Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Oct 28, 2012; 4(10): 421-430
Published online Oct 28, 2012. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v4.i10.421
Published online Oct 28, 2012. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v4.i10.421
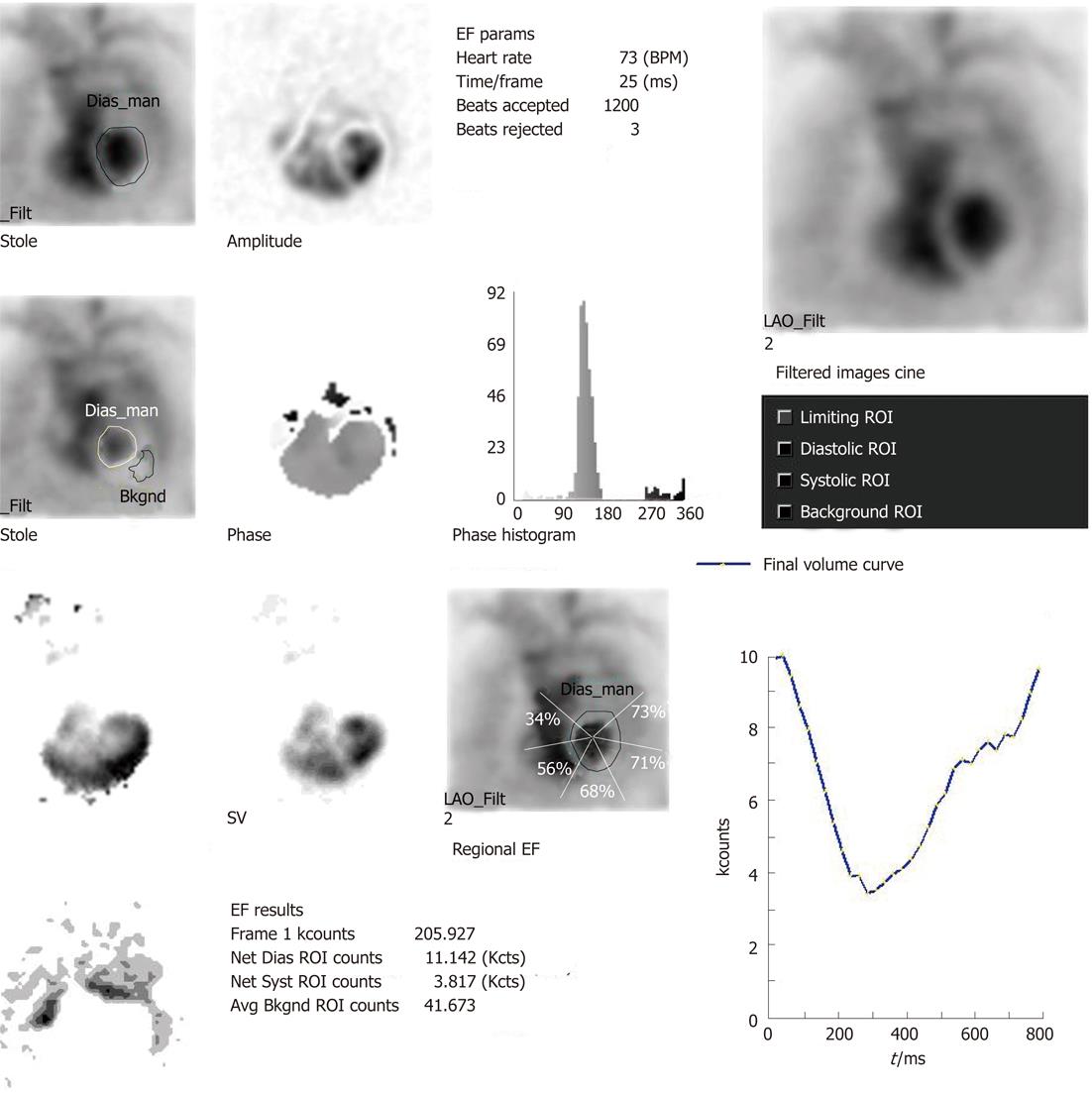
Figure 1 Normal multigated acquisition study with left ventricular ejection fraction of 66%.
The phase image shows synchronous contraction across the left ventricular (LV) myocardium with narrow phase histogram width. The left and right ventricular phases are in sync with each other and out of sync with the atrial phase. The amplitude image shows maximal count variation in the lateral wall of LV myocardium suggesting maximal contraction by lateral wall and paradox image does not show any wall of LV myocardium to be in paradox. LV time activity curve is normal. EF: Ejection fraction; ROI: Region of interest; LAO: Left anterior oblique; SV: Stroke volume; Syst: Systolic; Dias: Diastolic; Avg Bkgnd: Average backgroud.
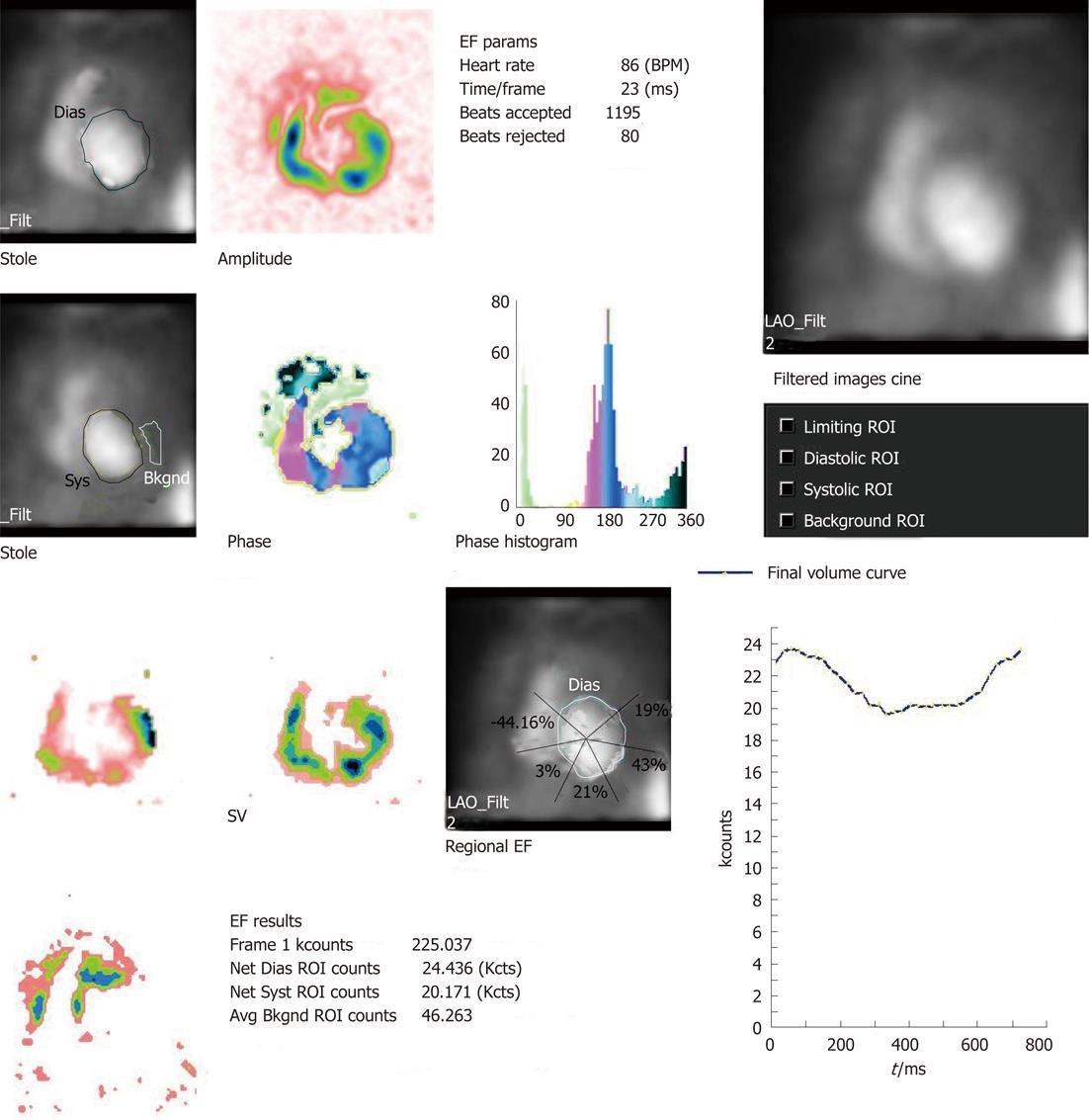
Figure 2 Multigated acquisition scan shows significantly reduced left ventricular ejection fraction of 17%.
The phase image shows dyssynchronous contraction in left ventricular (LV) myocardium and there is overlap of phases both in left and right ventricular myocardium. The width of the phase histogram is more than normal suggesting intra- and inter-ventricular dyssynchrony. The image also demonstrates regional ejection fraction (EF). The paradox image does not show any region of myocardium in paradox. The left ventricular time activity curve is abnormal. ROI: Region of interest; LAO: Left anterior oblique; SV: Stroke volume; Syst: Systolic; Dias: Diastolic; Avg Bkgnd: Average backgroud..
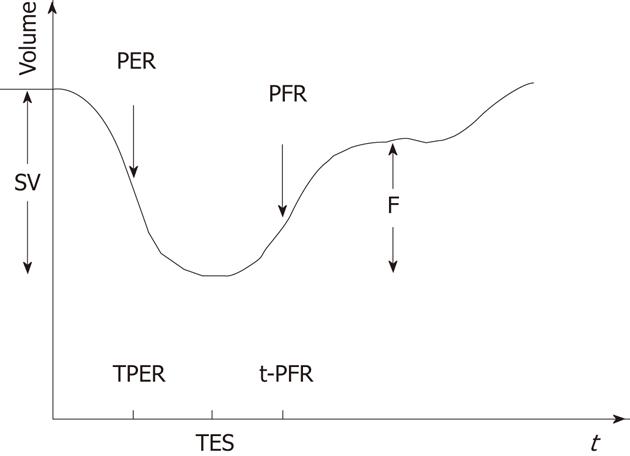
Figure 3 Left ventricular time activity curve from the first derivative showing different phases of cardiac cycle and parameters obtained.
SV: Stroke volume; PER: Peak emptying rate; TPER: TIme at peak emptying rate; PFR: Peak filling rate; t-PFR: Time to peak filling rate; TES: Time to end of systole; F: Part of SV achieved during rapid filling rate.
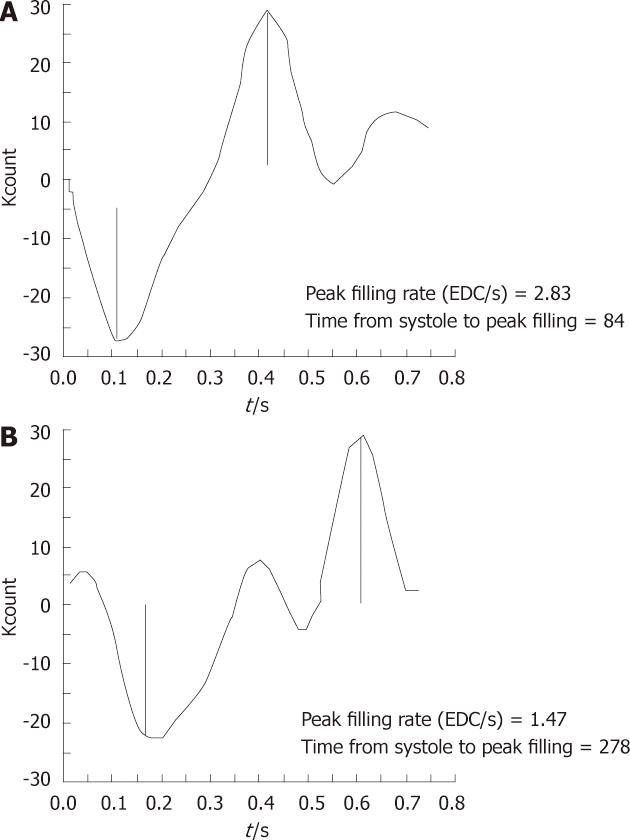
Figure 4 Multigated acquisition time activity curves with their first derivative.
A: Pattern of normal diastolic function; B: One with abnormal diastolic function.
- Citation: Mitra D, Basu S. Equilibrium radionuclide angiocardiography: Its usefulness in current practice and potential future applications. World J Radiol 2012; 4(10): 421-430
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v4/i10/421.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v4.i10.421