Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Radiol. Jan 28, 2021; 13(1): 29-39
Published online Jan 28, 2021. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v13.i1.29
Published online Jan 28, 2021. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v13.i1.29
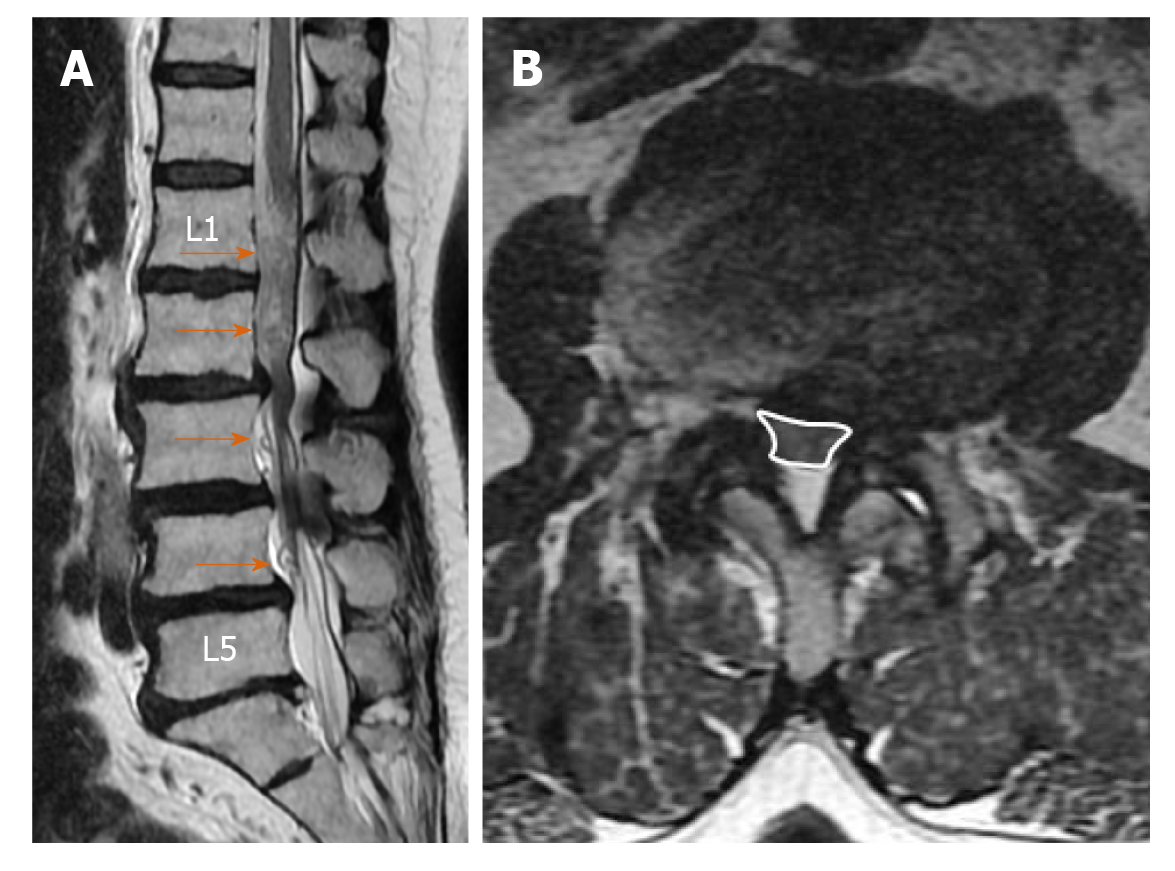
Figure 1 Seventy-one-year-old female patient with lumbar spondylosis.
A: Redundant nerve roots (arrows) secondary to the stenosis at both the superior and inferior of the stenosis at the L2-L3 level, which are more prominent at the superior, are shown; B: On the axial T2-weighted image, the cross-sectional area of the dural sac was 41.60 mm2 at the stenosis level (L2-L3).
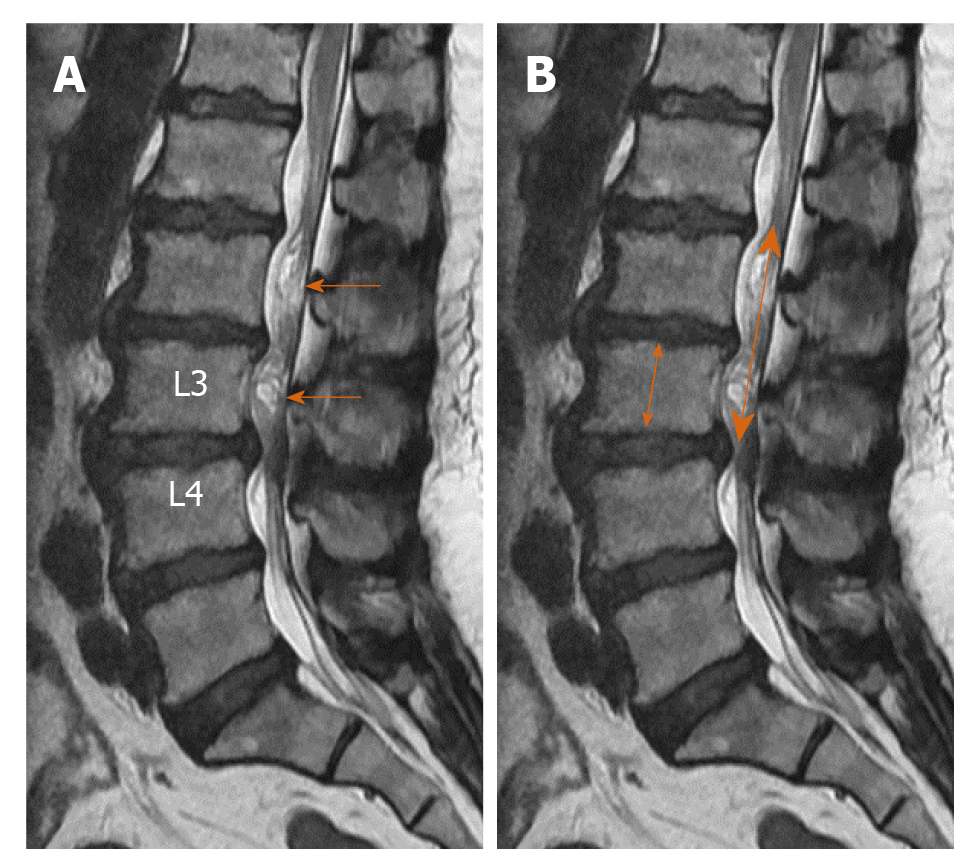
Figure 2 Seventy-one-year-old male patient with lumbar spondylosis.
A: On the sagittal T2-weighted image, redundant nerve roots (arrows) secondary to the stenosis at L2-L3 level are shown at the inferior of stenosis level; B: On the axial T2-weighted image passing through L2-L3 intervertebral disc space level, marked stenosis due to ligamentum flavum and facet joint hypertrophy and disc herniation (cross-sectional area was 41.33 mm2) are shown.
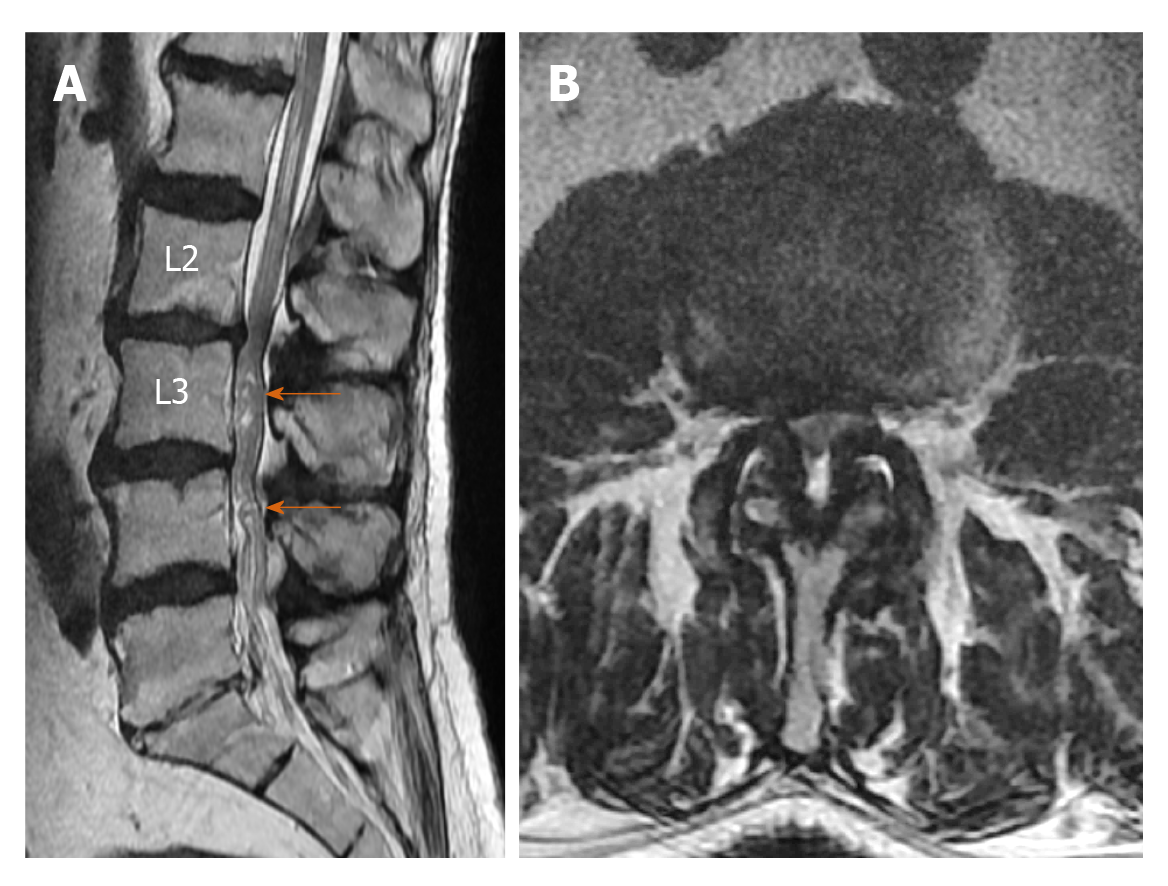
Figure 3 Forty-seven-year-old female patient with lumbar spondylosis.
A: On the sagittal T2-weighted image, redundant nerve roots at the superior of the stenosis level secondary to the stenosis at the L3-L4 intervertebral disc space (arrows) are shown; B: Relative length was calculated by dividing the length of redundant nerve roots (thick arrow) by the vertebra height at the superior of stenosis level (thin arrow).
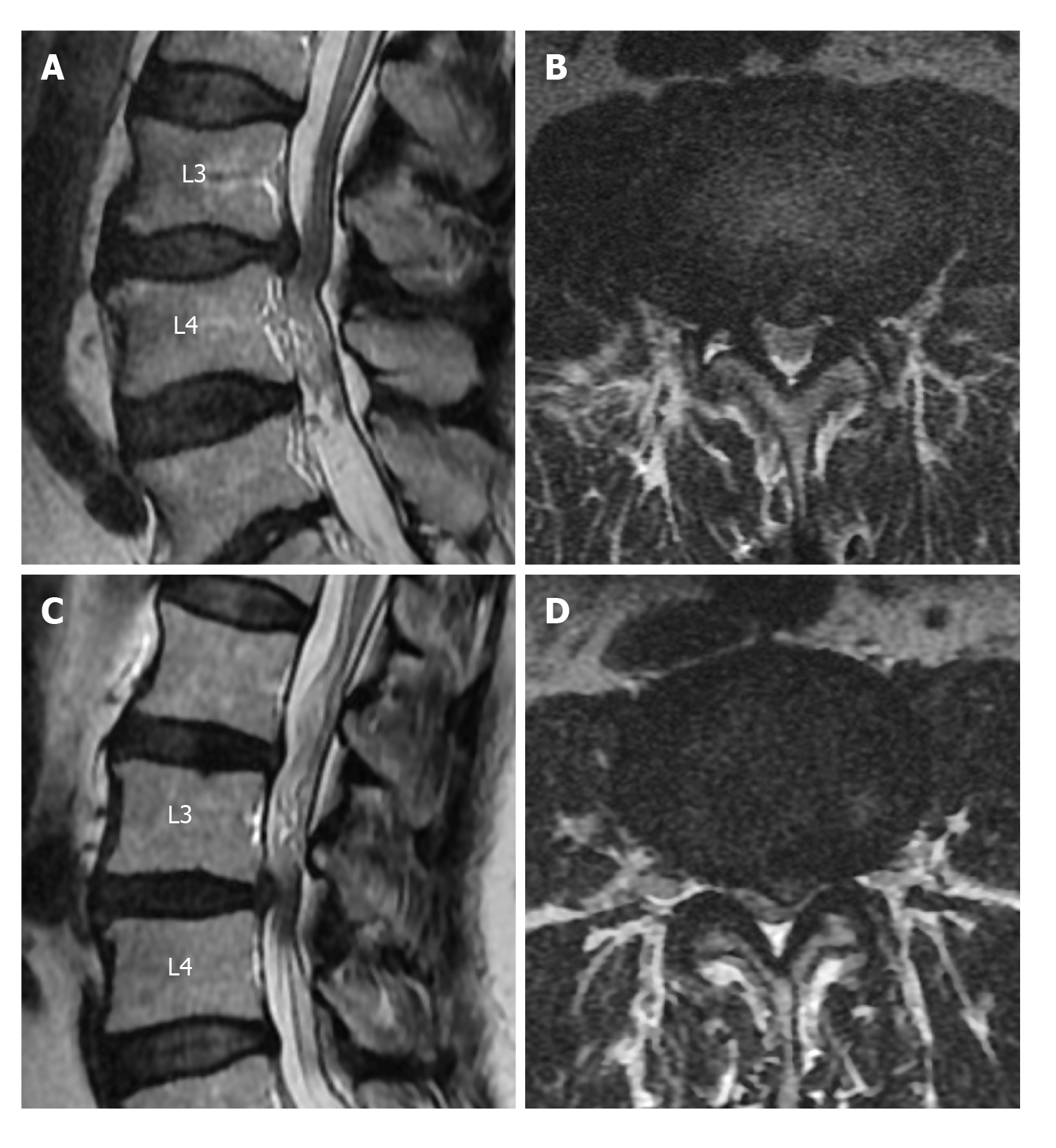
Figure 4 Soft and sharp margin types of disc herniation into the dural sac.
A: On the sagittal T2-weighted image, soft margin disc herniation at the level of L3-L4 intervertebral disc space and redundant nerve roots at the inferior of the stenosis are shown; B: The axial T2-weighted images of soft margin disc herniation are shown; C: On the sagittal T2-weighted image, sharp margin disc herniation at the L3-L4 intervertebral disc space and redundant nerve roots at its superior are shown; D: Axial T2-weighted image of sharp disc herniation is shown.
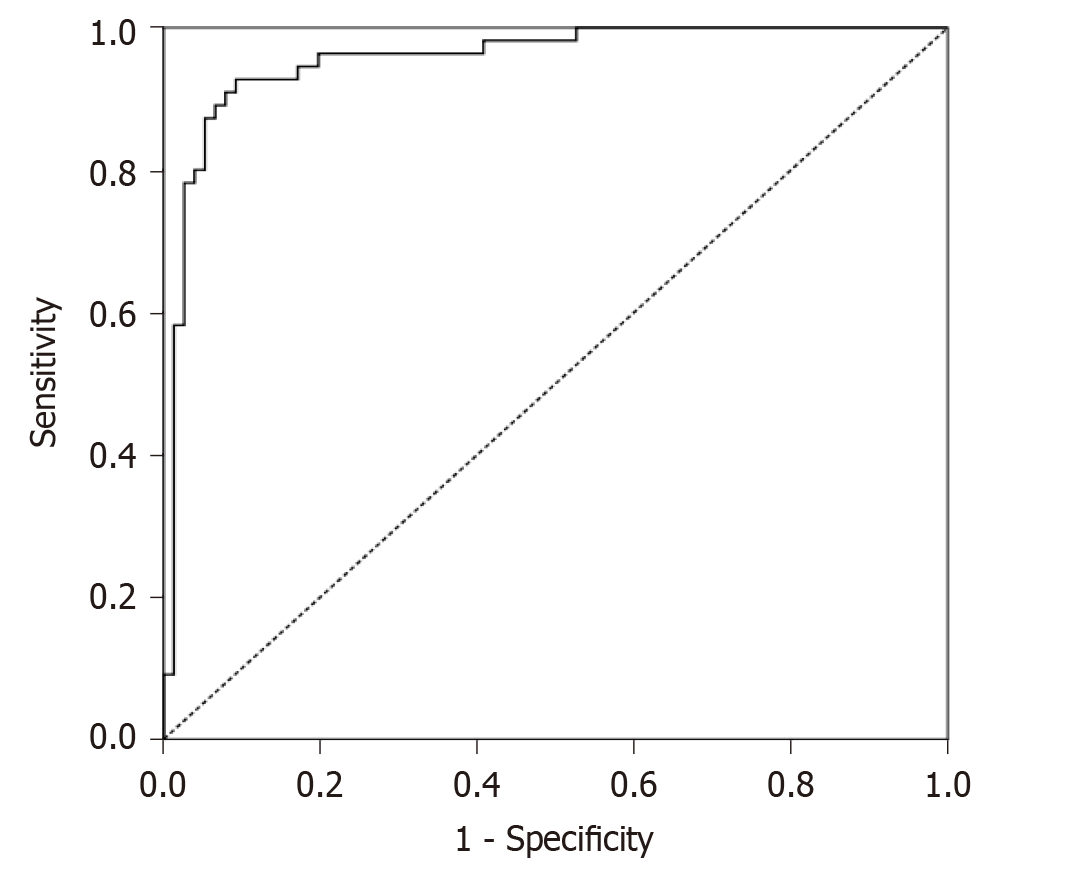
Figure 5 Receiver operating characteristic curve with a cut-off value of 55.
22 mm2 or less for the cross-sectional area of the dural sac.
- Citation: Gökçe E, Beyhan M. Magnetic resonance imaging findings of redundant nerve roots of the cauda equina. World J Radiol 2021; 13(1): 29-39
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v13/i1/29.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v13.i1.29