Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Diabetes. Jun 15, 2025; 16(6): 105711
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.105711
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.105711
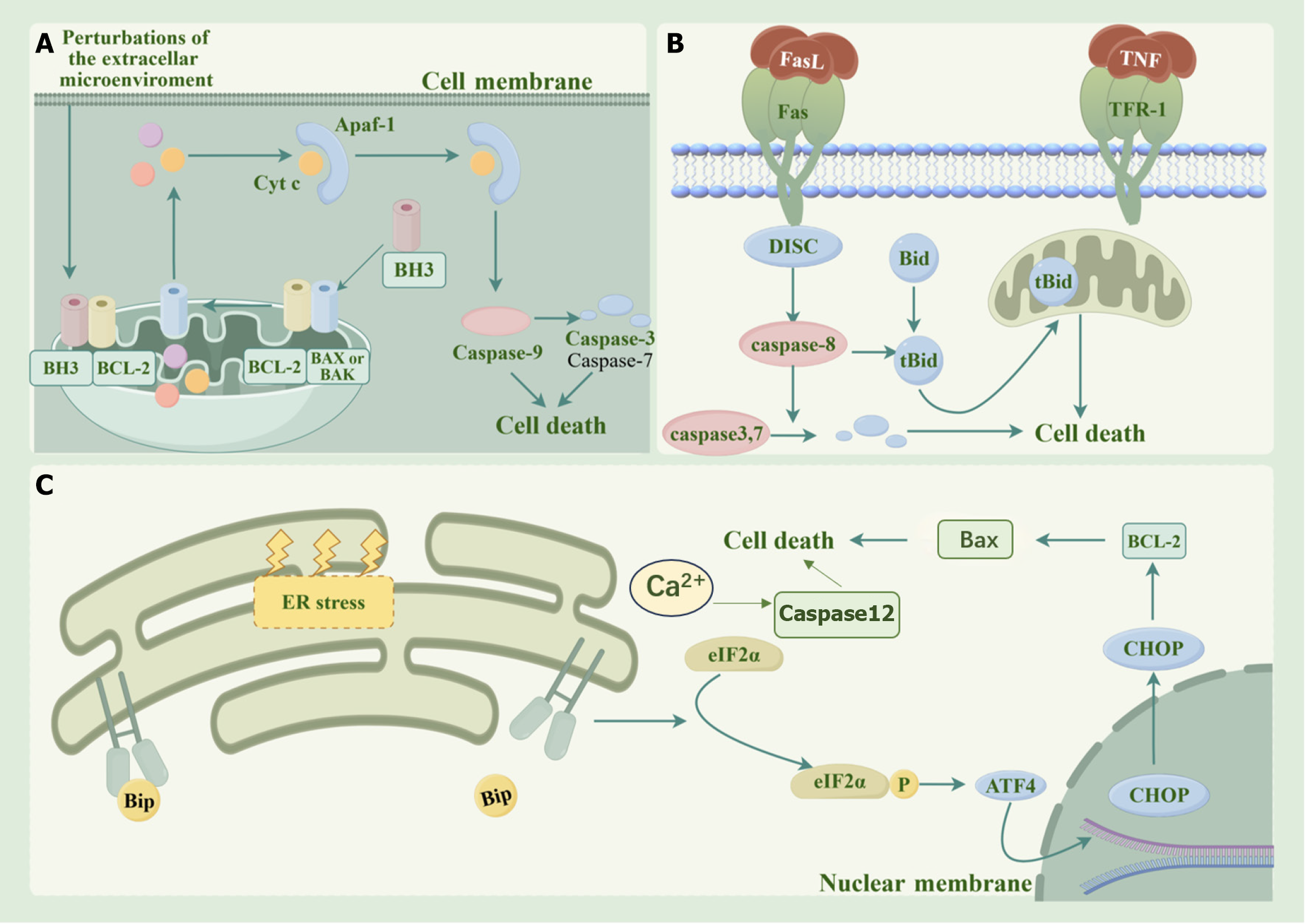
Figure 1 Pathways of apoptosis.
A: Mitochondrial pathway: When the inside of the cell is stimulated, pro-apoptotic proteins such as Bax and Bak are activated and inserted into the mitochondrial membrane, increasing the permeability of the mitochondrial membrane and releasing cytochrome C into the cytoplasm. Cytochrome C combines with Apaf-1 to form an apoptosome, which recruits and activates Caspase-9, and then activates downstream effector caspases, leading to apoptosis; B: Death receptor pathway: Apoptotic signaling molecules outside the cell, such as tumor necrosis factor-α and FasL, bind to the death receptors on the cell surface to form a death-inducing signaling complex. After Caspase-8 is activated, it directly activates downstream effector caspases to trigger apoptosis. It can also activate the endogenous mitochondrial pathway by cleaving the Bid protein to amplify the apoptotic signal; C: Endoplasmic reticulum pathway: When the endoplasmic reticulum undergoes stress due to the accumulation of misfolded proteins, etc., it initiates the unfolded protein response. Through pathways such as the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 pathway and the IRE1α pathway, it induces the expression of pro-apoptotic genes. At the same time, the endoplasmic reticulum releases calcium ions into the cytoplasm and activates relevant enzymes, such as Caspase-12, etc., ultimately inducing apoptosis. TNF: Tumor necrosis factor. It was drawn using Figdraw software.
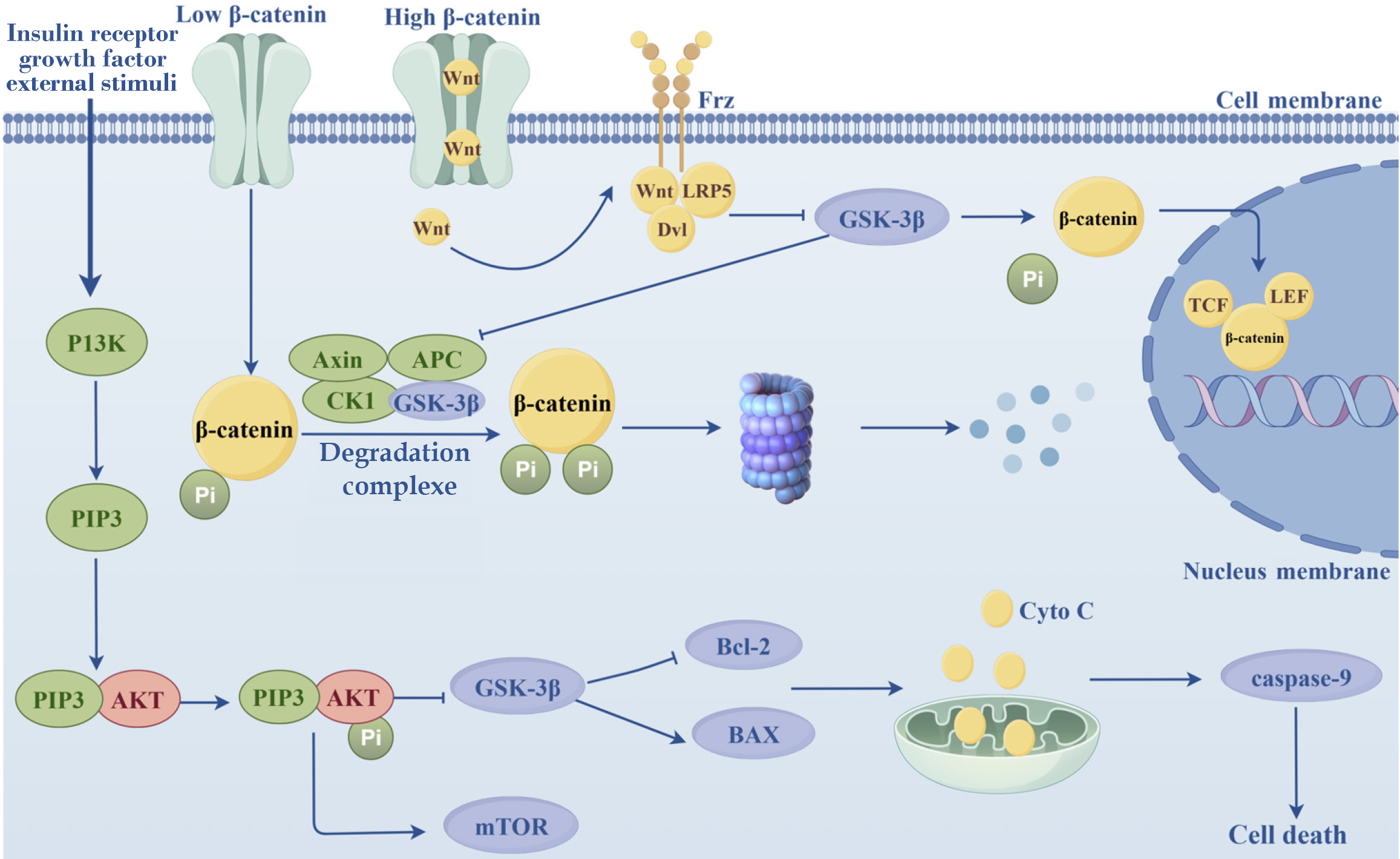
Figure 2 Common signaling pathways affecting apoptosis: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway and wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases; AKT: Protein kinase B; mToR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; GSK-3β: Glycogen synthase kinase-3β; Cyto C: Cytochrome C; APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli gene protein; CK1: Casein kinase 1; Dvl: Dishevelled; TCF: The nuclear T cell factor; LEF: Lymphoid enhancer binding factor. It was drawn using Figdraw software.
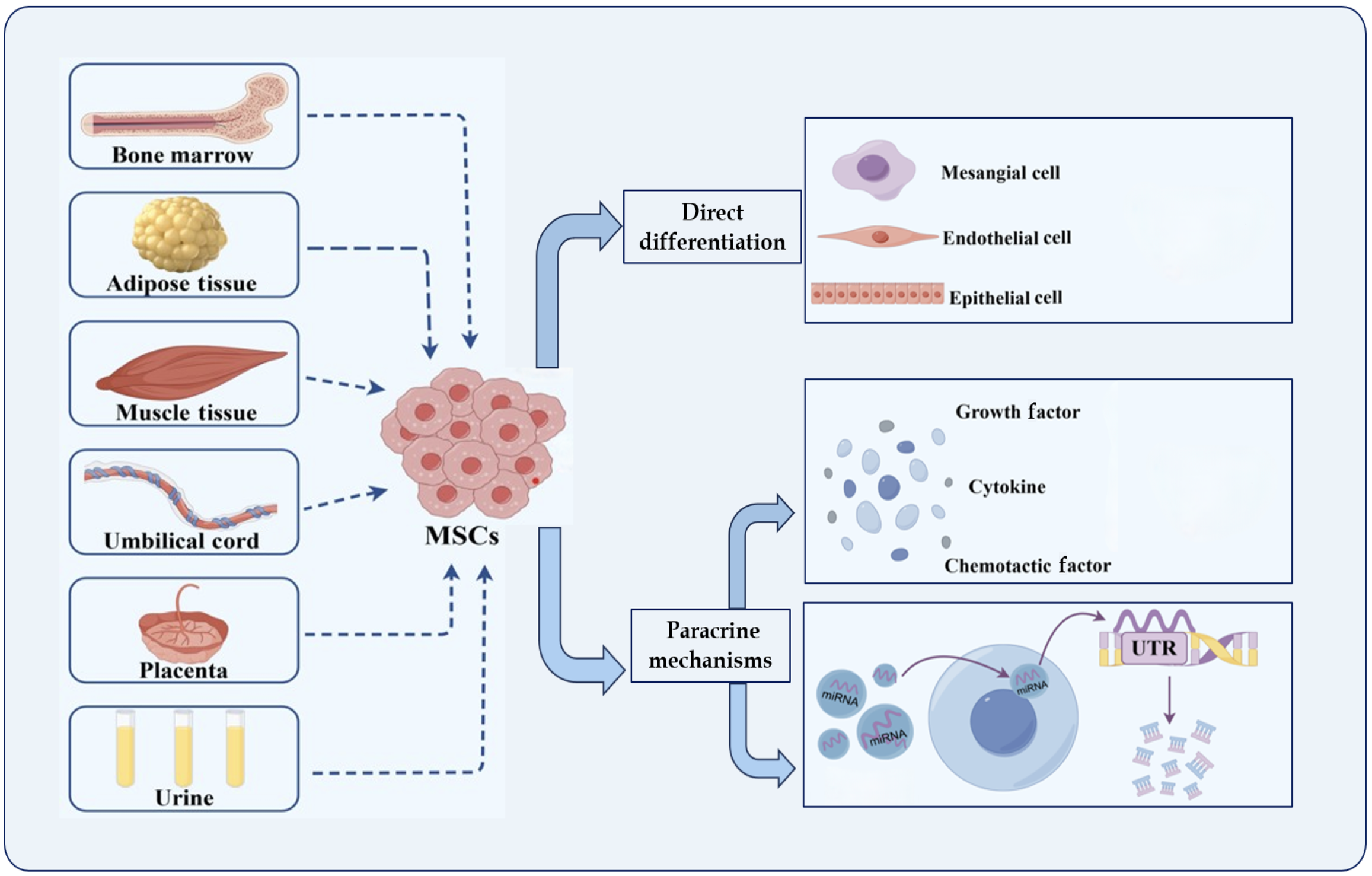
Figure 3 Sources of mesenchymal stem cells and mechanism of the amelioration of renal injury.
MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells. It was drawn using Figdraw software.
- Citation: Nie P, Qin W, Nie WC, Li B. Progress in the application of mesenchymal stem cells to attenuate apoptosis in diabetic kidney disease. World J Diabetes 2025; 16(6): 105711
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v16/i6/105711.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.105711