Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2010; 16(1): 21-29
Published online Jan 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i1.21
Published online Jan 7, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i1.21
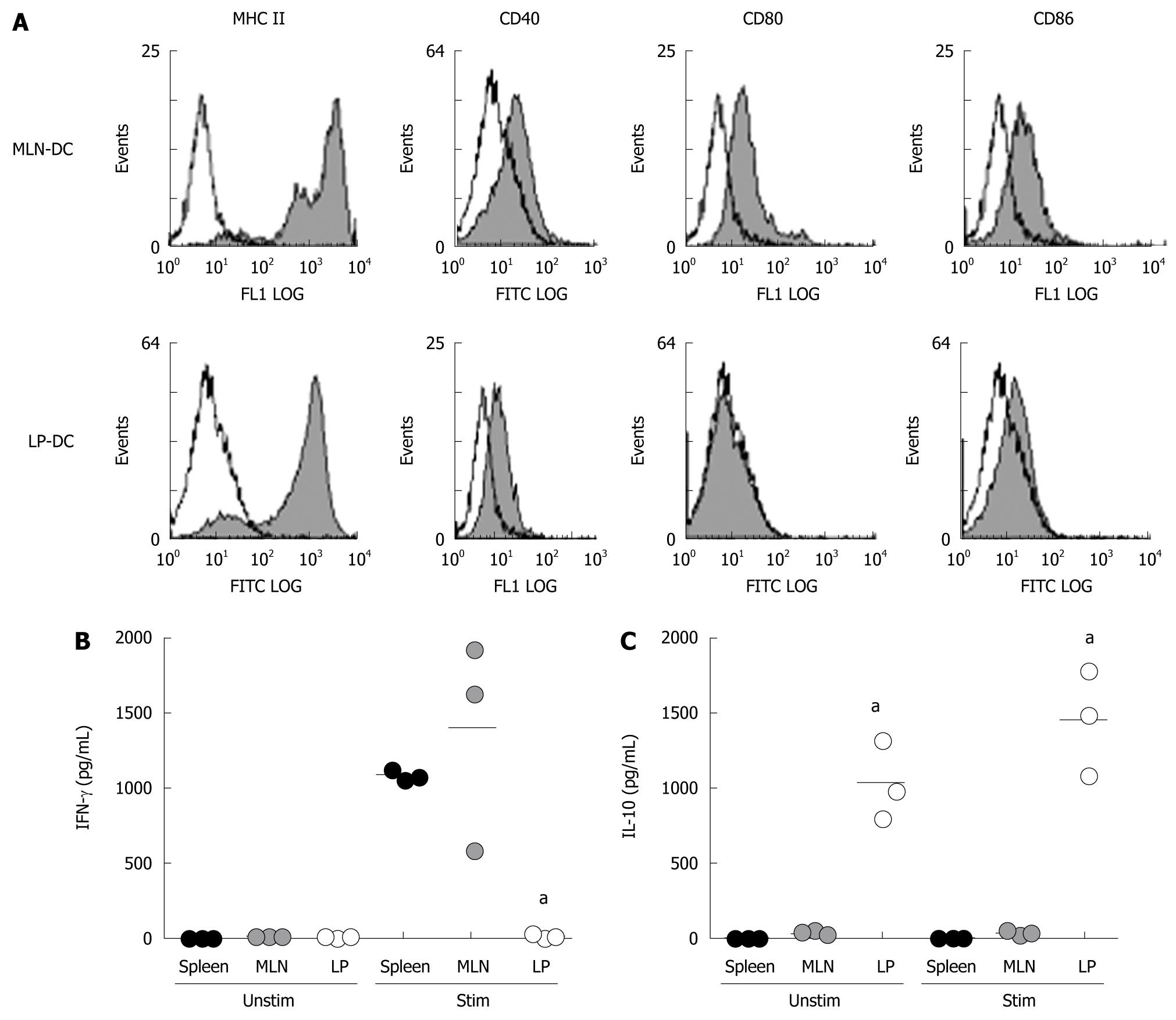
Figure 1 Phenotypic and functional analysis of DC derived from MLN and LP of healthy mice.
A: Primary DC were isolated from MLN (MLN-DC) and colonic LP (LP-DC) of healthy mice. CD11c+ DC were stained with FITC-conjugated mAbs for expression of MHC-class II and the costimulatory molecules CD40, CD80 and CD86; B: Isolated DC from spleen, MLN and LP were incubated for 24 h in complete medium partly stimulated with 5 μg/mL CpG (5 wells per situation). Cytokine levels were measured within the supernatant by ELISA. aP < 0.05. Data presented are representative of three independent experiments.
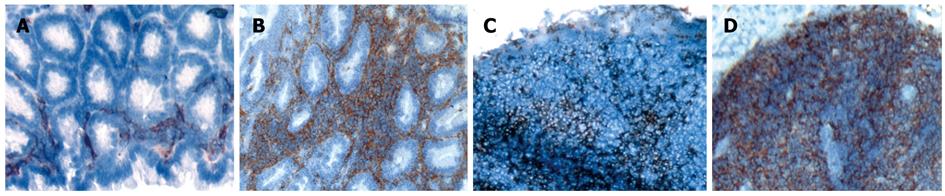
Figure 2 Inflammation induces infiltration of colonic LP and MLN with CD11c+ DC.
Tissue was harvested from colonic LP (A/B) and MLN (C/D) of healthy animals (A/C) and mice with colitis (B/D). Immunohistochemistry was performed using an anti-CD11c+ antibody to stain for intestinal DC. Staining with isotype control revealed no background staining (data not shown). Representative sections from 5 mice per group are shown (magnification 100 ×). Staining was performed on tissue derived from colitic animals with transfer colitis as well as chronic DSS colitis and revealed similar results. Sections shown within this figure are derived from animals with transfer colitis.
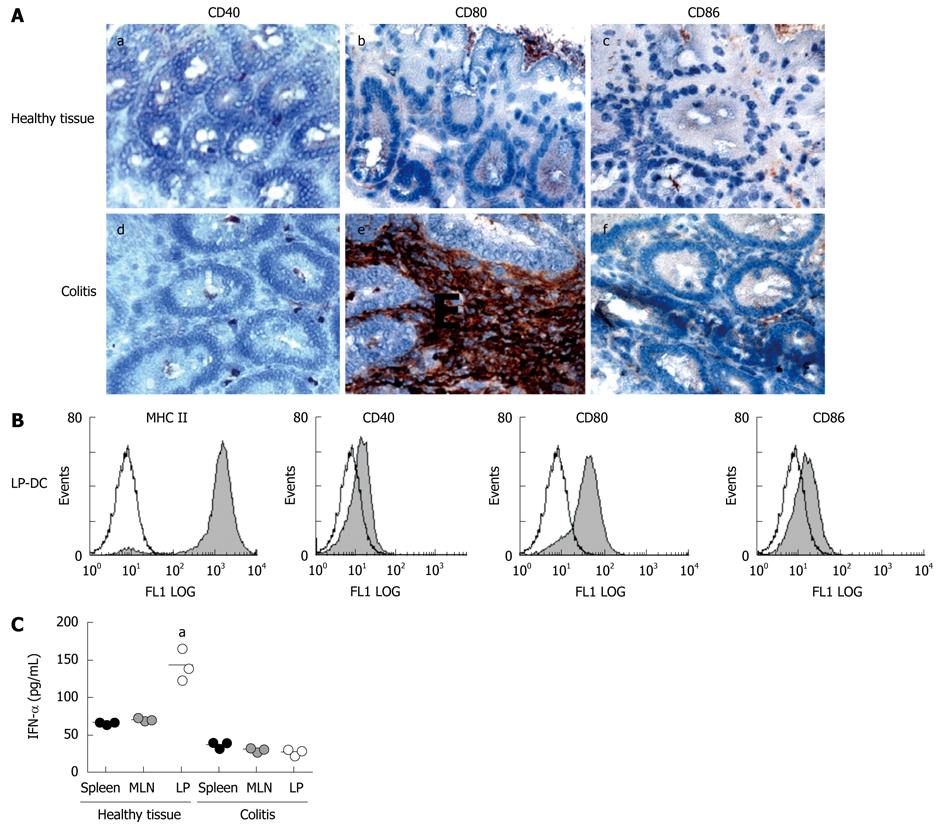
Figure 3 Intestinal DC are activated after induction of colitis.
A: Tissue was harvested from LP of healthy animals and from mice with colitis. Immunohistochemistry was performed with antibodies against the following costimulatory molecules: CD40 (a/d), CD80 (b/e), CD86 (c/f). Representative sections are shown (magnification 100 ×). Experiments were performed from 5 animals each group. Sections shown within this figure are derived from animals with transfer colitis, however staining was also performed on tissues derived from colitic animals with chronic DSS colitis and revealed similar results; B: LP-DC were isolated from inflamed intestinal tissue and FACS analysis was performed. CD11c+ DC were stained with FITC-conjugated mAbs for expression of MHC-class II and the costimulatory molecules CD40, CD80 and CD86. Data presented are representative of three independent experiments performed with cells derived from animals with transfer colitis. Similar results were generated in the DSS colitis model; C: Primary DC were isolated from different tissues (spleen, MLN, colonic LP) of healthy animals and mice with colitis. Isolated DC were incubated for 24 h in complete medium and levels of IFN-α were measured within the supernatants by ELISA (5 wells per situation). aP < 0.05. Data presented are from one of three independent experiments performed with cells derived from animals with transfer colitis. Similar results were generated in the DSS colitis model.
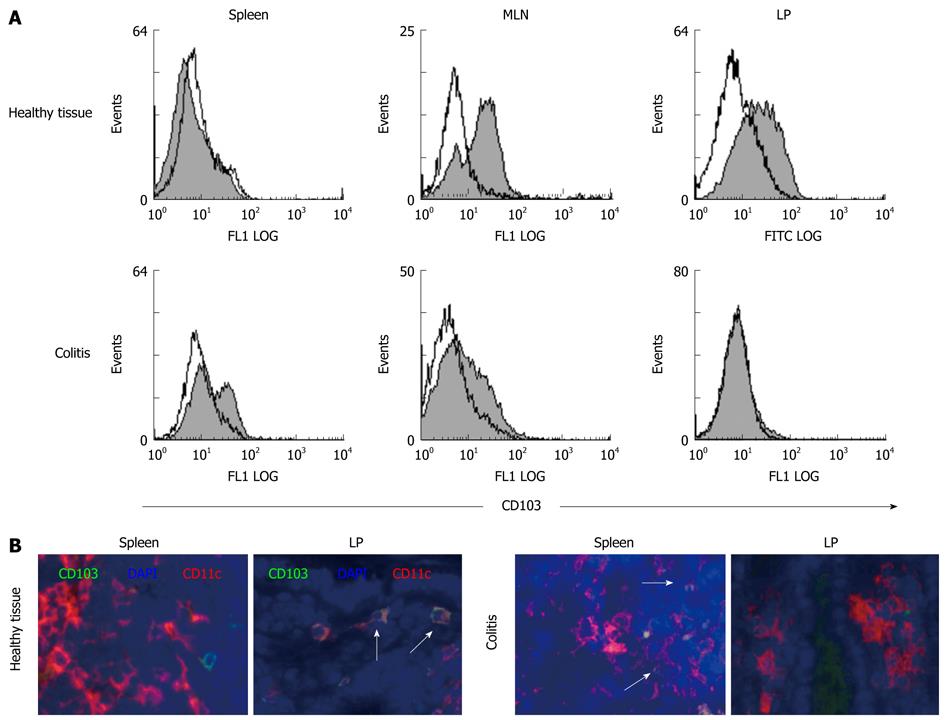
Figure 4 CD103+ DC are found in mucosal tissues of healthy mice and are lost during colitis.
A: Primary DC were isolated from different tissues (spleen, MLN, colonic LP) of healthy animals and mice with colitis. FACS analysis was performed after staining of CD11c+ DC with FITC-conjugated mAb against CD103, the integrin αEβ7. Data presented are representative of three independent experiments that were carried out with cells derived from animals with transfer colitis. Similar results were generated in the DSS colitis model; B: Tissue was harvested from spleen and LP of healthy animals and mice with colitis. Immunofluorescence was performed using an anti-CD11c+ mAb to stain for intestinal DC and an anti-CD103 mAb to recognize the integrin αEβ7. DAPI was used to visualize nuclei. Images show overlays of CD103 (green), CD11c (red) and DAPI (blue). DC coexpressing CD103 appear yellow (indicated by arrows). Representative sections from 5 mice per group are shown (magnification 100 ×). Staining was performed on tissue derived from colitic animals with transfer colitis as well as chronic DSS colitis and revealed similar results. Sections shown within this figure are derived from animals with transfer colitis.
- Citation: Strauch UG, Grunwald N, Obermeier F, Gürster S, Rath HC. Loss of CD103+ intestinal dendritic cells during colonic inflammation. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(1): 21-29
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i1/21.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i1.21