Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Dec 15, 2022; 14(12): 2367-2379
Published online Dec 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i12.2367
Published online Dec 15, 2022. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i12.2367
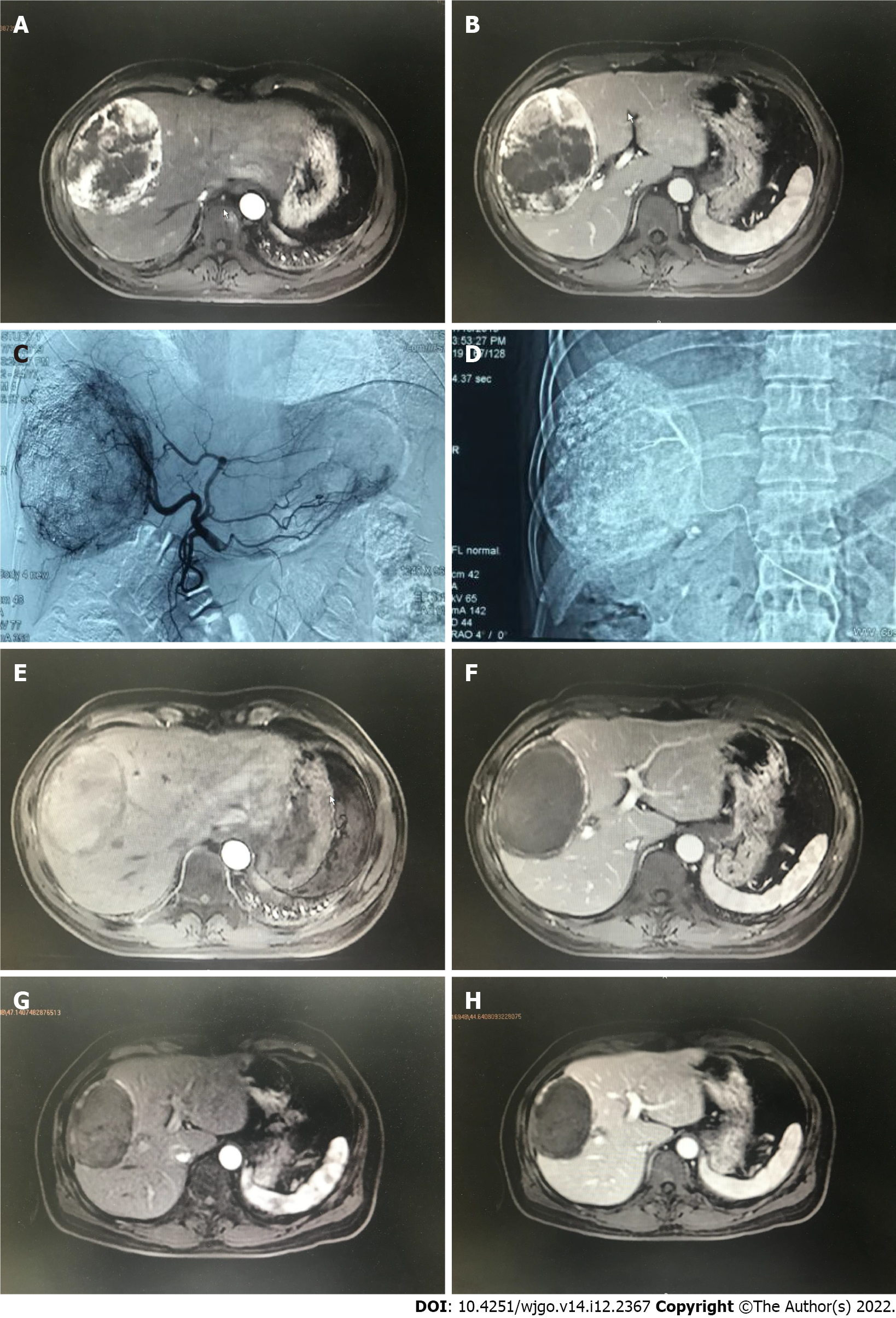
Figure 1 A 47 years old male diagnosed as primary liver cancer.
Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) T1WI enhanced axial position. A: In the arterial phase, there is a 105 mm × 85 mm × 119 mm uneven abnormal enhancement of the right lobe of the liver; B: The portal vein can be cleared. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization treatment with drug-loaded microspheres was performed in July 2019; C: Digital subtracted angiography under common hepatic arteriography during interventional surgery shows tumors with rich blood supply in the right lobe of the liver; D: Microcatheter superselection of the right hepatic artery for chemoembolization; E: A 103 mm × 69 mm × 109 mm mass in the right lobe of the liver can be seen in the arterial phase and no obvious enhancement is seen; F: There is no enhancement in the mass in the portal vein; G: MRI T1WI enhancement axis is re-examined 3 mo after the operation. The mass in the right lobe of the liver in the arterial phase is compared to the previous significantly reduced (86 mm × 57 mm × 88 mm); H: There was no enhancement of the portal venous mass.
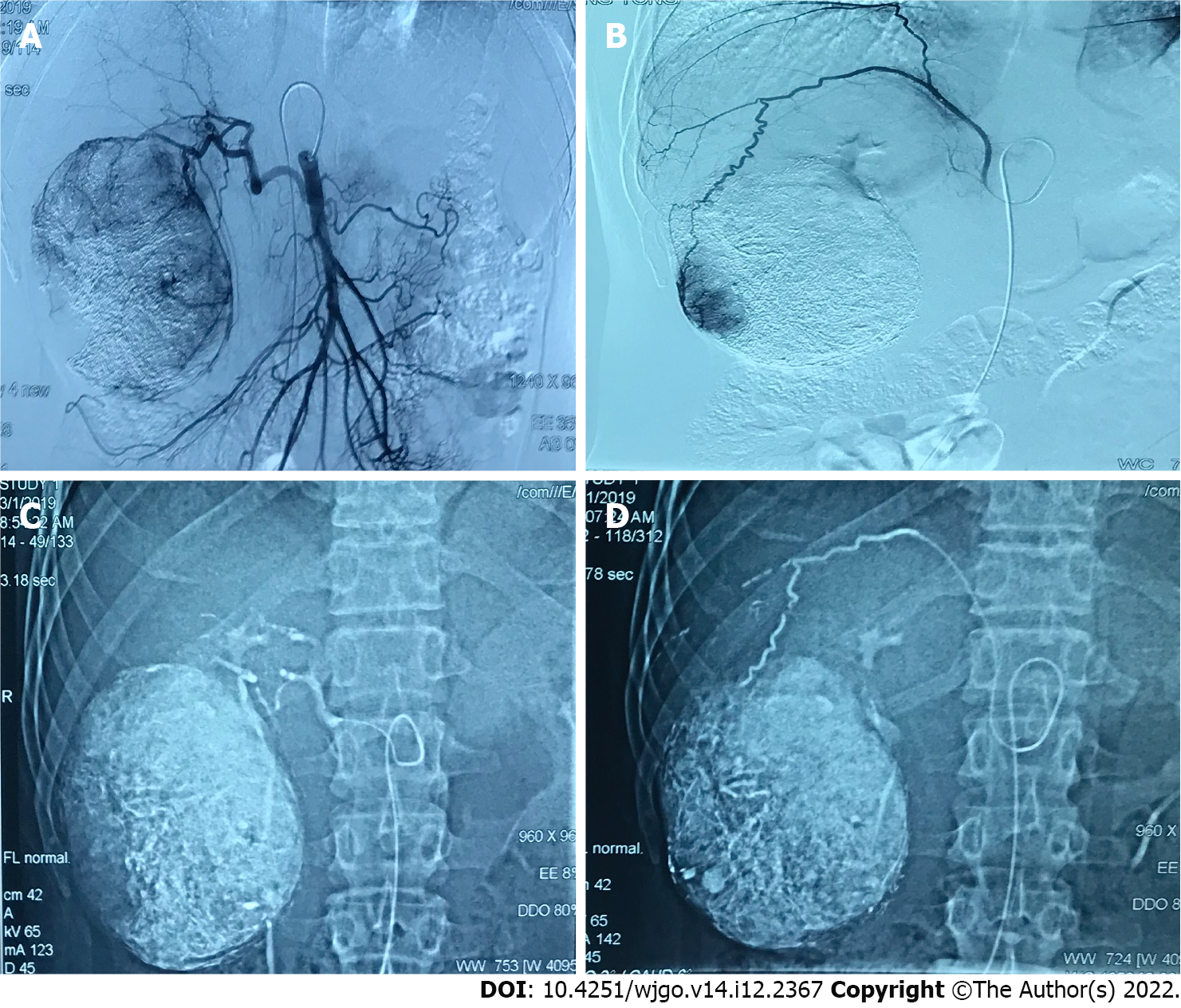
Figure 2 A 38 years old male diagnosed as primary liver cancer.
Traditional transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) treatment was performed in January 2019, and a follow-up examination was performed one month after the operation. Part of the lesion was alive. Later, the second traditional TACE treatment was performed in March 2019. A: Intraoperative digital subtracted angiography (DSA) angiography shows that the proper hepatic artery originates from the superior mesenteric artery, and the blood supply area of the right hepatic artery can be seen in the lesion; B: Intraoperative DSA angiography shows that the right inferior septal artery participates in the blood supply of the lesion; C: Intraoperative DSA Under the hepatic artery chemoembolization; D: Under DSA during the operation, the right inferior septal artery embolization was performed. Complete necrosis of the lesion was re-examined in January and March postoperative.
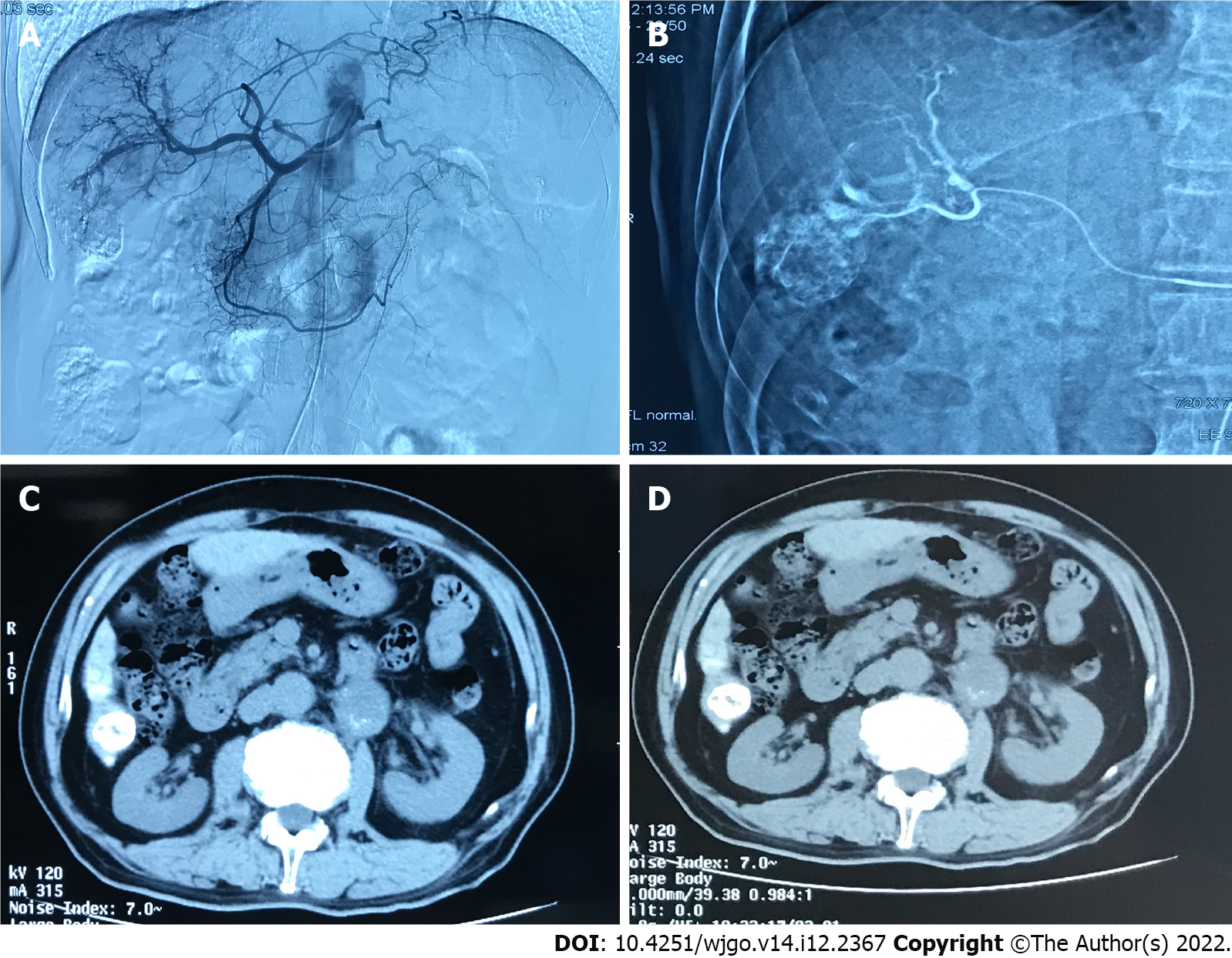
Figure 3 A 70 years old male diagnosed as primary liver cancer.
This patient underwent traditional transcatheter arterial chemoembolization treatment in May 2019. A: Intraoperative digital subtracted angiography (DSA) can be seen on angiography, and the blood supply area of the right hepatic artery can be seen in the lesion; B: Intraoperative DSA, superselective right hepatic artery branch chemoembolization; C: Abdominal computed tomography (CT) axial examination 1 mo after surgery, The lipiodol deposition in the lesion was good, and the lesion was completely necrotic; D: 3 mo after the operation, the abdominal CT axial examination was performed again, and the lipiodol deposition in the lesion was good, and no tumor recurrence was found.
- Citation: Ye T, Shao SH, Ji K, Yao SL. Evaluation of short-term effects of drug-loaded microspheres and traditional transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in the treatment of advanced liver cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 14(12): 2367-2379
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v14/i12/2367.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v14.i12.2367