Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2015; 21(10): 2883-2895
Published online Mar 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.2883
Published online Mar 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.2883
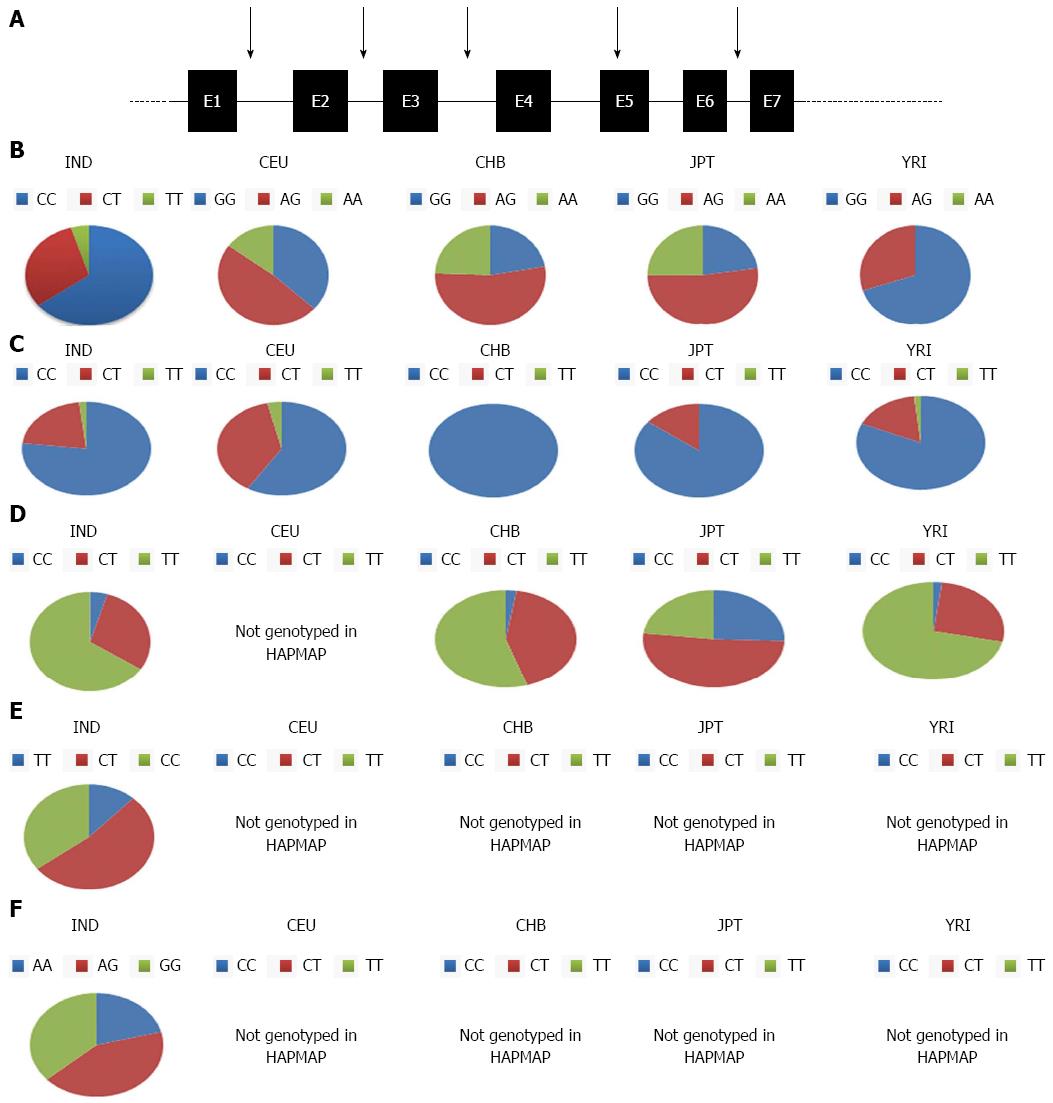
Figure 1 Genotypic allelic distribution of interleukin 1 beta.
IL-1B exonic polymorphisms investigated in Indian as well as the HAPMAP project have been illustrated (A), allelic distribution of (B) rs000025 (C) rs 1143629 (D) rs 3136558 (E) rs 1143634 (F) rs1143643 in Indian (IND), Caucasian (CEU), CEPH (Utah residents with ancestry from northern and western Europe), Yoruba in Ibadan, Nigeria (YRI) Japanese in Tokyo, Japan (JPT), Han Chinese in Beijing, China (CHB) are plotted as pie charts. This figure depicts the variation in allelic frequencies in different population. IL-1B: Interleukin 1 beta.
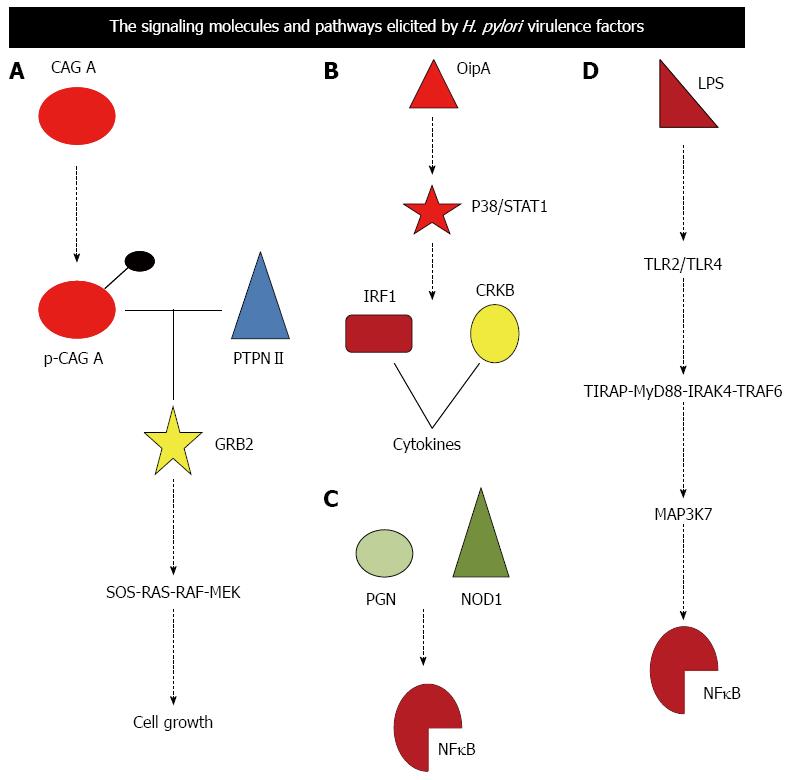
Figure 2 Signaling molecules and pathway elicited by Helicobacter pylori virulence factors are illustrated.
A-D: Depicts signaling pathway elicited by Cag A, OipA, PGN and LPS respectively. Cag A: Cytotoxin; PGN: Peptidoglycan; LPS: Lipopolysaccheride; PTPN11: Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 11; TLR: Toll like receptor; GRB2: Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; SOS: Son of sevenless homolog; NFkB: Nuclear factor kappa beta; TIRAP: Toll-interleukin 1 receptor domain containing adaptor protein; MYD88: Myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88; IRAK4: Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4; TRAF6: TNF receptor associated factor; MAP3K7: Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7; NOD1: Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 1.
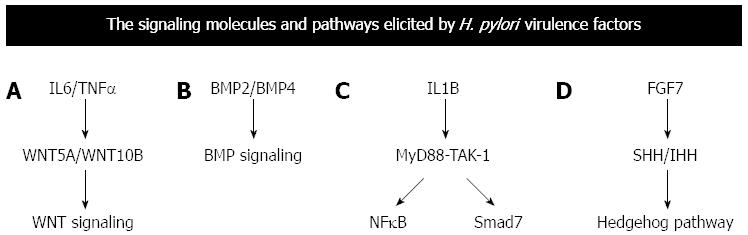
Figure 3 Signaling pathway elicited by the virulence factors elicits various transcription factors or cytokines that in turn influences other molecular cascades.
A-D: Depicts common molecular cascades elicited by cytokines or messengers. The cytokines or other molecular messengers are expressed due to signaling pathways described in Figure 2. IL-1B: Interleukin 1 beta; TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; BMP: Bone morphogenetic protein; WNT: Wingless-type; BMP: Bone morphogenetic protein; IHH: Indian hedgehog; MYD88: Myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88; NFκB: Nuclear factor kappa beta.
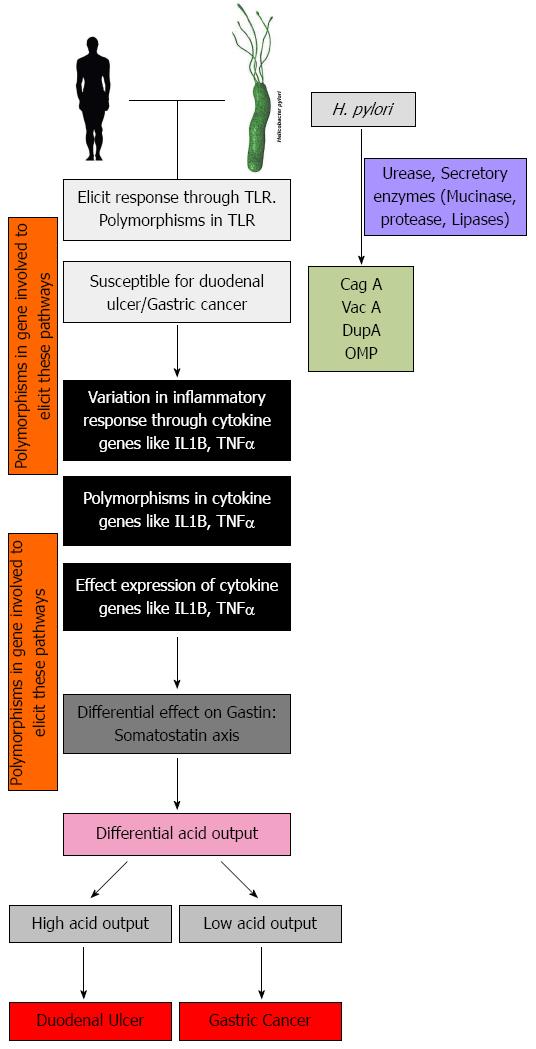
Figure 4 These model illustrates the different important host genes that are involved when Helicobacter pylori infection is established.
Variation in any one or several of these gene add to heterogeneity in disease manifestation. H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori; TLR: Toll like receptor; IL-1B: Interleukin 1 beta; TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor alpha.
-
Citation: Datta De D, Roychoudhury S. To be or not to be: The host genetic factor and beyond in
Helicobacter pylori mediated gastro-duodenal diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(10): 2883-2895 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i10/2883.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.2883