Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2013; 19(14): 2249-2255
Published online Apr 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i14.2249
Published online Apr 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i14.2249
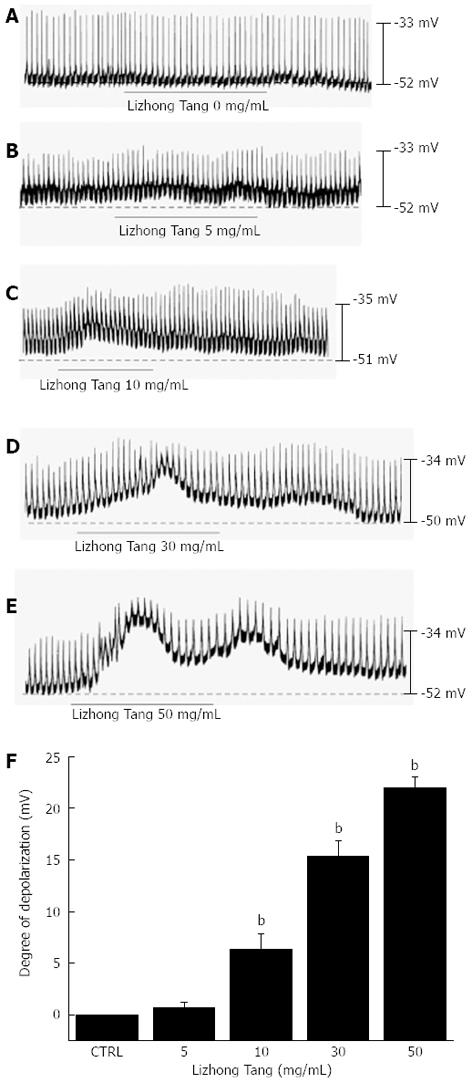
Figure 1 Effects of Lizhong Tang on pacemaker potentials in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal from murine small intestines.
A-E: Pacemaker potentials in interstitial cells of Cajal exposed to Lizhong Tang (0-50 mg/mL) in current-clamp mode (I = 0); F: The responses to Lizhong Tang are summarized. Bars represent mean ± SE. bP < 0.01 vs control group. CTRL: Control.
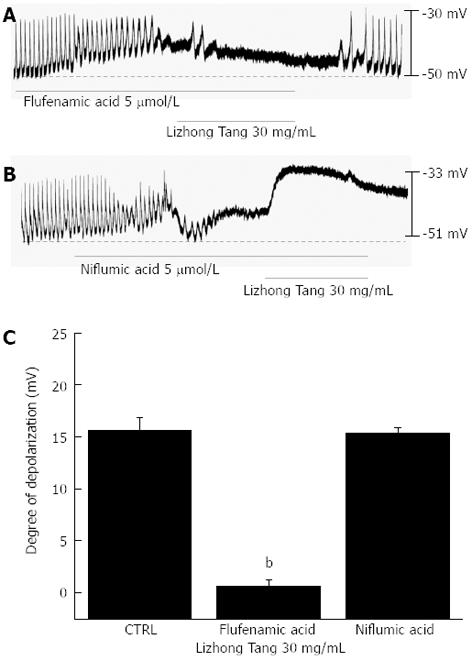
Figure 2 Effects of flufenamic acid (a nonselective cation channel blocker) or niflumic acid (a Cl- channel blocker) on Lizhong Tang-induced pacemaker potentials in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal from murine small intestines.
A: The application of flufenamic acid (5 μmol/L) abolished the generation of pacemaker potentials, and in the presence of flufenamic acid, Lizhong Tang (30 mg/mL) did not cause membrane depolarization; B: In contrast, although niflumic acid (5 μmol/L) abolished the generation of pacemaker potentials, it did not block Lizhong Tang-induced (30 mg/mL) membrane depolarization; C: The responses to Lizhong Tang in the presence of flufenamic acid or niflumic acid are summarized. Bars represent mean ± SE. bP < 0.01 vs control group. CTRL: Control.
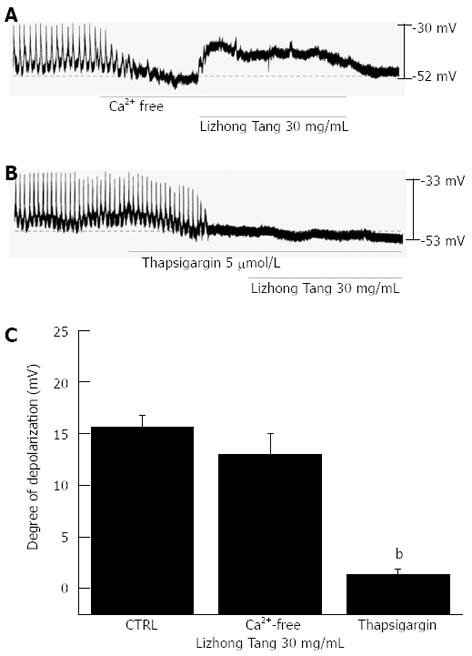
Figure 3 Effects of an external Ca2+-free solution, thapsigargin (an inhibitor of Ca 2+-ATPase in the endoplasmic reticulum), or U-73122 (an active phospholipase C inhibitor) on Lizhong Tang-induced pacemaker potentials in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal.
A: External Ca2+-free solution abolished the generation of pacemaker potentials, but failed to block Lizhong Tang-induced (30 mg/mL) membrane depolarization; B: Thapsigargin (5 μmol/L) abolished the generation of pacemaker potentials, and blocked Lizhong Tang-induced (30 mg/mL) membrane depolarization; C: The responses to Lizhong Tang in external Ca2+-free solution in the presence of thapsigargin are summarized. Bars represent mean ± SE. bP < 0.01 vs control group. CTRL: Control.
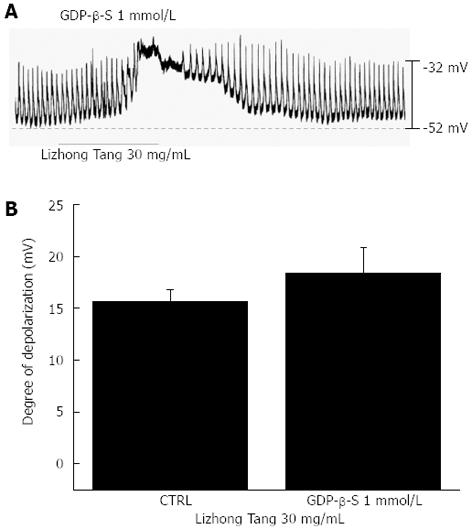
Figure 4 Effects of GDP-β-S in the pipette on Lizhong Tang-induced pacemaker potentials in cultured murine small intestine interstitial cells of Cajal.
A: Pacemaker potentials in interstitial cells of Cajal exposed to Lizhong Tang (30 mg/mL) in the presence of GDP-β-S (1 mmol/L) in the pipette. Under these conditions, Lizhong Tang (30 mg/mL) caused membrane depolarization; B: The responses to Lizhong Tang in the presence of GDP-β-S in the pipette are summarized. Bars represent mean ± SE. CTRL: Control.
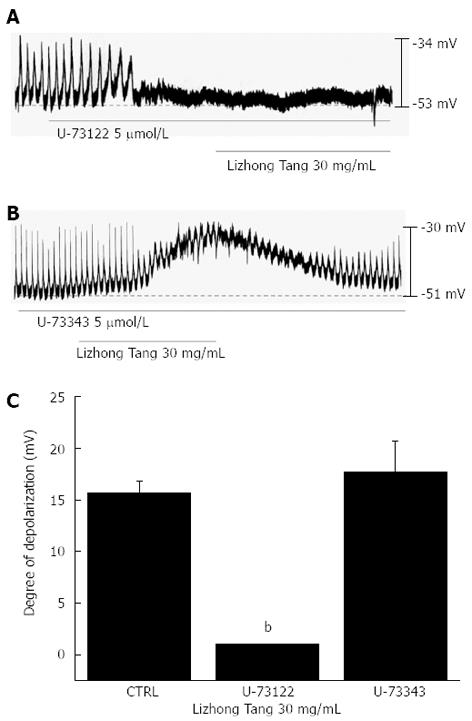
Figure 5 Effects of phospholipase C inhibitors on Lizhong Tang-induced potentials in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal.
A: U-73122 (5 μmol/L; a phospholipase C inhibitor) abolished the generation of pacemaker potentials, and blocked Lizhong Tang-induced (30 mg/mL) membrane depolarization; B: The application of U-73343 (5 μmol/L) did not influence the generation of pacemaker currents or block Lizhong Tang-induced (30 mg/mL) membrane depolarization; C: The responses to Lizhong Tang in the presence of phospholipase C inhibitors are summarized. Bars represent mean ± SE. bP < 0.01 vs control group. CTRL: Control.
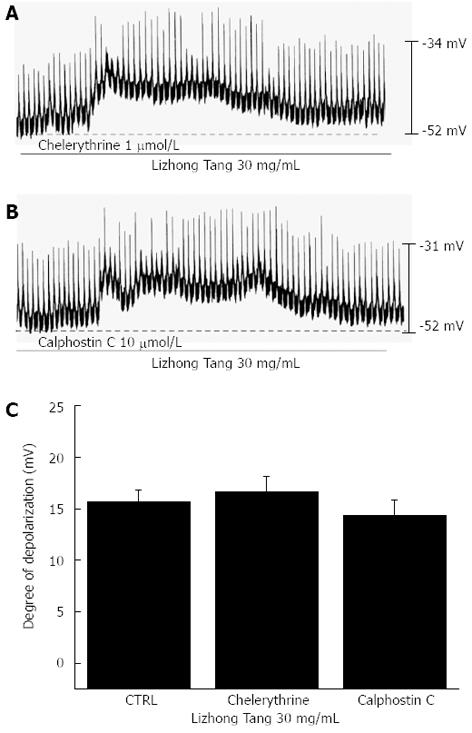
Figure 6 Effects of chelerythrine or calphostin C (inhibitors of protein kinase C) on Lizhong Tang-induced pacemaker potentials in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal.
A, B: Pacemaker potentials in interstitial cells of Cajal exposed to Lizhong Tang (30 mg/mL) in the presence of chelerythrine (1 μmol/L) or calphostin C (10 μmol/L). Lizhong Tang caused membrane depolarization in the presence of both inhibitors; C: The responses to Lizhong Tang in the presence of chelerythrine or calphostin C are summarized. Bars represent mean ± SE. CTRL: Control.
- Citation: Hwang MW, Kim JN, Song HJ, Lim B, Kwon YK, Kim BJ. Effects of Lizhong Tang on cultured mouse small intestine interstitial cells of Cajal. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(14): 2249-2255
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i14/2249.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i14.2249