Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2015; 21(43): 12361-12369
Published online Nov 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i43.12361
Published online Nov 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i43.12361
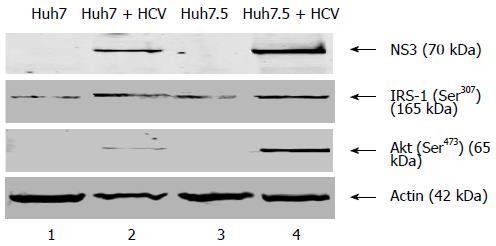
Figure 1 Hepatitis C virus infection modulates insulin signaling in hepatitis C virus infected human hepatoma cells.
Cellular lysates were made from mock and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infected Huh7 and Huh7.5 cells. An equal amount of cellular lysates were subjected to Western blot assay using p-IRS-1 Ser307and p-Akt Ser473. HCV NS3 protein expression represents the level of HCV infection. Cellular actin was used as an internal control to verify protein loading in each lane. IRS: Insulin receptor substrate; NS: Nonstructural protein.
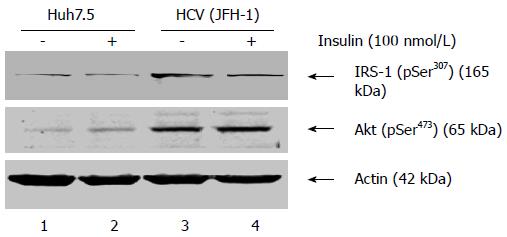
Figure 2 Status of p-Ser307 insulin receptor substrate-1 and p-Ser473 Akt phosphorylation in hepatitis C virus infected hepatoma cells upon insulin treatment.
Total cellular lysates were prepared from hepatitis C virus (HCV) infected and mock infected Huh7.5 cells that were treated or untreated with insulin (100 nmol/L). An equal amount of cellular lysates were subjected to Western blot assay using anti-p-IRS-1 Ser307 and anti-p-Akt Ser473. Cellular actin was used as a protein loading control in each lane. IRS: Insulin receptor substrate.
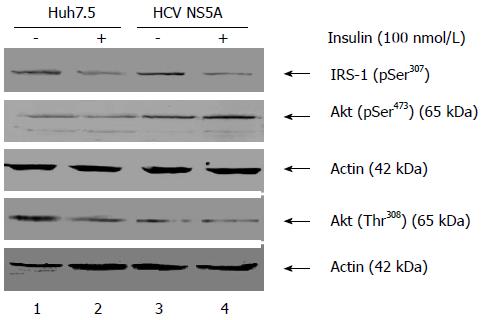
Figure 3 Hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A modulates phosphorylation levels of key insulin signaling molecules.
Untransfected and nonstructural protein 5A (NS5A) transfected cells were incubated with insulin (100 nmol/L) for 3 h. An equal amount of cellular lysates were subjected to Western blot assay using anti-p-Akt Ser473, anti-p-Akt Thr308 and anti-p-IRS-1 Ser307. Cellular actin was used as an internal control to verify protein loading in each lane. IRS: Insulin receptor substrate.
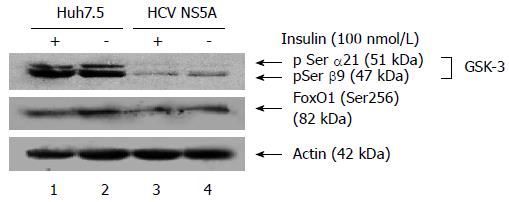
Figure 4 Effect of hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A on the phosphorylation levels of Fox01 Ser256 and GSK-3β Ser9.
Using the cellular lysates from nonstructural protein 5A (NS5A) transfected cell line and the controlled treated hepatoma cell line, Western blot assay was performed using anti-p-GSK3 Ser (α21/β9) and anti-p-Fox01 Ser256. HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
Figure 5 Hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A favors gluconeogenic gene expression.
Total cellular RNA was extracted from hepatitis C virus (HCV, A) nonstructural protein 5A (NS5A, B) transfected cells and control cells. The quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was performed for the targeted genes as described in Materials and Methods. 18S rRNA was used as a housekeeping gene. Data represent mean of three independent experiments. aP < 0.05 vs control group. Data were analyzed with Graph Pad Prism, and 2-tail error bars represent SE of the data. TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; PEPCK: Phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase; G6P: Glucose-6-phosphatase; CREB: CRE-binding protein.
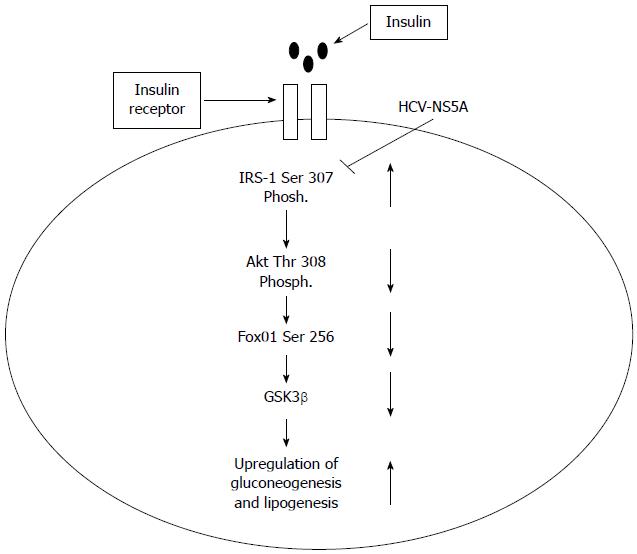
Figure 6 Schematic representation of hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A induced insulin resistance.
Based on our findings, a model has been proposed that depicts various check points in the insulin signaling pathway that gets modulated by nonstructural protein 5A (NS5A) protein. The up and down arrows represent upregulation and downregulation of proteins involved in insulin signaling cascades. The blunt headed line represents the check point that gets blocked by NS5A as this protein favors serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) while under normal conditions tyrosine phosphorylation is known to take place. HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
- Citation: Parvaiz F, Manzoor S, Iqbal J, Sarkar-Dutta M, Imran M, Waris G. Hepatitis C virus NS5A promotes insulin resistance through IRS-1 serine phosphorylation and increased gluconeogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(43): 12361-12369
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i43/12361.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i43.12361