Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 15, 2003; 9(10): 2226-2231
Published online Oct 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i10.2226
Published online Oct 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i10.2226
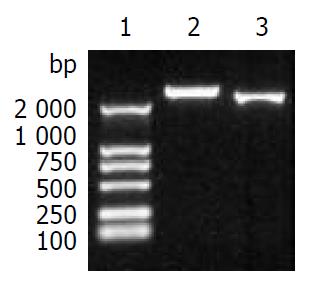
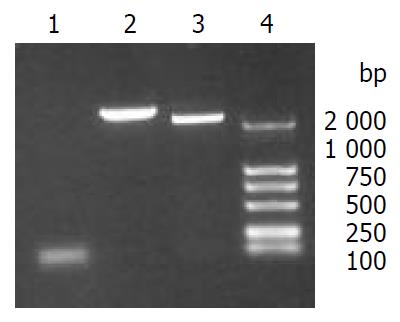
Figure 1 PCR products of HCV structural protein genes.
Lane1: DNA molecular weight marker (DL-2000), lane2: 5’NCR-CE1E2, lane3: CE1E2.
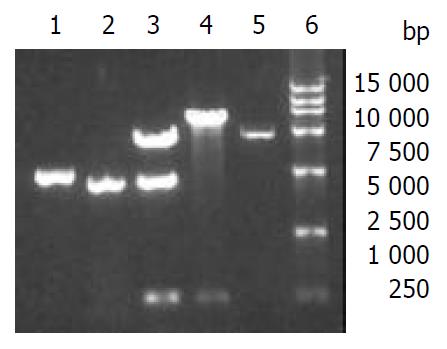
Figure 2 Confirmation of recombinant baculovirus donor plasmids.
Lane1: PCR of pFB1-CS, lane 2: PCR of pFB1-CE1E2, lane 3: pFB1-CS digested by XhoI/Hind III, lane 4: pFB1-CE1E2 digested by XhoI/Hind III, lane 5: pFastBacI digested by BamHI/Hind III, lane 6: DL-15000 marker.
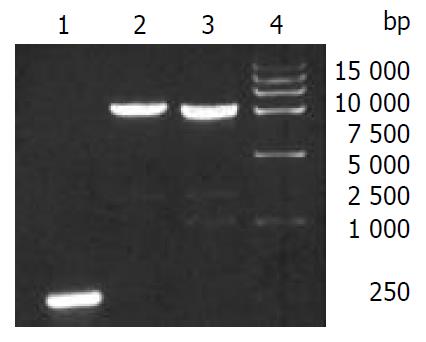
Figure 3 Confirmation of recombinant bacmids by PCR.
Lane 1: bacmid/0 control, lane 2: bacmid/CS, lane 3: bacimd/CE1E2, lane 4: DL-15000 marker.
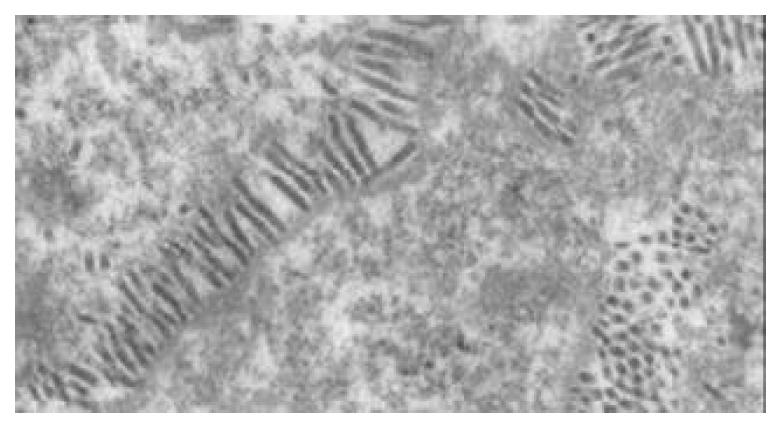
Figure 4 Baculoviruses in nuclei of Sf9 cells transfected with recombinant bacmid DNA (× 25000).
Figure 5 Confirmation of recombinant baculoviruses by PCR.
Lane 1: BV/Bac control, lane 2: reBV/CS, lane 3: reBV/CE1E2, lane 4: DL-2000 marker.
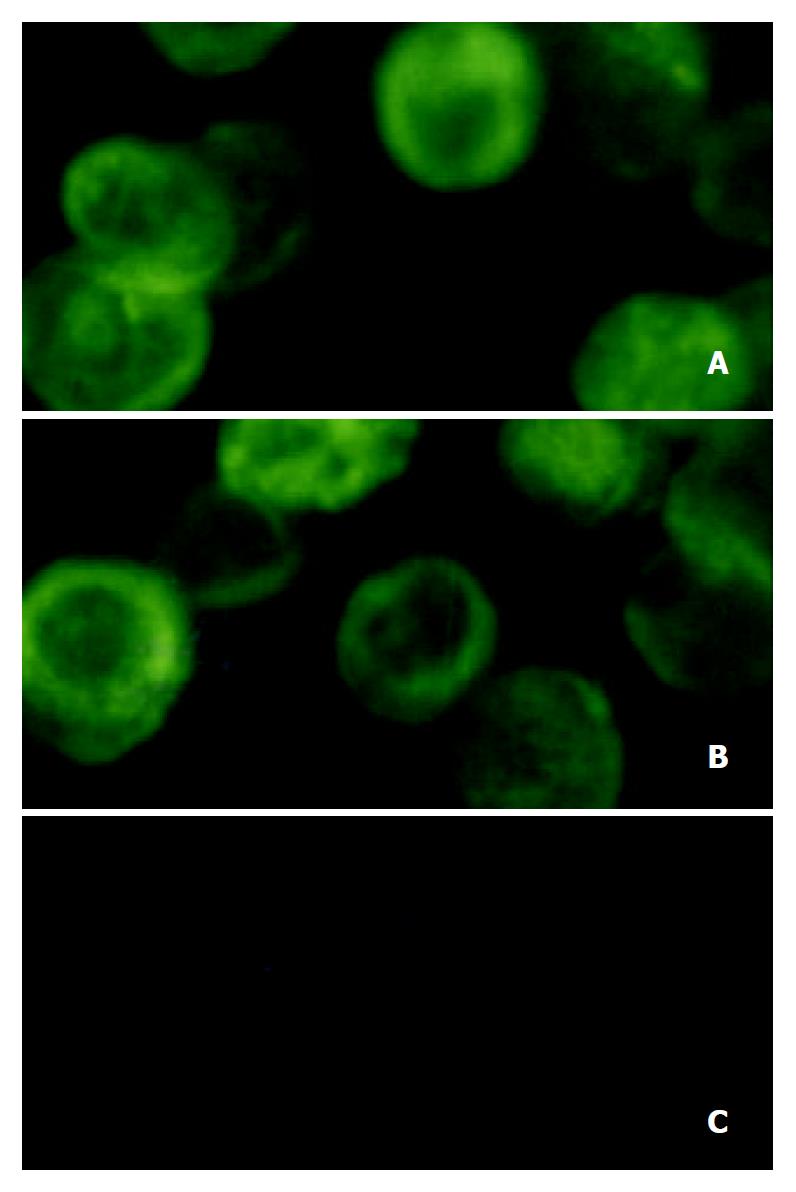
Figure 6 Immunofluorescence analysis of expression of HCV structural proteins in Sf9 cells.
Sf9 cells infected with A: reBV/CS, B: reBV/CE1E2, C: control BV/Bac.
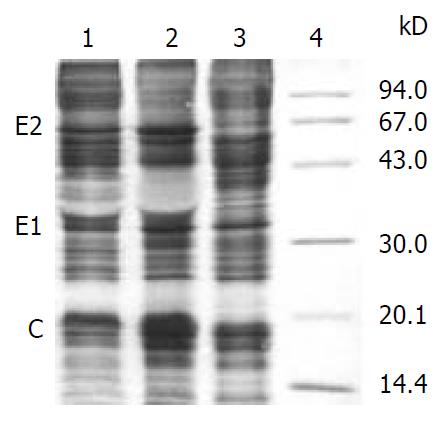
Figure 7 Identification of HCV structural proteins expressed in Sf9 cells by SDS-PAGE.
Lanes 1-2: cells infected with reBV/CS and reBV/CE1E2 respectively, lane 3: control cells infected with BV/Bac, lane 4: molecular weight marker.
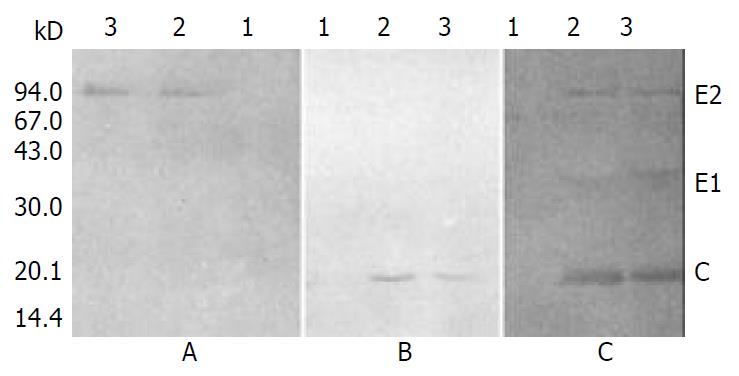
Figure 8 Immunoblotting of anti-E2 antibody immunoprecipi-tated proteins with anti-E2 mAb (A), anti-C mAb (B) and anti-HCV serum from HCV-infected patients (C).
Lane 1: control BV/Bac, lane 2: reBV/CE1E2, lane 3: reBV/CS.
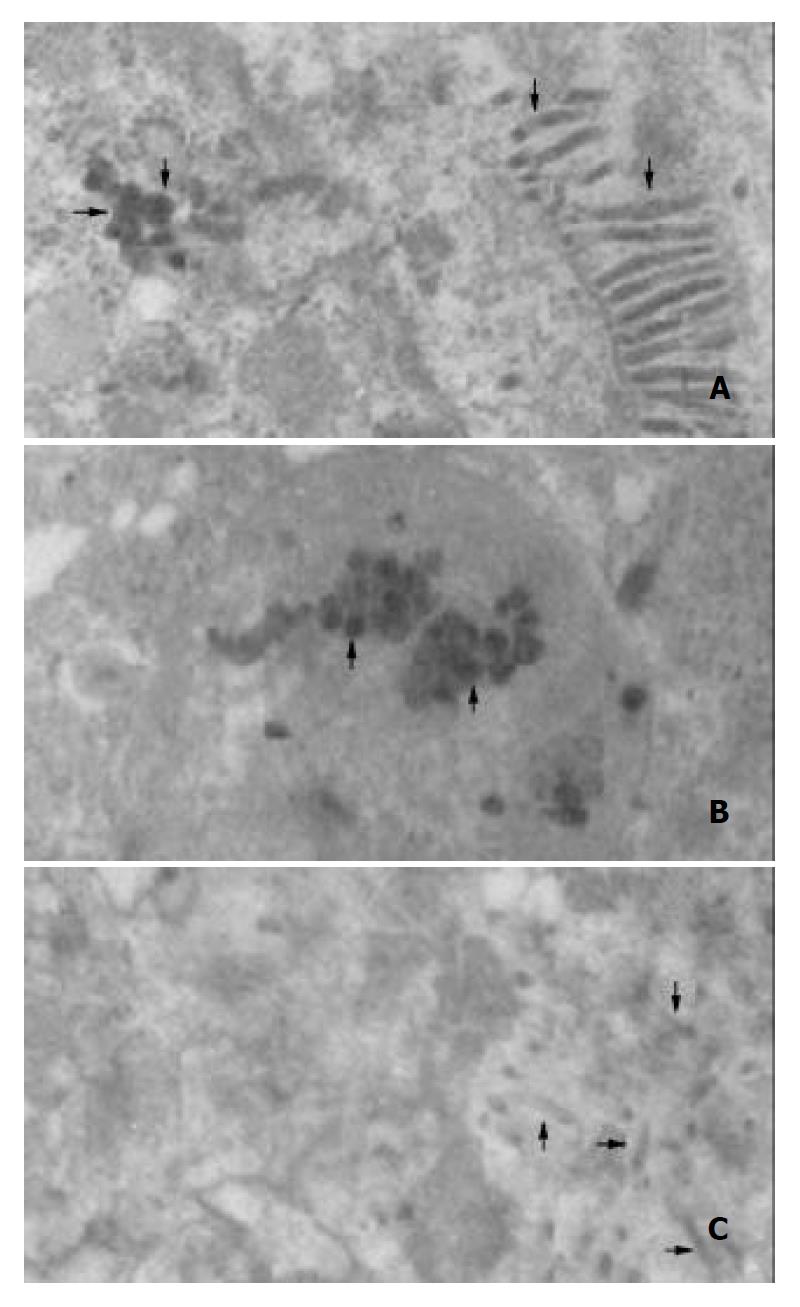
Figure 9 Electron micrographs of baculovirus-infected Sf9 cells (× 25000).
Sf9 cells infected with A: reBV/CS, B: reBV/CE1E2, C: control BV/Bac.
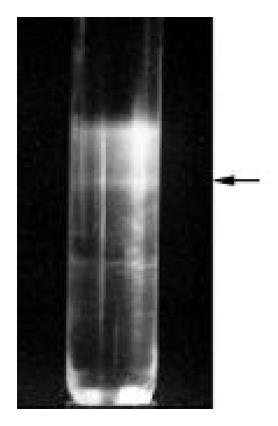
Figure 10 VLP band (indicated by arrow) in sucrose gradient centrifugation.
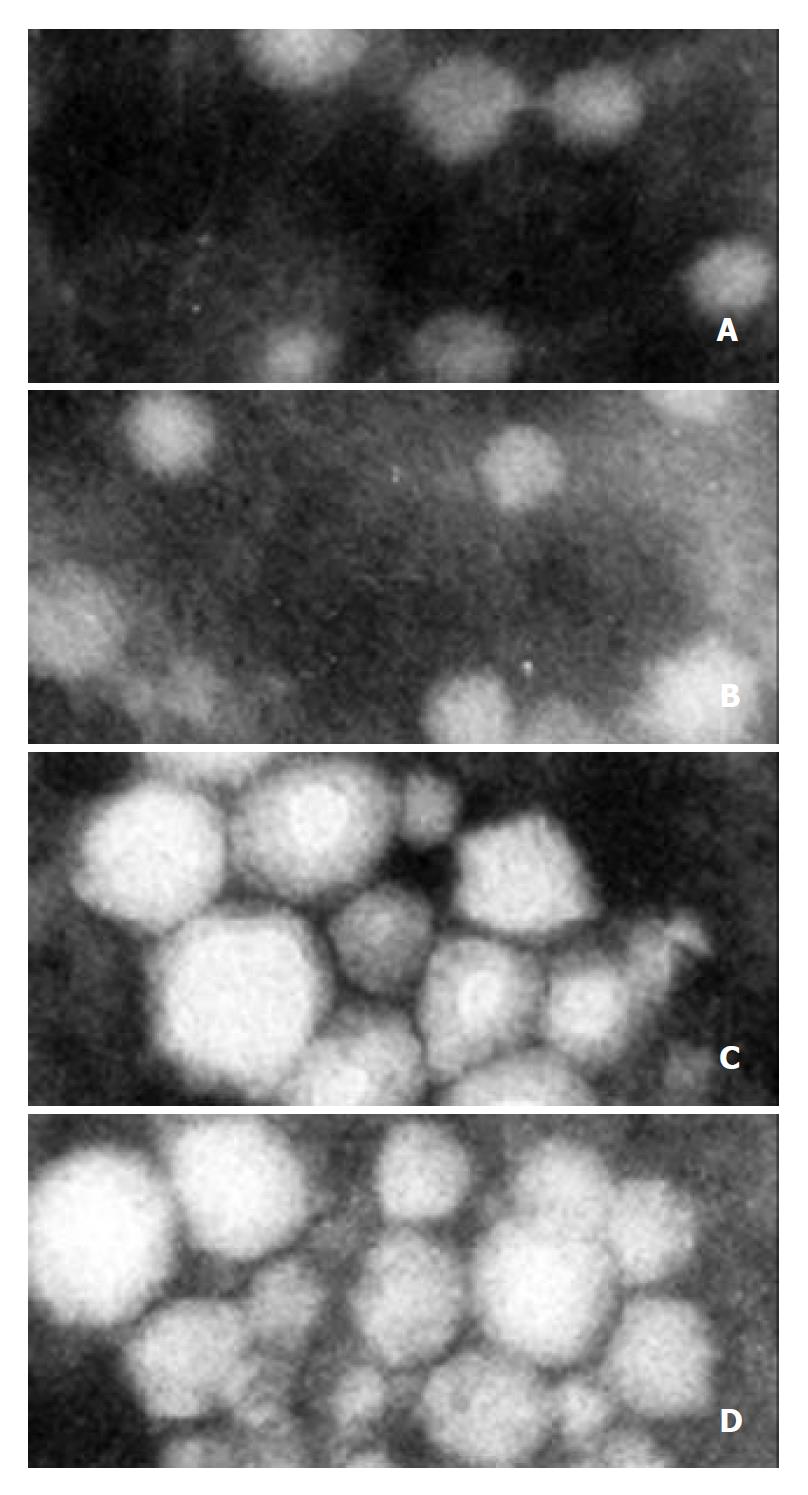
Figure 11 Electron microscopy and immune aggregation elec-tron microscopy analysis of VLPs (negative staining).
A and B (× 100000): VLPs isolated from Sf9 cells infected with reBV/CS and reBV/CE1E2, respectively. C and D (× 150000): Immune aggregation of VLPs from A and B with anti-HCV serum, respectively.
- Citation: Zhao W, Liao GY, Jiang YJ, Jiang SD. No requirement of HCV 5’NCR for HCV-like particles assembly in insect cells. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(10): 2226-2231
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i10/2226.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i10.2226