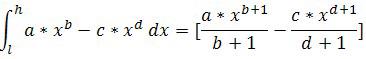Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Nov 28, 2013; 5(11): 421-429
Published online Nov 28, 2013. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v5.i11.421
Published online Nov 28, 2013. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v5.i11.421
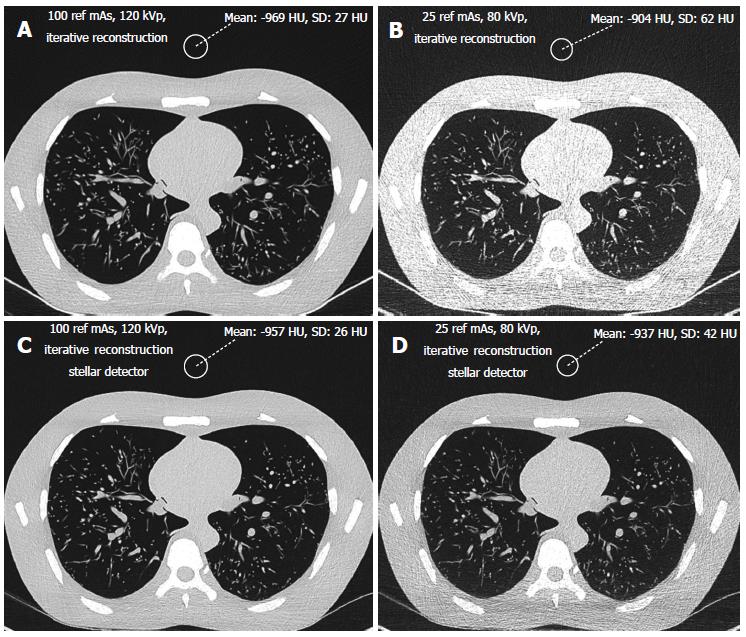
Figure 1 Imaging of the lung using iterative reconstruction with (C, D) and without (A, B) the Stellar detector.
The chest phantom was scanned at a standard dose level with a 100 reference mAs tube current time and a 120 kVp voltage (A, C) and the lowest dose level of 25 ref mAs and 80 kVp. At the standard dose level both images with and without the Stellar detector (A,C) had similar noise levels (20-30 HU), while at the lowest dose, the image quality was obviously better with the Stellar detector (D).
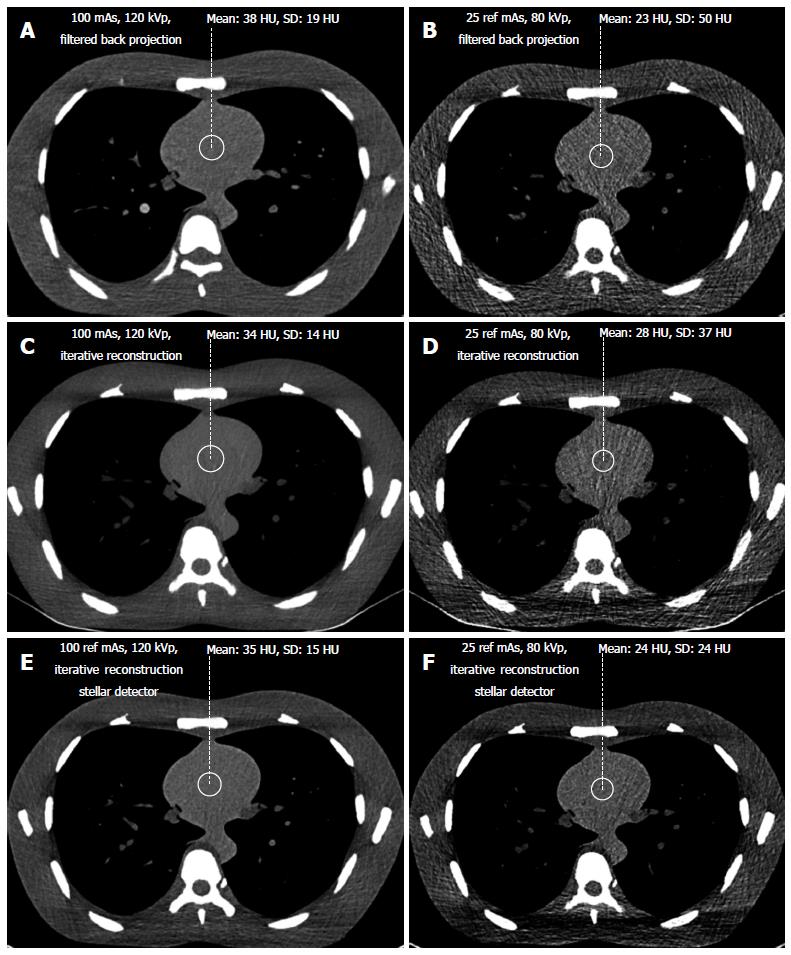
Figure 2 Soft tissue imaging using filtered back projection (A, B), iterative reconstruction (C, D, E, F) and the Stellar detector (E, F).
At standard dose levels (A, C, E), image quality decreased from left to right. At the lowest dose level (B, D, F), the difference in noise increased. The image quality of the low dose image with the Stellar detector (F) was close to the image quality of that for a standard dose with a filtered back projection (A).
Math 1 Math(A1).
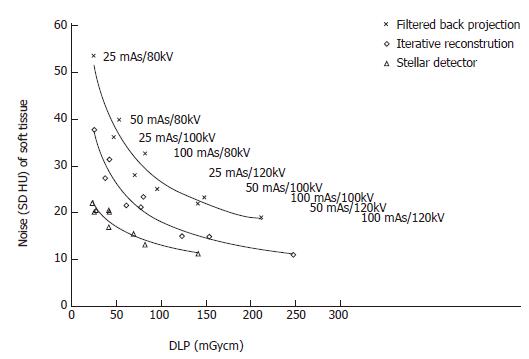
Figure 3 Noise for soft tissue imaging vs the radiation dose (dose-length product) for the different scanners.
The improvement in the noise/dose was about the same for iterative reconstruction and the Stellar detector. The average noise reduction was approximately 30%. For the same image quality, the dose could be reduced by over 50%.
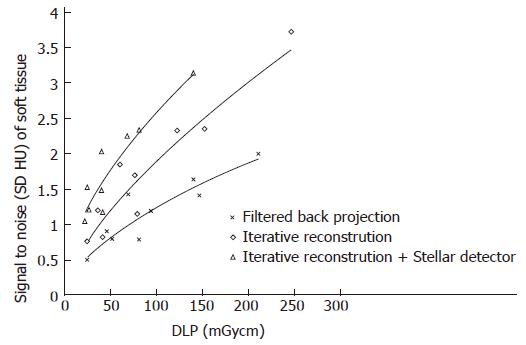
Figure 4 Signal to noise ratio vs radiation dose for the different scanners.
Image quality was increased by 36% and 38% using iterative reconstruction and the Stellar detector, respectively.
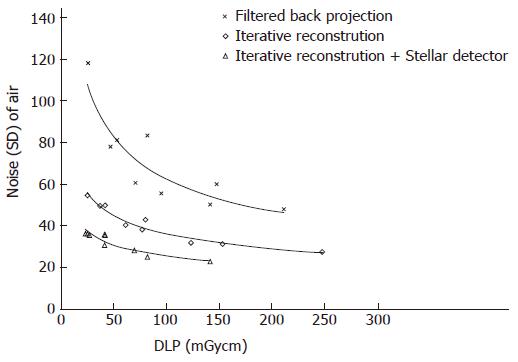
Figure 5 Image noise vs radiation dose in air.
For pulmonary imaging, the noise reduction was 45% and 31% for iterative reconstruction and filtered back projection, respectively. For the Stellar detector and iterative reconstruction alone, the average dose reduction was 80% and 70%, respectively.
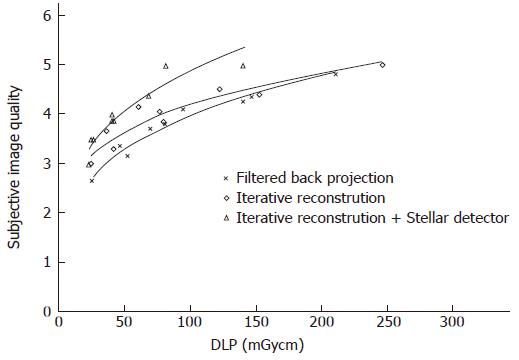
Figure 6 Subjective image quality vs dose.
Subjective image quality increased on average from 0.2 to 0.5 using iterative reconstruction and the Stellar detector on a scale from 1 to 5, 5 being the maximum.
- Citation: Christe A, Heverhagen J, Ozdoba C, Weisstanner C, Ulzheimer S, Ebner L. CT dose and image quality in the last three scanner generations. World J Radiol 2013; 5(11): 421-429
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v5/i11/421.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v5.i11.421