A: Time-density curve of digital subtraction angiography lateral view. The change in the concentration of the contrast media, visualized as a change in brightness, was calculated; B: The parameters calculable by the “Flow-Insight” application; C: Lateral view of a pre-operative qualitative image of cerebral blood flow in Case 2; D: Pre-operative N-isopropyl-p-[123I] iodoamphetamine-single-photon emission computed tomography image.
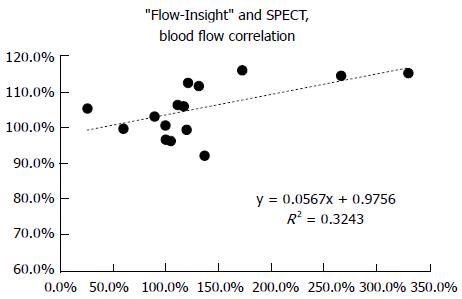
Figure 2 Horizontal axis: Rate of change of the “Flow-Insight” (%); Vertical axis: Rate of the rise of the ipsilateral cerebellum ratio as determined postoperatively by N-isopropyl-p-[123I] iodoamphetamine-single-photon emission computed tomography.
SPECT: Single-photon emission computed tomography.
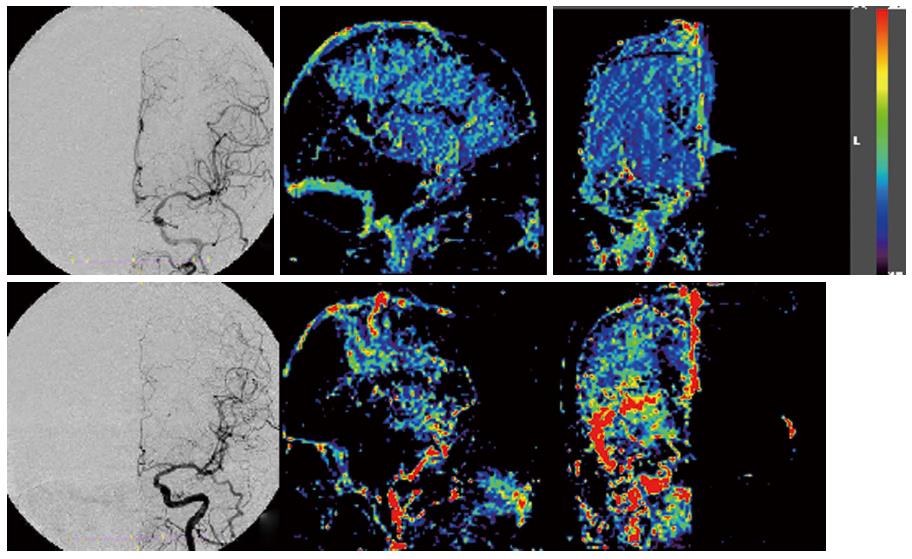
Figure 3 Upper panel: Digital subtraction angiography anterior-posterior view, lateral view showing the blood flow increase ratio, and the anterior-posterior view in Case 1; and Lower panel: Case 2, same series.
Pre-operative digital subtraction angiography in Cases 1 and 2 did not reveal blood flow to the operative side via the anterior communicating artery. In Case 1, a wide and slight increase was noted in the area in the middle cerebral artery territory. In Case 2, the increase was only noted in a part of the middle cerebral artery perfusion area; the rate of increase was high.
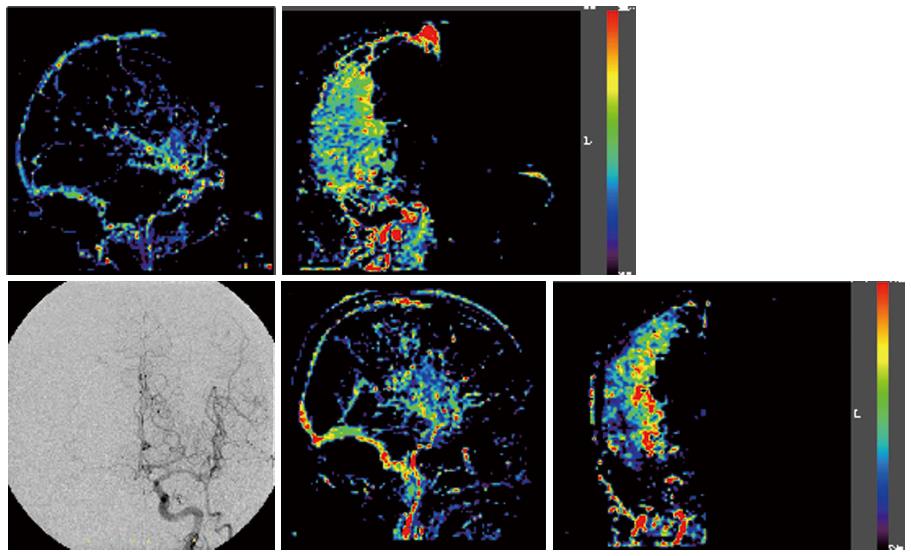
Figure 4 Upper panel: Digital subtraction angiography anterior-posterior view, lateral view showing the blood flow increase ratio, and the anterior-posterior view in Case 3; and Lower panel: Case 4, same series.
Pre-operative digital subtraction angiography in Cases 3 and 4 revealed blood flow to the operative side via the anterior communicating artery. A wide and uniform increase in the area in the middle cerebral artery territory was noted in Case 3. In Case 4, the increase was only noted in a part of the middle cerebral artery perfusion area, especially in the basal ganglia; the rate of increase was high.
- Citation: Wada H, Saito M, Kamada K. Evaluation of changes of intracranial blood flow after carotid artery stenting using digital subtraction angiography flow assessment. World J Radiol 2015; 7(2): 45-51
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v7/i2/45.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v7.i2.45