Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Diabetes. May 15, 2022; 13(5): 387-407
Published online May 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i5.387
Published online May 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i5.387
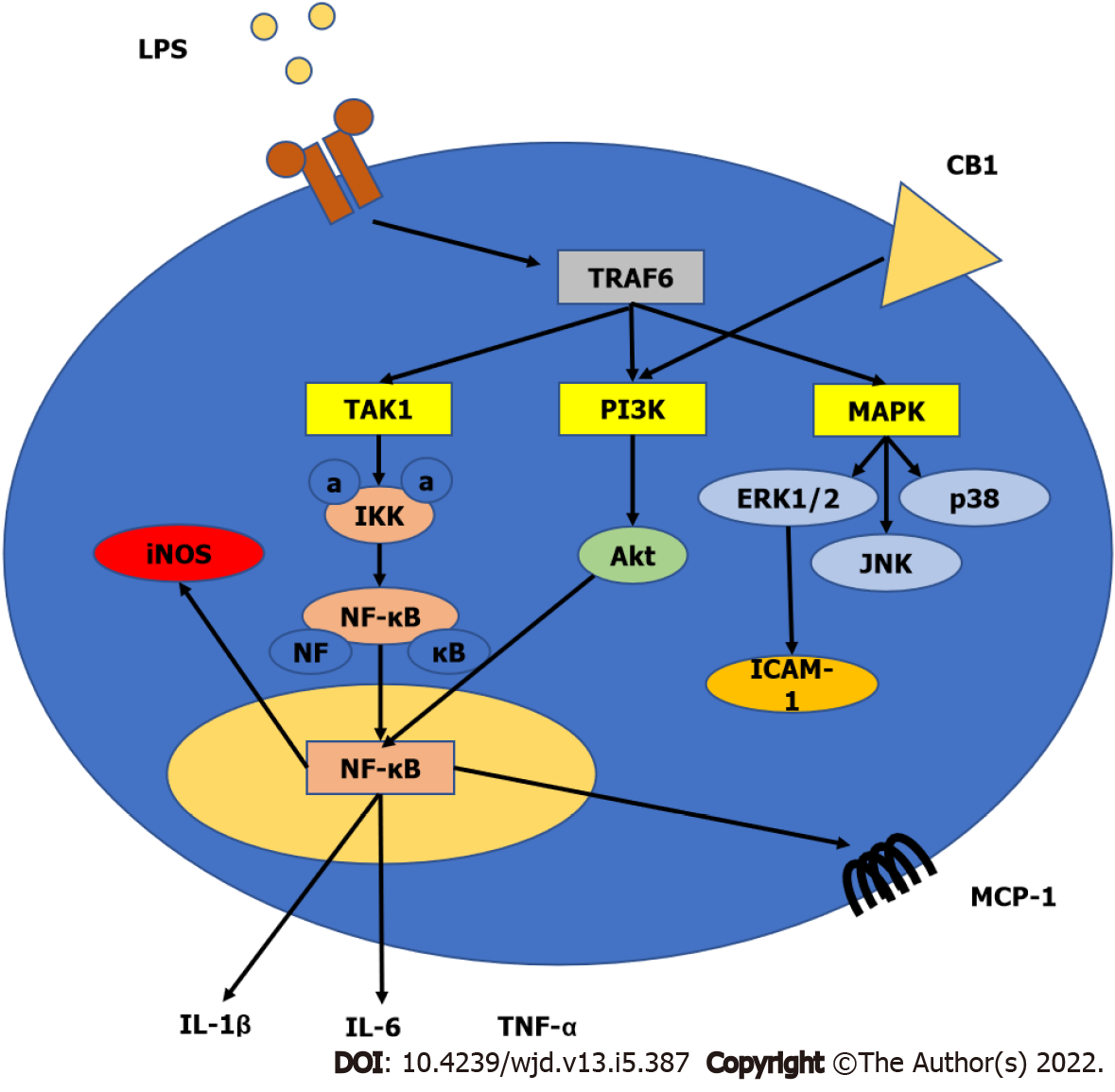
Figure 3 Role of cannabinoid receptors in inflammation.
Activation of toll-like receptor 4 induces tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6, which activates transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. This will induce the formation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and the subsequent increase in inflammatory cytokines levels such as interleukin 6 (IL-6), IL-1β, and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) in addition to the activation of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and monocyte chemoattractant ptotein-1 (MCP-1). Stimulation of cannabinoid receptors will increase the PI3K activity leading to increased activity of protein kinase B (Akt/PKB), which in turn enhances the nuclear translocation of NF-κB. TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; TRAF6: Tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α; MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1.
- Citation: El-Azab MF, Wakiel AE, Nafea YK, Youssef ME. Role of cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system in modulation of diabetic cardiomyopathy. World J Diabetes 2022; 13(5): 387-407
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v13/i5/387.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v13.i5.387