Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2012; 18(20): 2586-2590
Published online May 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i20.2586
Published online May 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i20.2586
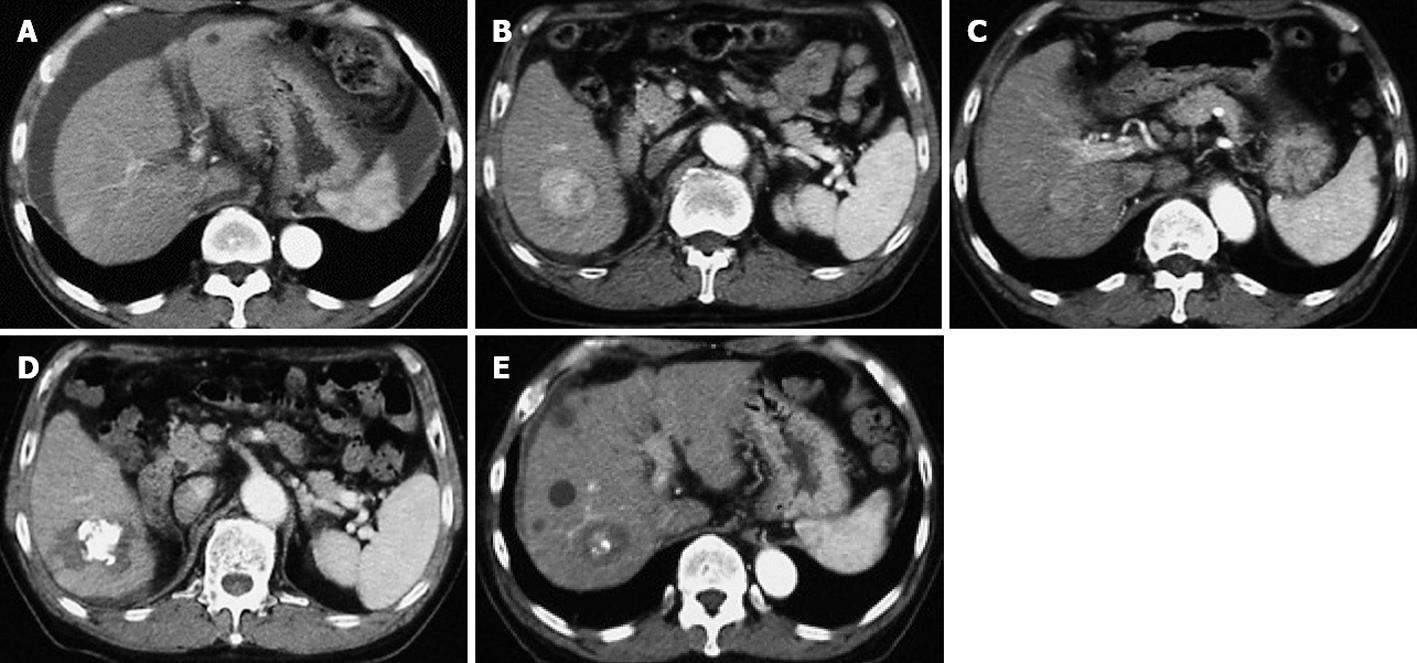
Figure 1 Computed tomography in our patient.
It shows a cirrhotic pattern of the liver and massive ascites at first admission (A); Dynamic computed tomography revealed two hepatocellular carcinomas, 4.5 cm (B) and 2.5 cm (C) in diameter, in the right lobe; These two lesions were treated by transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation (D, E).
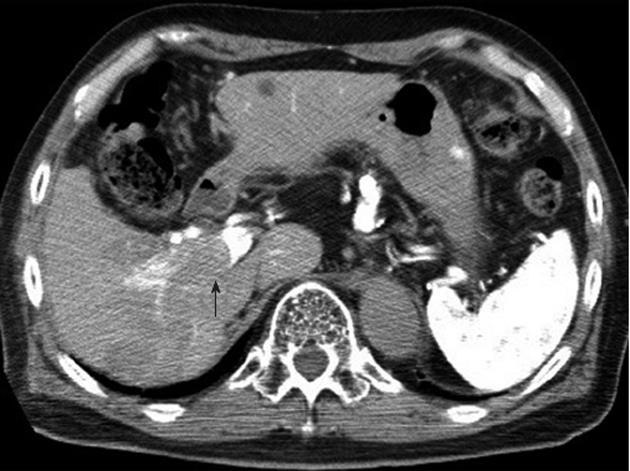
Figure 2 Computed tomography during hepatic arteriography, showing a portal tumor thrombus (arrow) in the right portal vein.
Hepatocellular carcinoma was not detected in the left lobe.
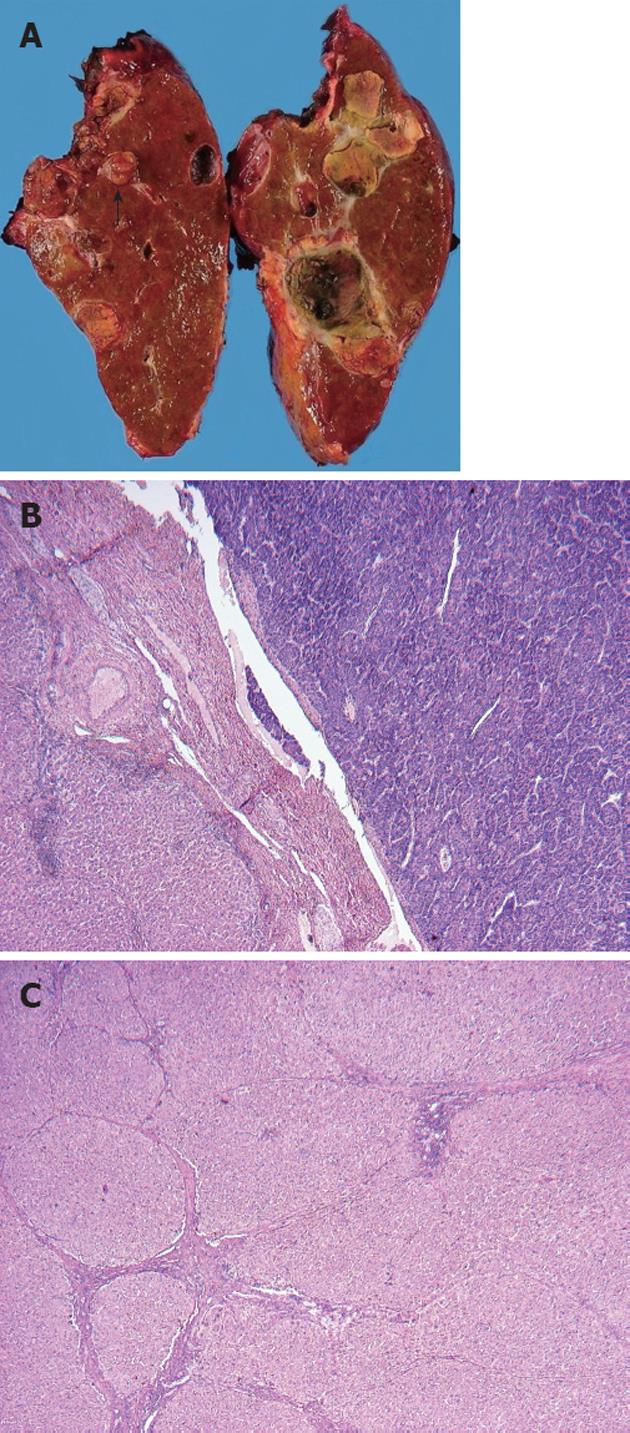
Figure 3 Macroscopic and microscopic appearance of the resected liver.
A: A tumor thrombus was detected in the right portal vein (arrow); B: A moderately differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma with a trabecular pattern was seen in the right portal vein [hematoxylin and eosin (HE) stain, ×40]; C: Fibrosis of varying extent was observed in the cancer-free area. Some pseudolobules with severe fibrosis were present in the left part of the photograph (HE stain, ×40).
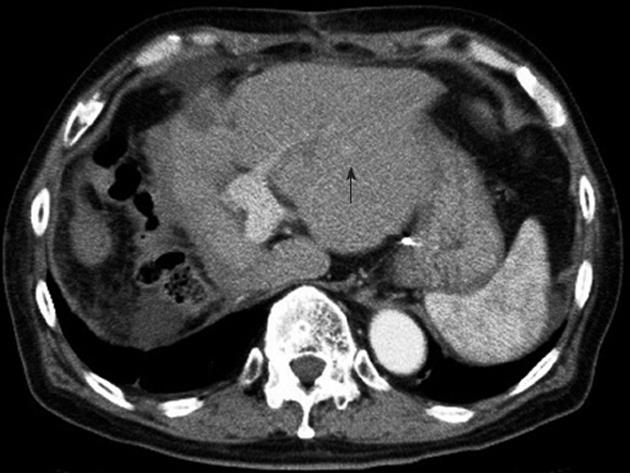
Figure 4 Abdominal computed tomography showing the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma (arrow) in the left lobe two months after right hepatectomy.
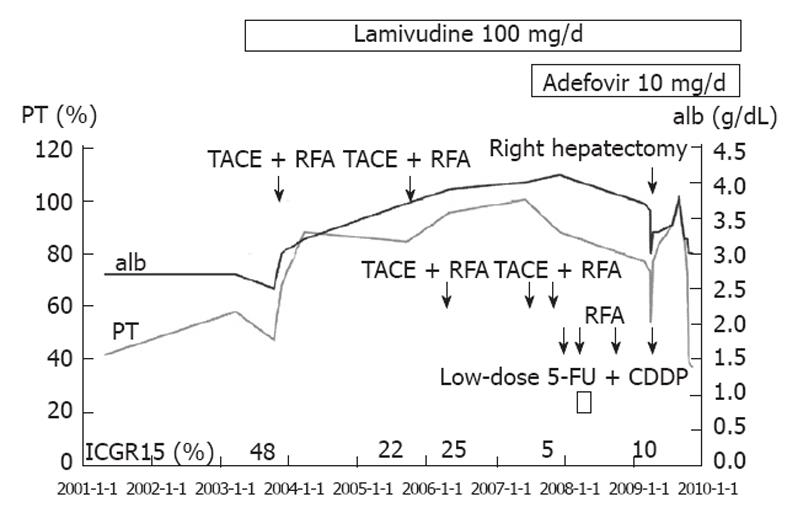
Figure 5 Clinical course of the patient.
After lamivudine administration, his liver function gradually improved despite repeated treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and his indocyanine green at 15 min after injection (ICGR15) test score was 5% 4 years after initiation of lamivudine treatment. He underwent a successful right hepatectomy for HCC 5 years after beginning lamivudine treatment. alb: Albumin; PT: Prothrombin time; TACE: Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization; RFA: Radiofrequency ablation; 5-FU: 5-Fluorouracil; CDDP: Cisplatin.
- Citation: Honda K, Seike M, Maehara SI, Tahara K, Anai H, Moriuchi A, Muro T. Lamivudine treatment enabling right hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma in decompensated cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(20): 2586-2590
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i20/2586.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i20.2586