Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. May 15, 2025; 17(5): 104172
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.104172
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.104172
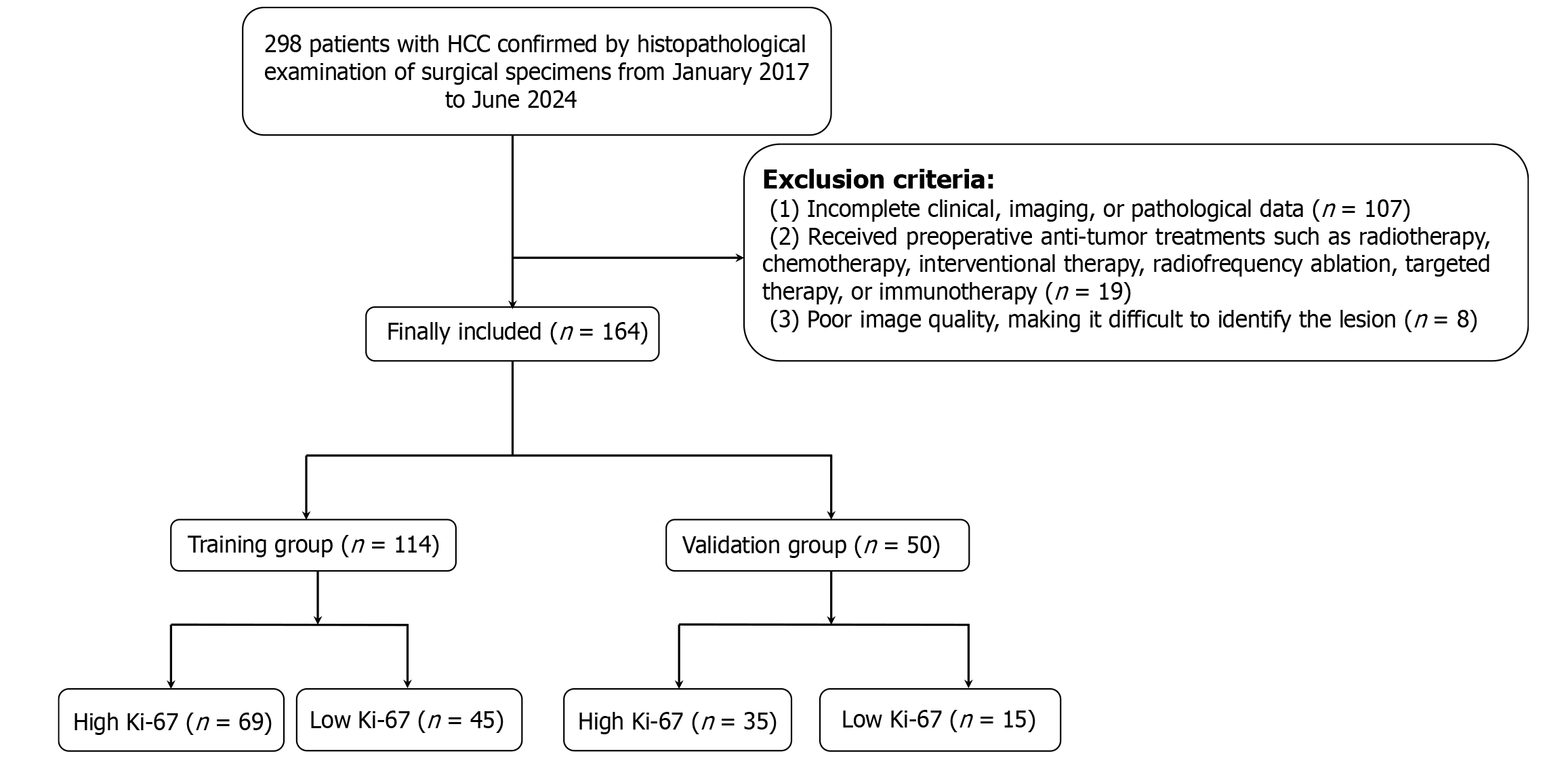
Figure 1 Flowchart for the inclusion and exclusion of hepatocellular carcinoma patients in this study.
HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
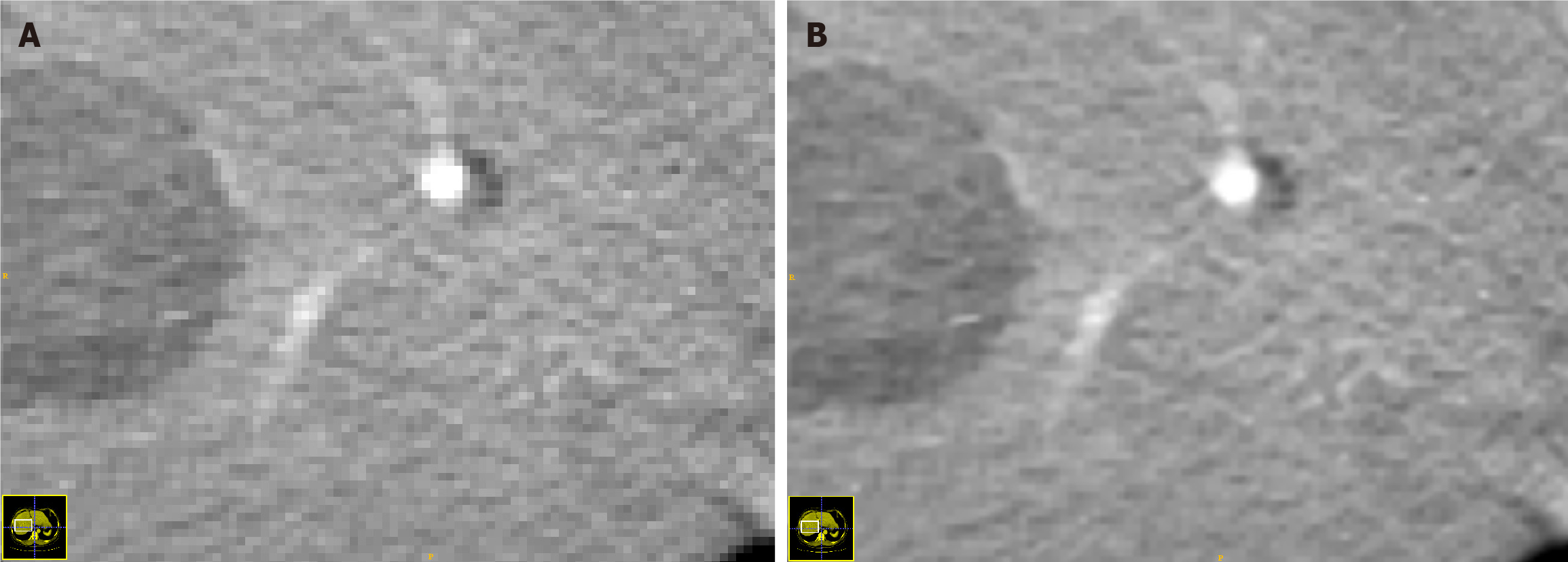
Figure 2 Computed tomography images before and after superresolution reconstruction.
A: Image from a normal resolution; B: Image after superresolution reconstruction.
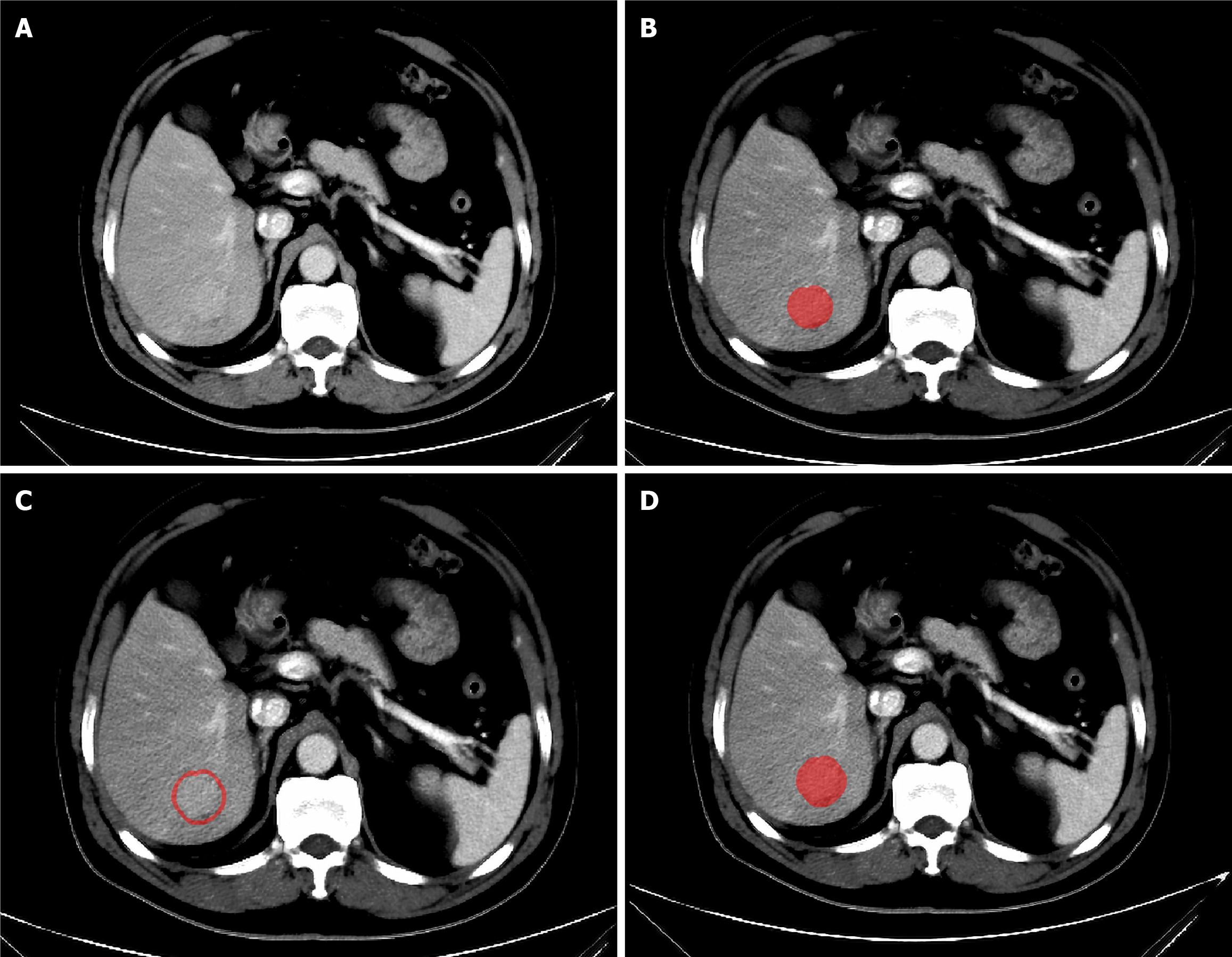
Figure 3 Examples of regions of interest delineated on computed tomography images with ITK-SNAP software.
A: Original image; B: Intratumoral regions of interest (ROI); C: Peritumoral ROI; D: Fusion ROI (intratumoral tissue + peritumoral tissue).
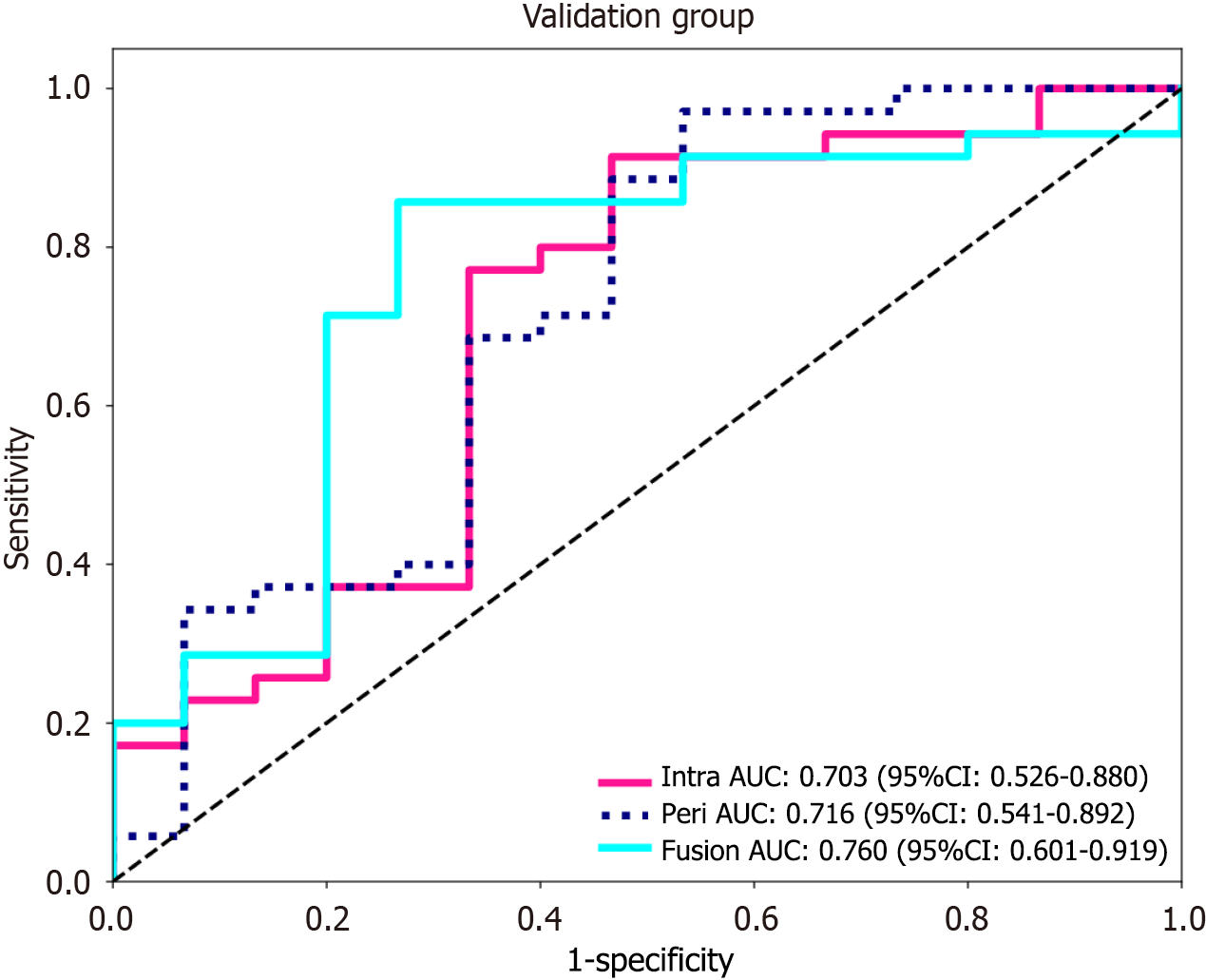
Figure 4 The receiver operating characteristic curves were used to compare the intratumoral model, peritumoral model, and fusion model from the validation cohort.
AUC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; CI: Confidence interval.
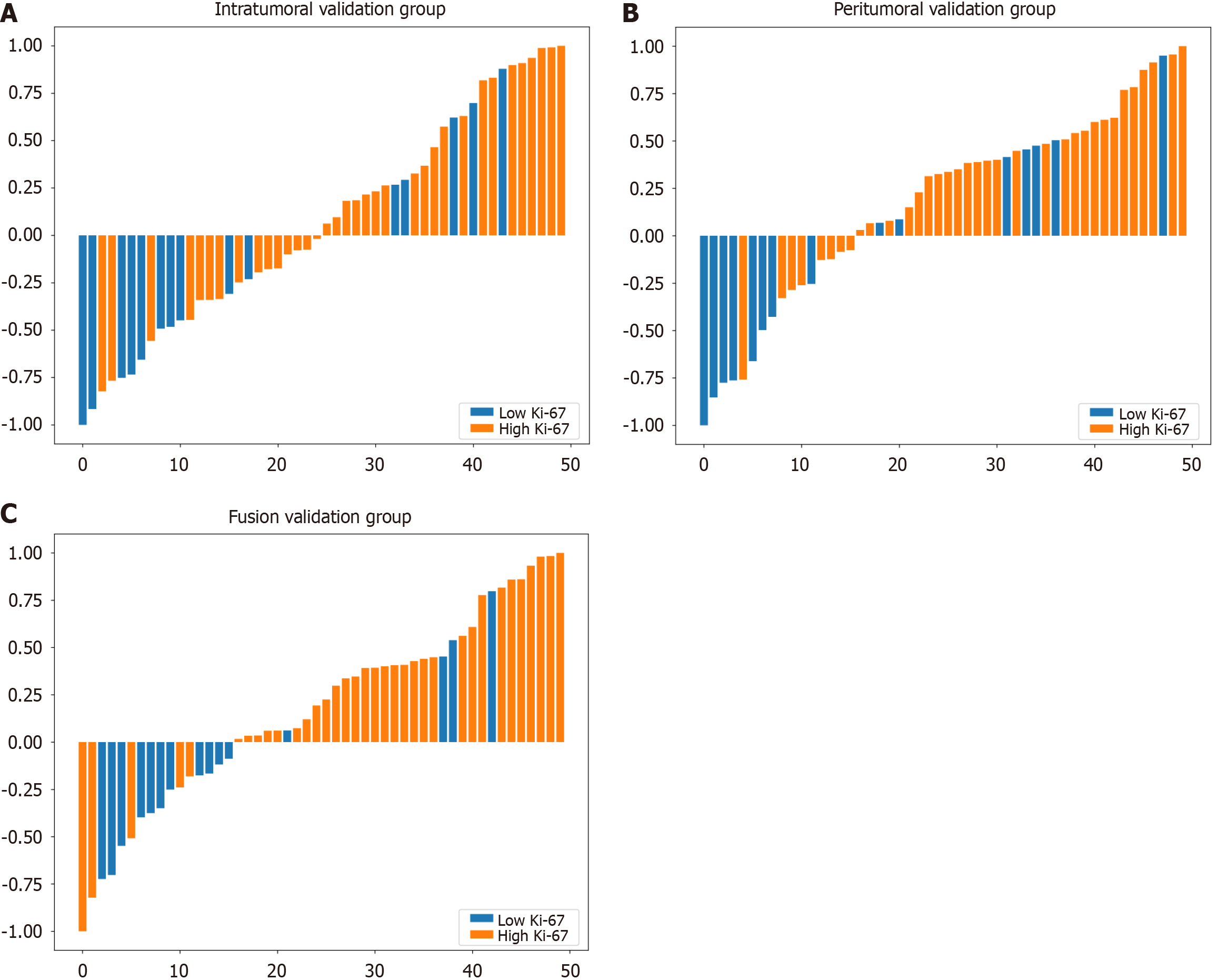
Figure 5 Waterfall plot showing the model performance across the validation sets of the three models.
A: Intratumoral model; B: Peritumoral model; C: Fusion model. Each bar in the plot represents the difference between the model’s predicted value and the established cut-off value. The bars extending above the Y = 0 line indicate model predictions of high Ki-67 expression, whereas the bars below the Y = 0 line signify predictions of low Ki-67 expression.
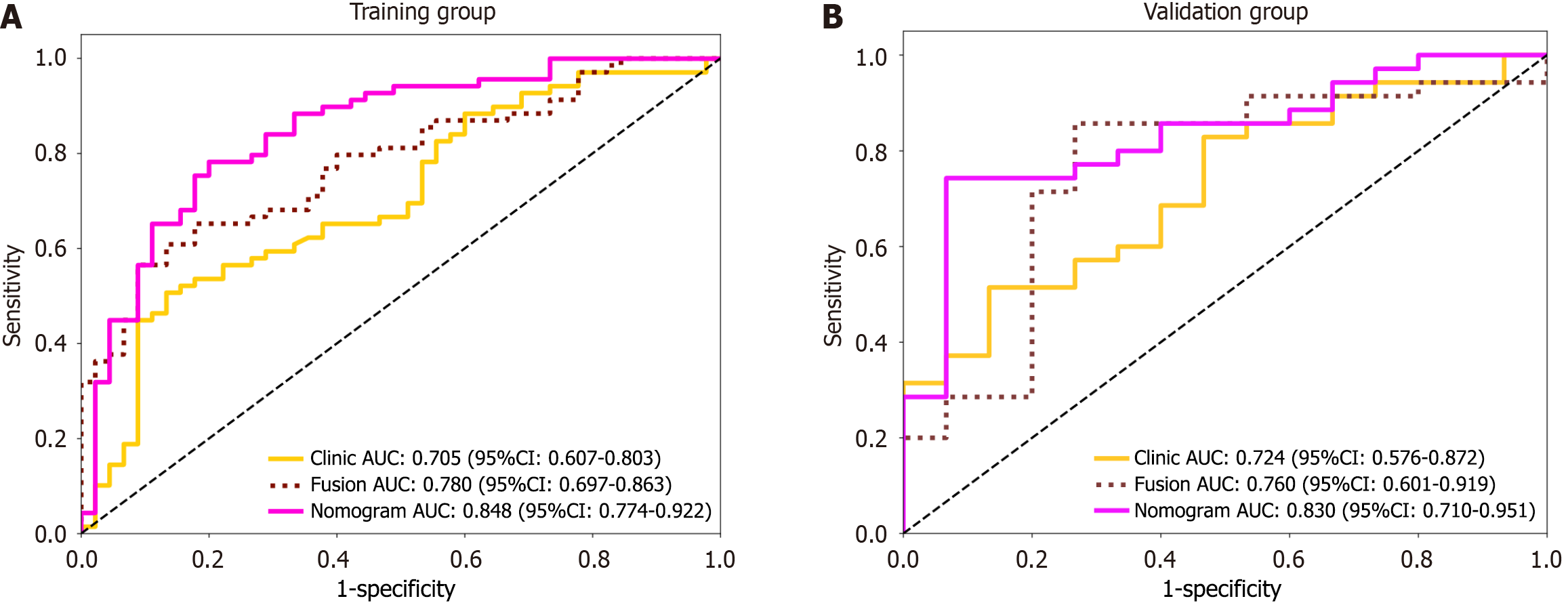
Figure 6 The receiver operating characteristic curve shows the performance of the different models in predicting Ki-67 expression.
A: Receiver operating characteristic curve comparison of the training group for the three models; B: Receiver operating characteristic curve comparison of the validation group for the three models. AUC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; CI: Confidence interval.
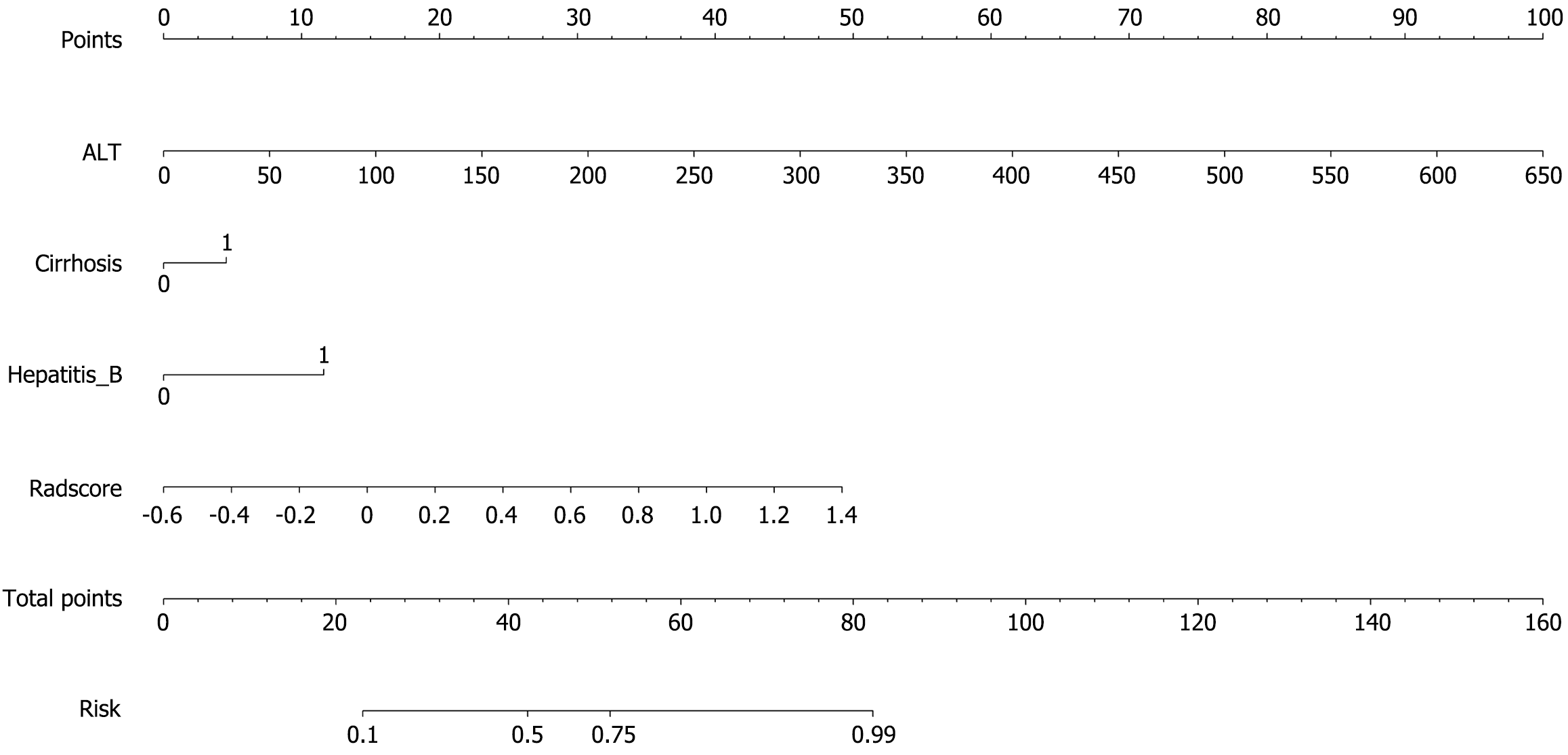
Figure 7 Clinical-radiomic nomogram.
ALT: Alanine aminotransferase.
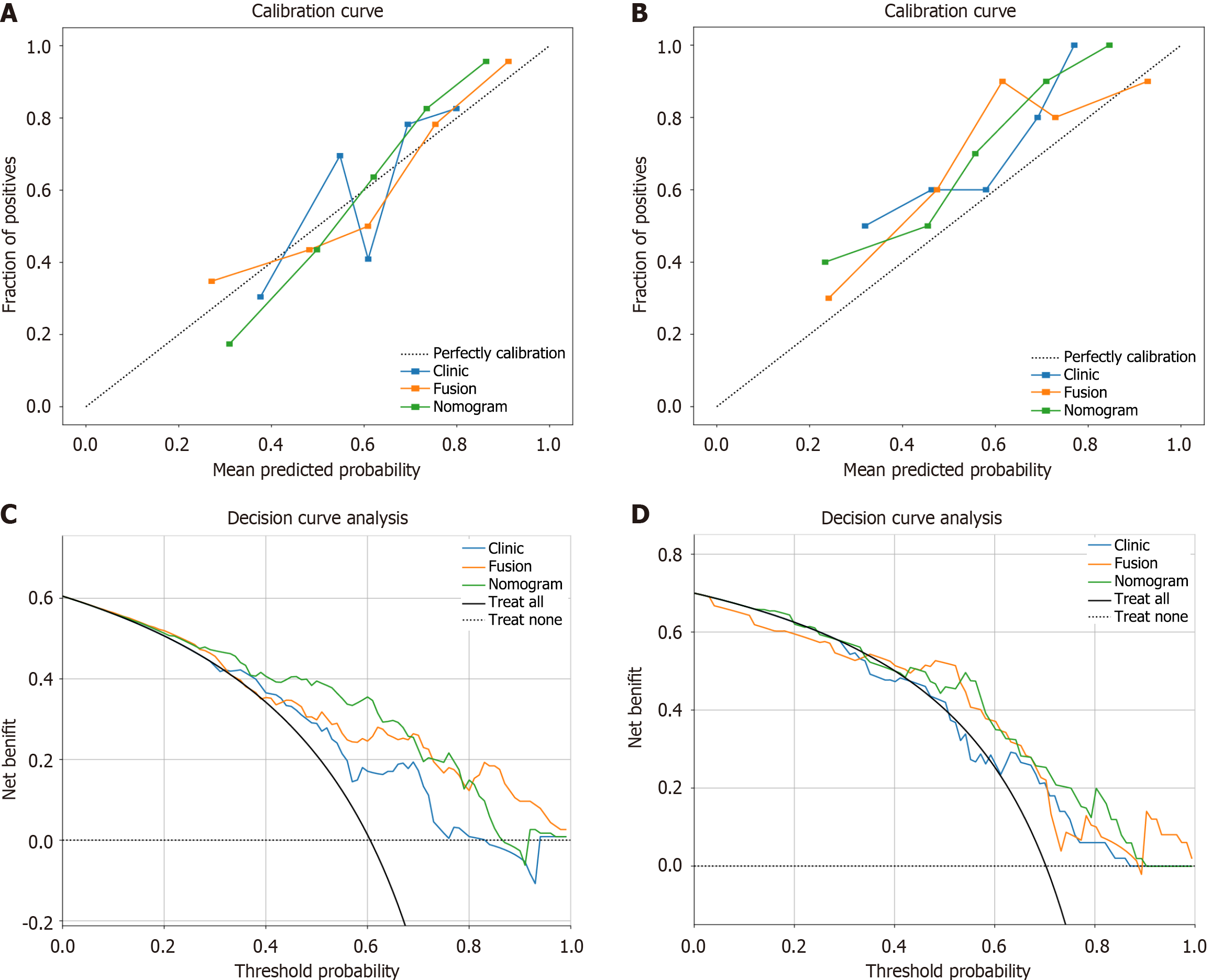
Figure 8 Decision curve analysis and calibration curves of different models.
A: Calibration curves for three models (training group); B: Calibration curves for three models (validation group); C: Decision curve analysis for three models (training group); D: Decision curve analysis for three models (validation group).
- Citation: Zhu ZW, Wu J, Guo Y, Ren QY, Li DN, Li ZY, Han L. Prediction of Ki-67 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma with machine learning models based on intratumoral and peritumoral radiomic features. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(5): 104172
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i5/104172.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.104172