Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2007; 13(48): 6529-6537
Published online Dec 28, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i48.6529
Published online Dec 28, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i48.6529
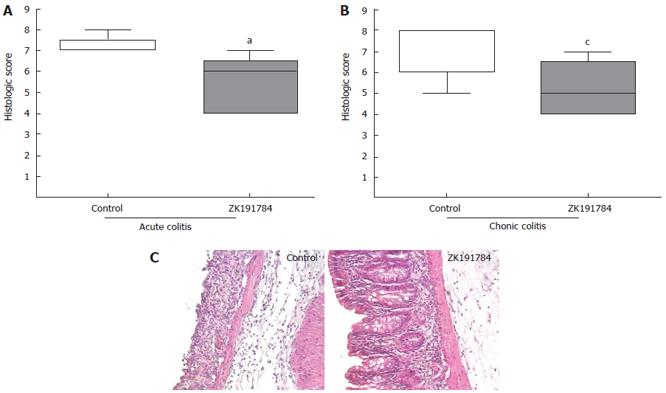
Figure 1 Treatment with ZK191784 ameliorates intestinal inflammation in acute and chronic DSS colitis.
A: Acute DSS colitis was induced by administration of 3% DSS for 7 d. aP < 0.05, n = 5 mice per group. Data presented are representative of three independent experiments; B: Administration of ZK191785 was started after the first and the third cycle of DSS administration for induction of chronic colitis. cP < 0.05, n = 8 or 9 mice per group. Data show one of two independent experiments. Data are displayed as box plots in which the box contains the middle half of the scores in the distribution, the median is shown as a line across the box, and the largest value below the upper hinge and the smallest value above the lower inner fence are indicate the distribution; C: Representative colonic hematoxylin/eosin sections from animals with acute DSS colitis treated with ZK191784 or vehicle (× 100).
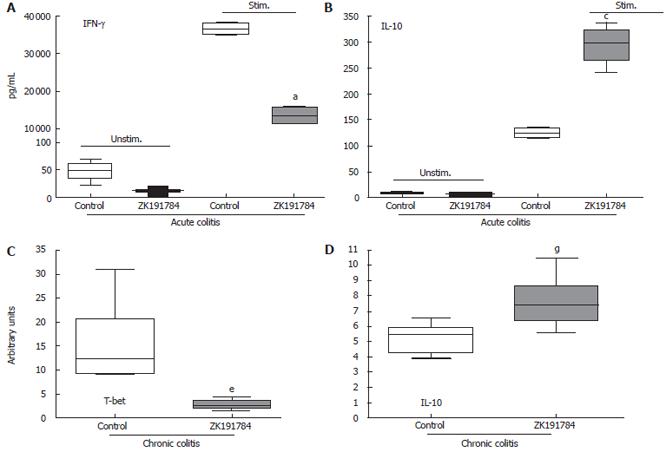
Figure 2 Effects of ZK191784 treatment on cytokine production in acute and chronic colitis.
(A and B) aP < 0.05, cP < 0.05, n = 5 animals. Data presented are representative of three independent experiments. (C and D) n = 8 or 9 animals per group. Data presented show one of two independent experiments. eP < 0.05, gP < 0.05. Data are displayed as box plots, in which the box contains the middle half of the scores in the distribution, the median is shown as a line across the box, and the largest value below the upper hinge and the smallest value above the lower inner fence indicate the distribution.
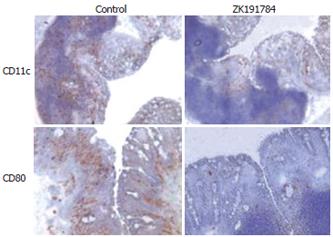
Figure 3 Effects of ZK191784 treatment on the distribution of CD11c+ DCs in the colonic mucosa.
Sections were stained for CD11c or the costimulatory molecule CD80 (× 100). Staining with isotype controls revealed no background staining (data not shown). Representative sections from one of three mice per group are shown.
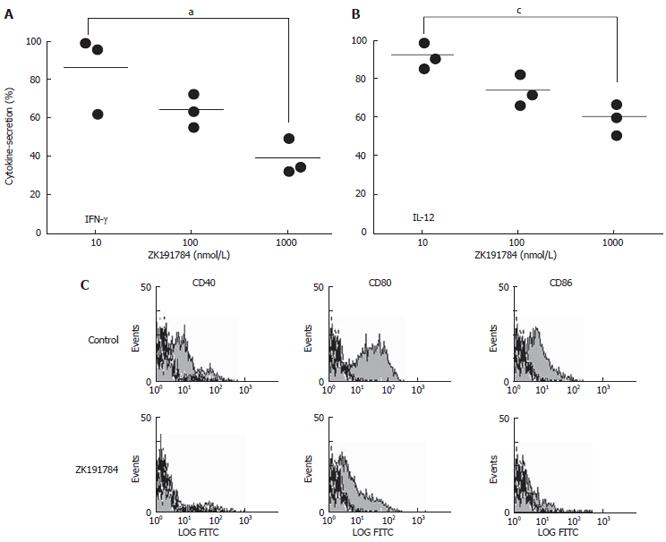
Figure 4 Effects of ZK191784 treatment on the secretion of cytokines and expression of costimulatory molecules by BM-DCs.
DCs were generated from bone marrow of mice and stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL) overnight in the presence of different concentrations of ZK191784 (10, 100 or 1000 nmol/L). Concentrations of the proinflammatory cytokines IFN-γ (A) and IL-12 (B) were measured within the supernatants by ELISA. aP < 0.05, cP < 0.05, data presented are representative of three independent experiments. BM-DCs were cultured in the presence of ZK191784 (1000 nmol/L) or vehicle, and were stimulated overnight with LPS. CD11c+ DCs were stained with FITC-conjugated mAbs for expression of the costimulatory molecules CD40, CD80 and CD86. Isotype controls are shown with dark lines, and positive staining is shown in grey (C).
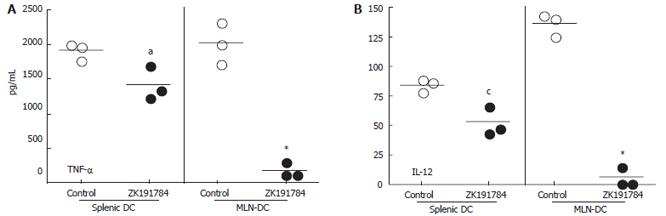
Figure 5 Effects of ZK191784 treatment on the secretion of cytokines by primary DCs derived from spleen and MLNs.
CD11c+ DCs were isolated from the spleen and MLNs of animals pretreated with ZK191784 or vehicle. Cells were stimulated overnight with CpG. Triplicate cultures were analyzed for each condition. Concentrations of the proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α (A) and IL-12 (B) were measured within supernatants by ELISA. aP < 0.05, cP < 0.05, data presented are representative of three independent experiments.
- Citation: Strauch UG, Obermeier F, Grunwald N, Dunger N, Rath HC, Schölmerich J, Steinmeyer A, Zügel U, Herfarth H. Calcitriol analog ZK191784 ameliorates acute and chronic dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis by modulation of intestinal dendritic cell numbers and phenotype. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(48): 6529-6537
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i48/6529.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i48.6529