Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Cardiol. Feb 26, 2017; 9(2): 92-108
Published online Feb 26, 2017. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v9.i2.92
Published online Feb 26, 2017. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v9.i2.92
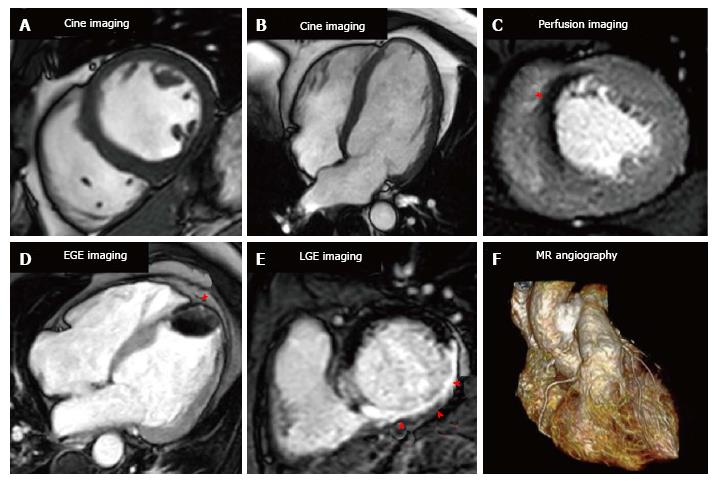
Figure 1 Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging techniques.
A and B show short axis and 4 chamber cine images respectively for anatomical and functional assessment; C shows stress perfusion with a septal perfusion defect (arrow); D shows early gadolinium enhancement imaging with a large apical thrombus (arrow); E is late gadolinium enhanced imaging with a transmural inferior infarction (arrows); F is 3D whole heart magnetic resonance angiography. LGE: Late gadolinium enhancement; EGE: Early gadolinium enhancement.
Figure 2 Cardiovascular magnetic resonance multi-parametric protocols for the investigation of suspected coronary artery disease.
A shows a typical multi-parametric cardiovascular magnetic resonance protocol for the investigation of stable coronary artery disease with adenosine stress perfusion; and B with incremental dose dobutamine stress.
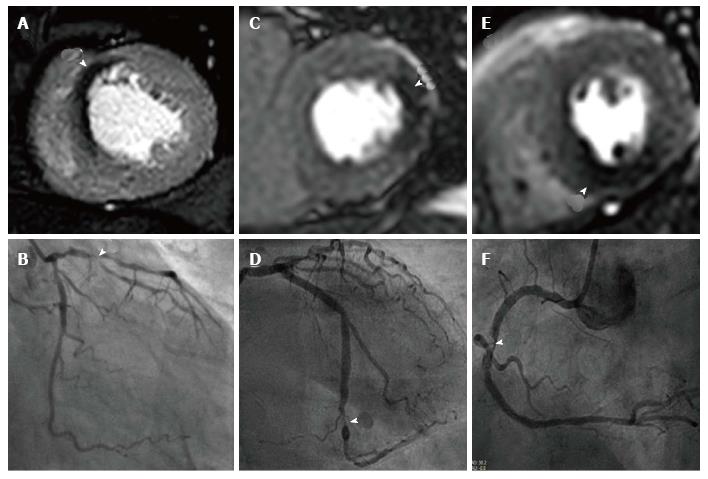
Figure 3 Cardiovascular magnetic resonance perfusion techniques.
A is a high spatial resolution k-t BLAST stress perfusion CMR study at 3.0T showing an antero-septal perfusion defect with corresponding left anterior descending lesion at angiography in B; C shows a transmural lateral perfusion defect at standard resolution at 1.5T with corresponding circumflex lesion in D; E shows a transmural inferior perfusion defect at standard resolution at 1.5T with corresponding right coronary artery lesion in F. BLAST: Broad-use linear acquisition speed-up technique; CMR: Cardiovascular magnetic resonance.
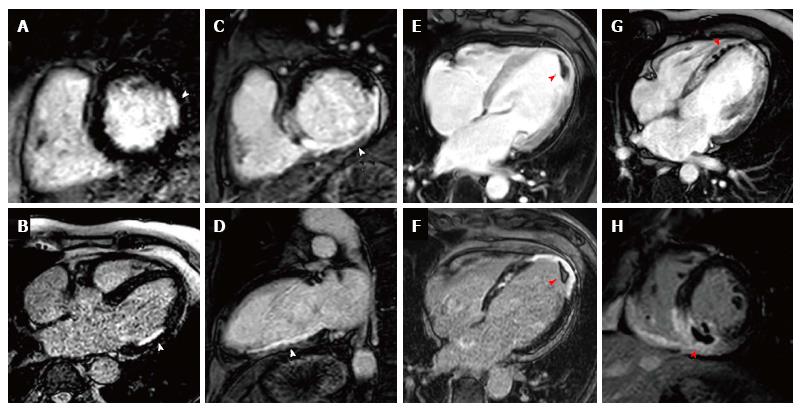
Figure 4 Early and late gadolinium enhancement.
A and B show a lateral sub-endocardial infarction on short axis and 4 chamber LGE respectively; C and D show a full thickness inferior infarction on LGE imaging on short axis and VLA respectively; E and F show EGE and LGE imaging respectively of a full thickness apical infarction with an apical thrombus appearing black (highlighted by red arrow); G shows an extensive acute antero-apical infarction with a core of microvascular obstruction visible within the hyperenhancement on EGE (red arrow); H shows an acute inferior wall infarction with MVO and extension into the right ventricle on LGE (red arrow) imaging. LGE: Late gadolinium enhancement; EGE: Early gadolinium enhancement; MVO: Mitral orifice.
- Citation: Foley JRJ, Plein S, Greenwood JP. Assessment of stable coronary artery disease by cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging: Current and emerging techniques. World J Cardiol 2017; 9(2): 92-108
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v9/i2/92.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v9.i2.92