Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2022; 13(5): 387-407
Published online May 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i5.387
Published online May 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i5.387
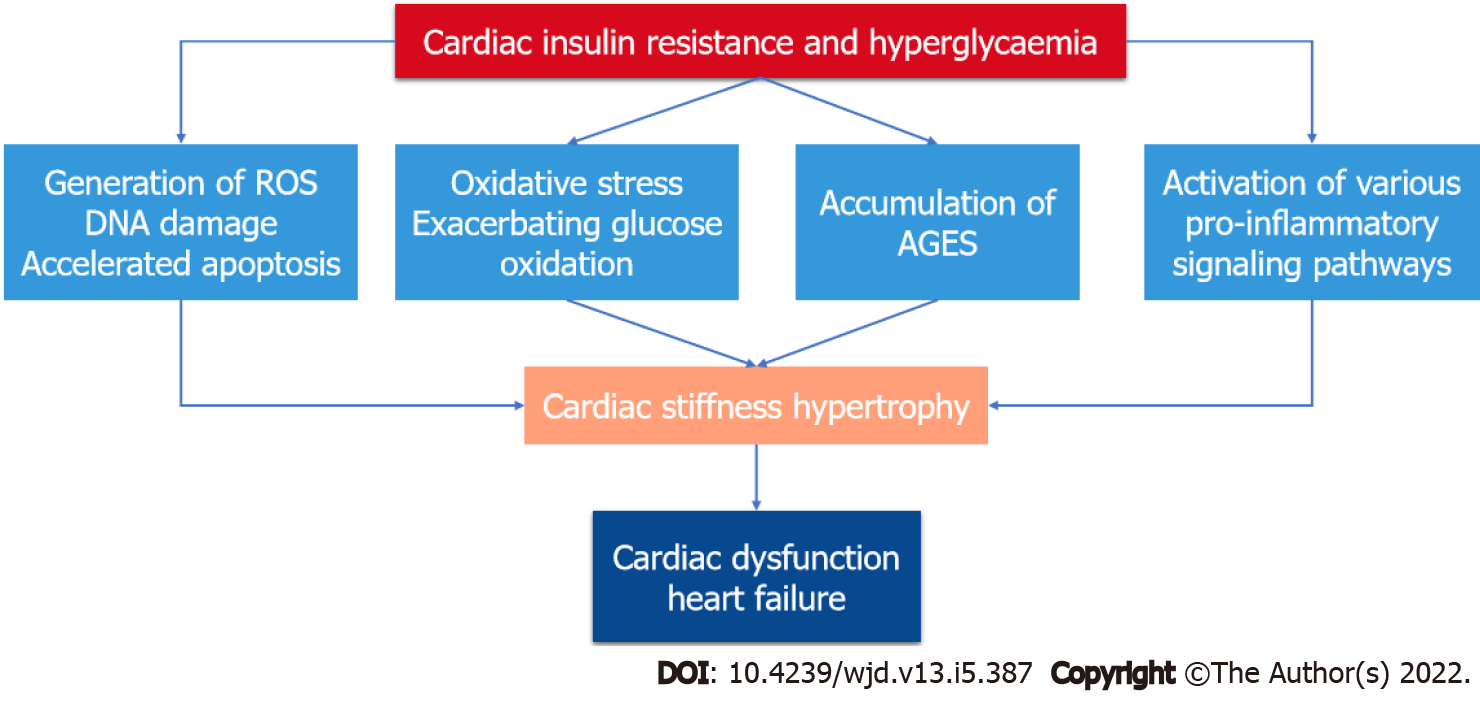
Figure 1 Molecular mechanisms of diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Hyperglycemia and insulin resistance increase reactive oxygen species formation, oxidative stress, advanced glycation end-products formation, and the recruitment of various inflammatory pathways leading to cardiac dysfunction and heart failure. ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
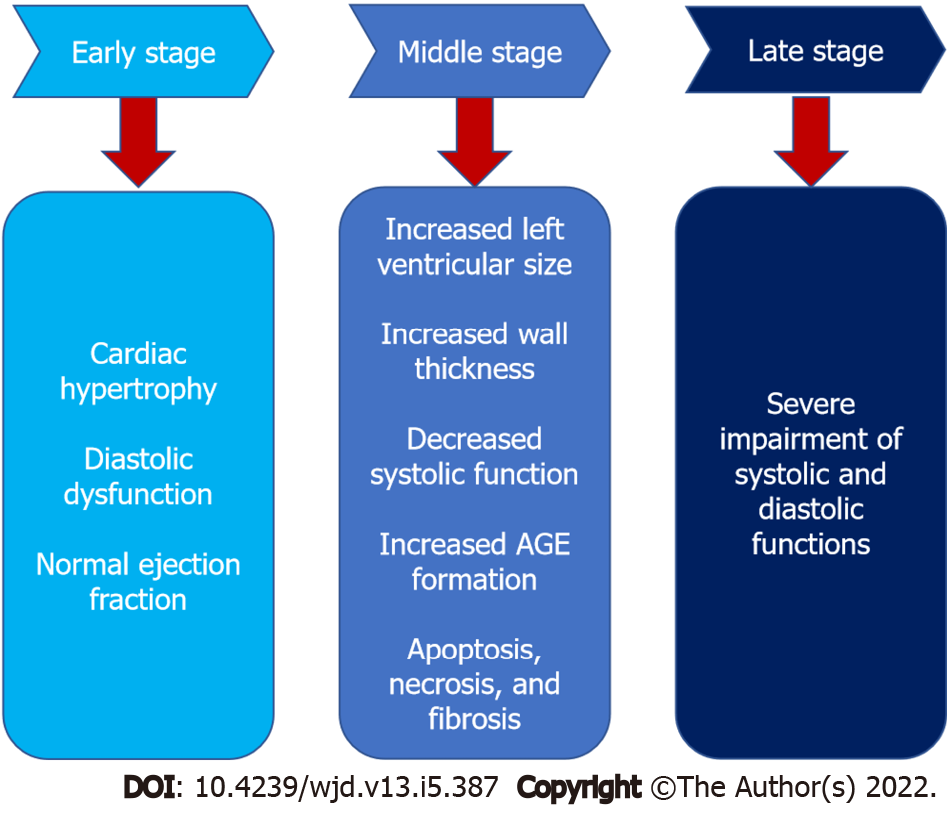
Figure 2 Stages of diabetic cardiomyopathy progression.
Diabetic cardiomyopathy progresses from early development of hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction that then progress to decreased systolic activity, apoptosis and cardiac fibrosis leading to severe impairment in both systolic and diastolic functions. AGE: Advanced glycation end products.
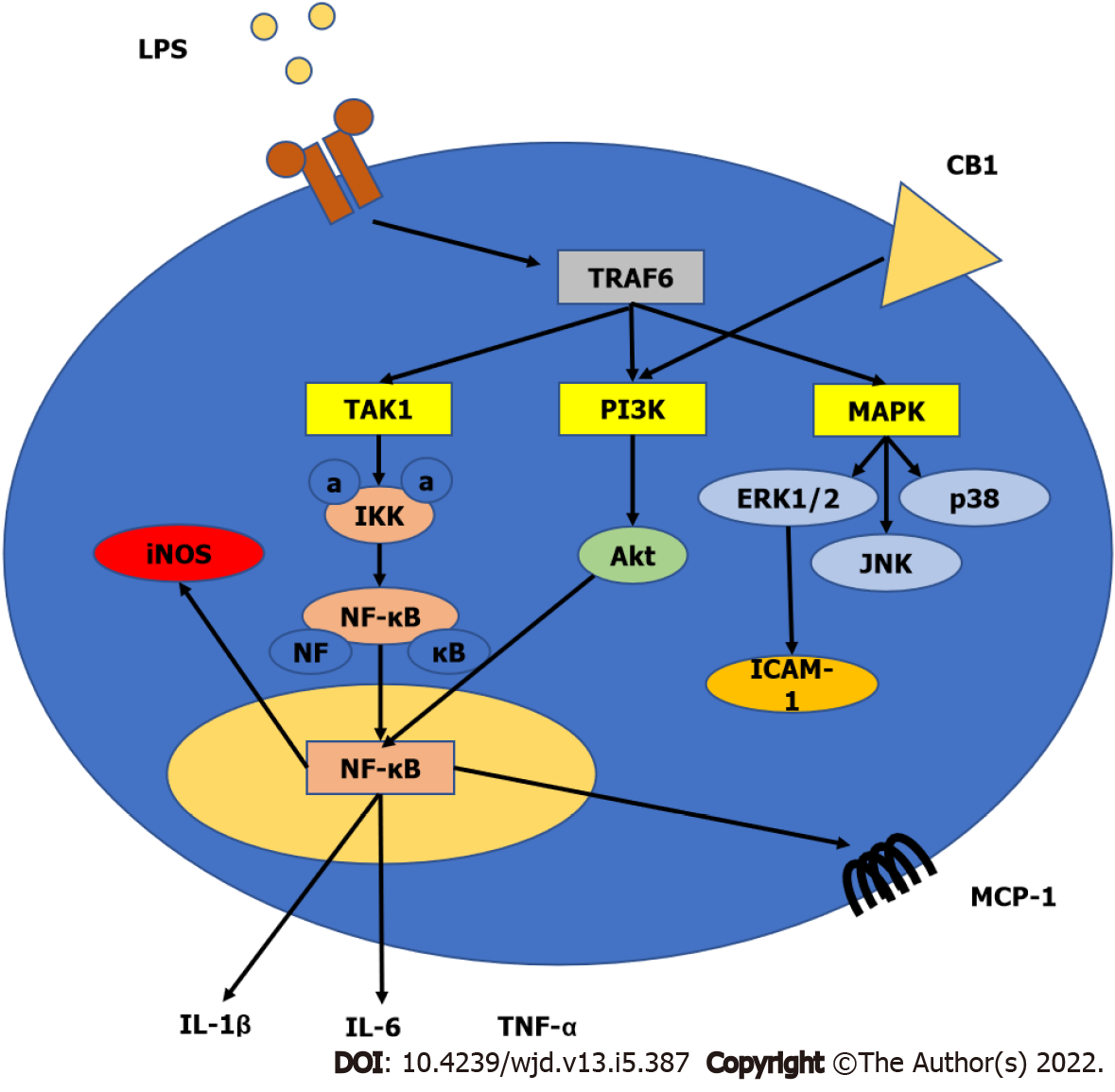
Figure 3 Role of cannabinoid receptors in inflammation.
Activation of toll-like receptor 4 induces tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6, which activates transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. This will induce the formation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and the subsequent increase in inflammatory cytokines levels such as interleukin 6 (IL-6), IL-1β, and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) in addition to the activation of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and monocyte chemoattractant ptotein-1 (MCP-1). Stimulation of cannabinoid receptors will increase the PI3K activity leading to increased activity of protein kinase B (Akt/PKB), which in turn enhances the nuclear translocation of NF-κB. TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; TRAF6: Tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α; MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1.
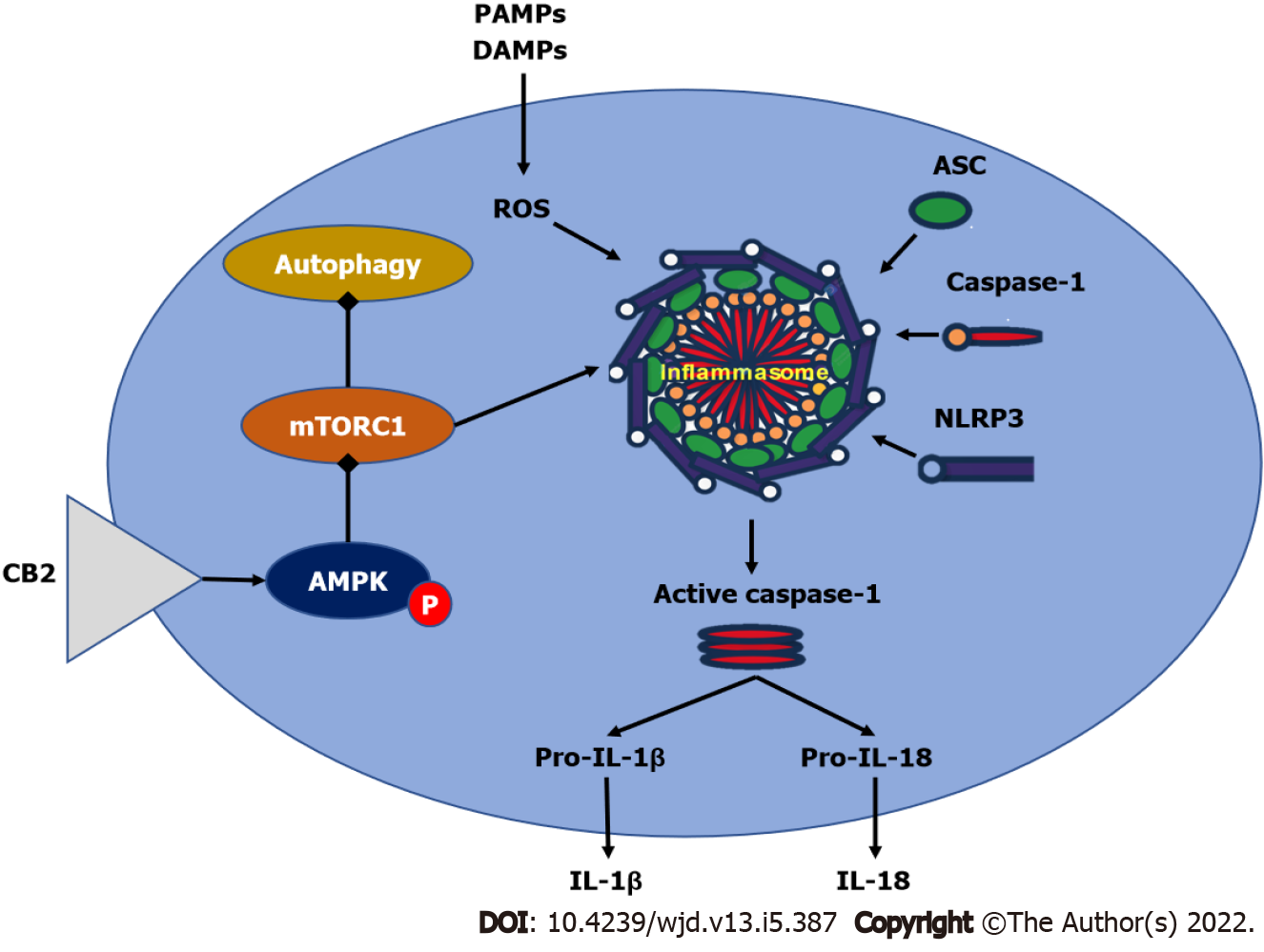
Figure 4 Effect of cannabinoid receptors on adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1/NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 signaling.
Cannabinoids enhance the phosphorylation of adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase (AMPK), which reduces the stimulatory effect of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) on inflammasome assembly. Depressed activation of NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) will diminish the activation of procaspase-1 leading to a decrease in interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and IL-18 production. Additionally, the inhibitory effect of phosphorylated AMPK on mTORC1 will enhance autophagy. AMPK: Adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase; mTORC1: Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; NLRP3: NLR family pyrin domain containing 3; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: El-Azab MF, Wakiel AE, Nafea YK, Youssef ME. Role of cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system in modulation of diabetic cardiomyopathy. World J Diabetes 2022; 13(5): 387-407
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v13/i5/387.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v13.i5.387