Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2019; 25(19): 2271-2278
Published online May 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i19.2271
Published online May 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i19.2271
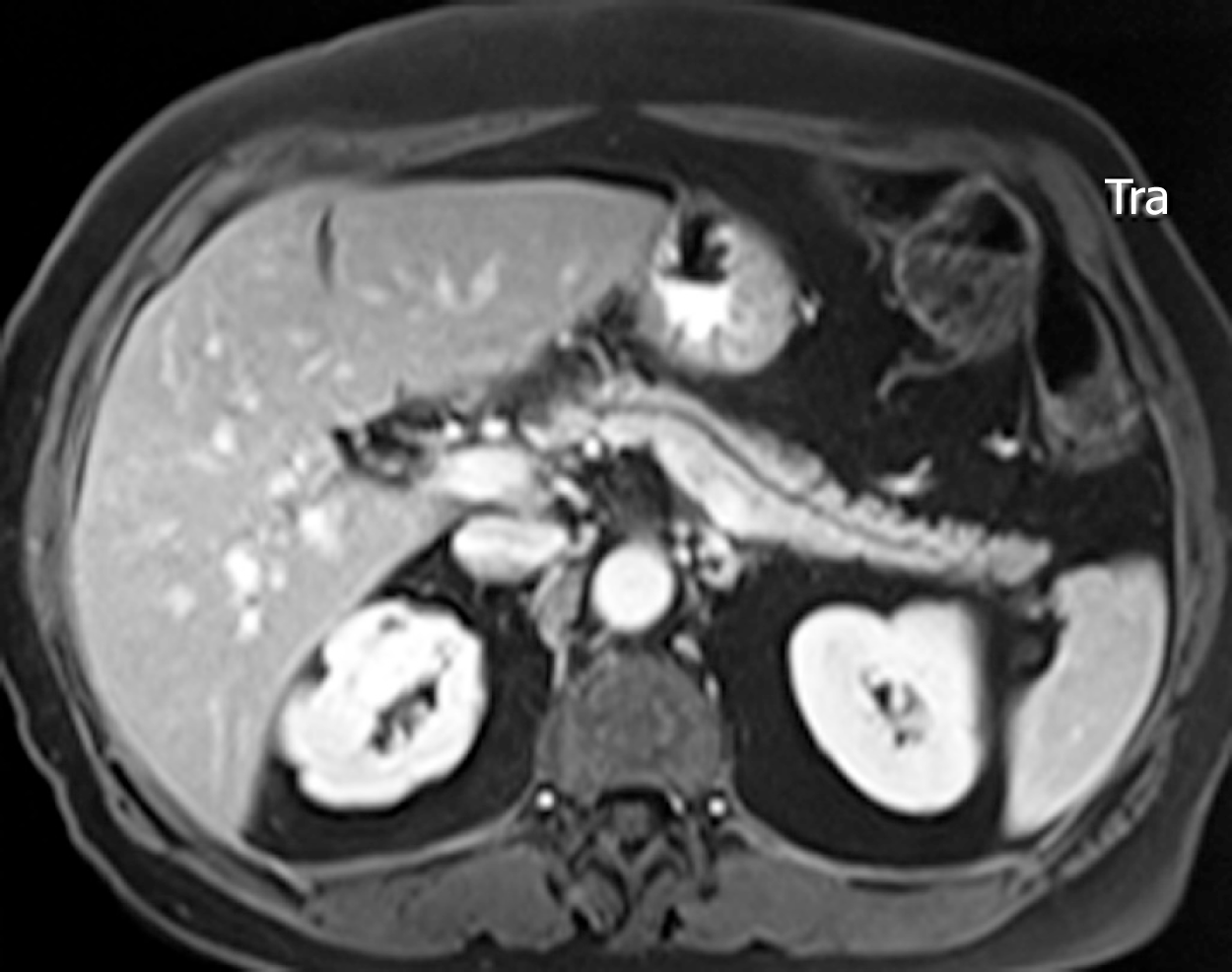
Figure 1 Main duct-intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms.
Magnetic resonance imaging of a uniform dilation of the main pancreatic duct.
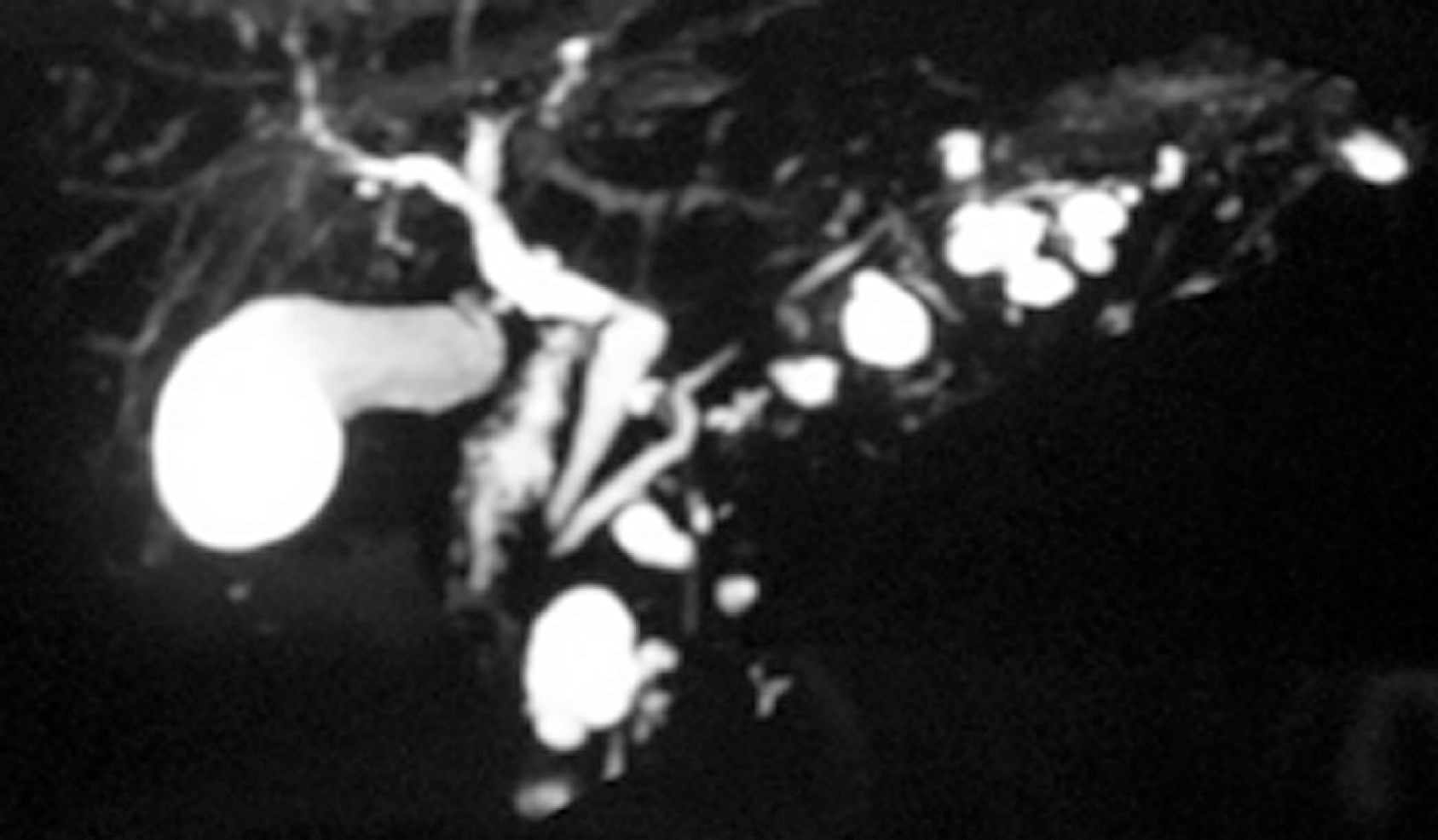
Figure 2 Branch duct—intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms.
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography demonstrating a nondilated main pancreatic duct with multiple cystic dilated side branch ducts.
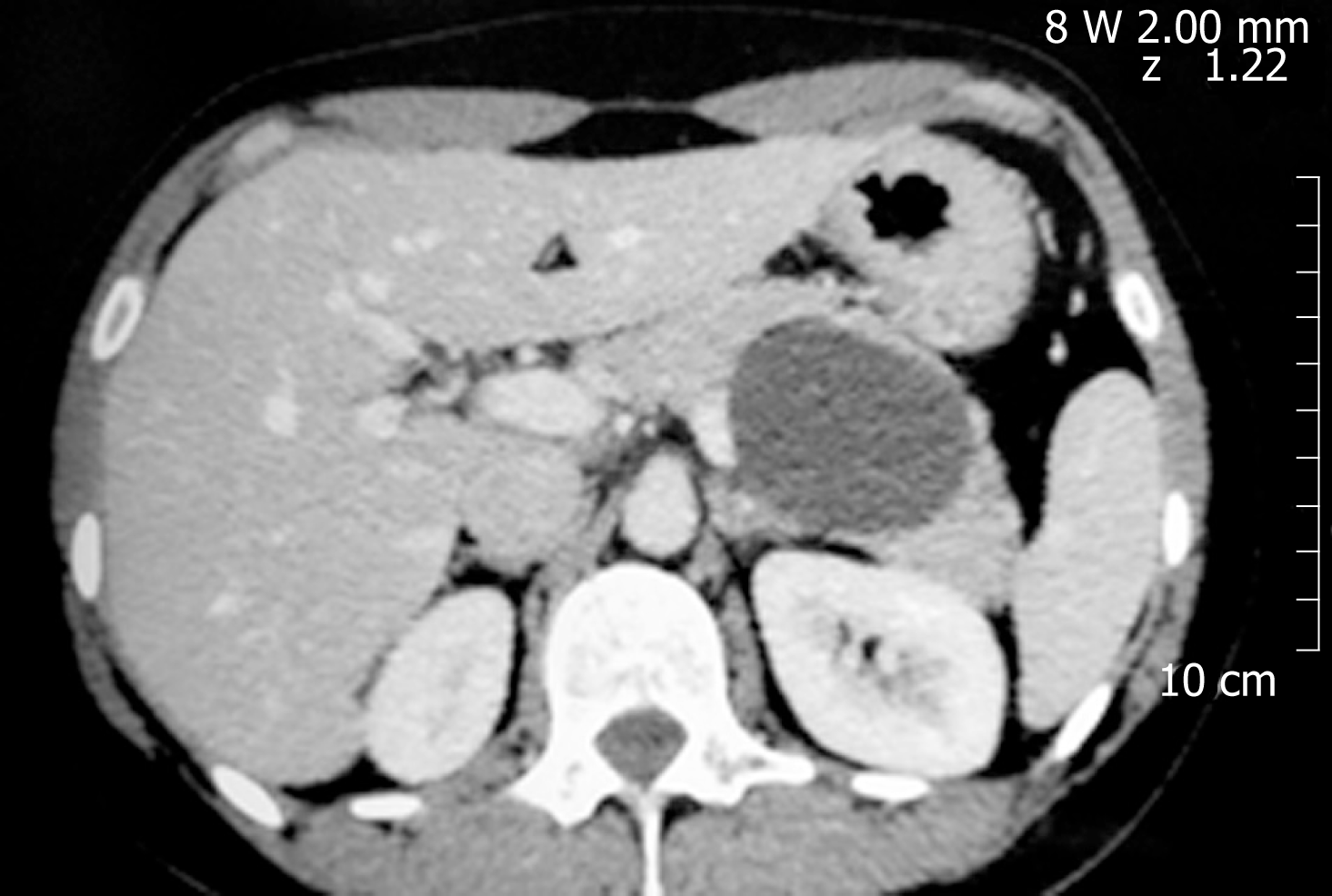
Figure 3 Mixed-intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms.
The main pancreatic duct is markedly dilated in the pancreatic head with multiple dilated side branches throughout the pancreas.
Figure 4 Mucinous cystic neoplasm.
An unilocular cyst with thin walls and homogeneous content on computed tomography in the pancreatic body.
- Citation: Lopes CV. Cyst fluid glucose: An alternative to carcinoembryonic antigen for pancreatic mucinous cysts. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(19): 2271-2278
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i19/2271.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i19.2271