Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 26, 2020; 8(6): 1142-1149
Published online Mar 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i6.1142
Published online Mar 26, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i6.1142
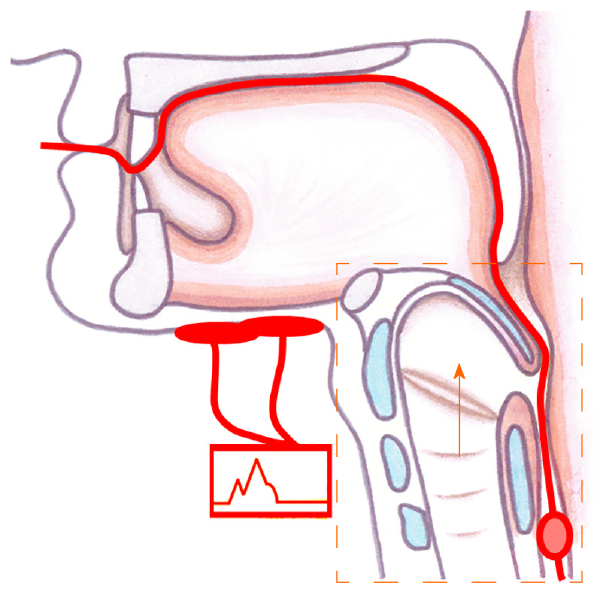
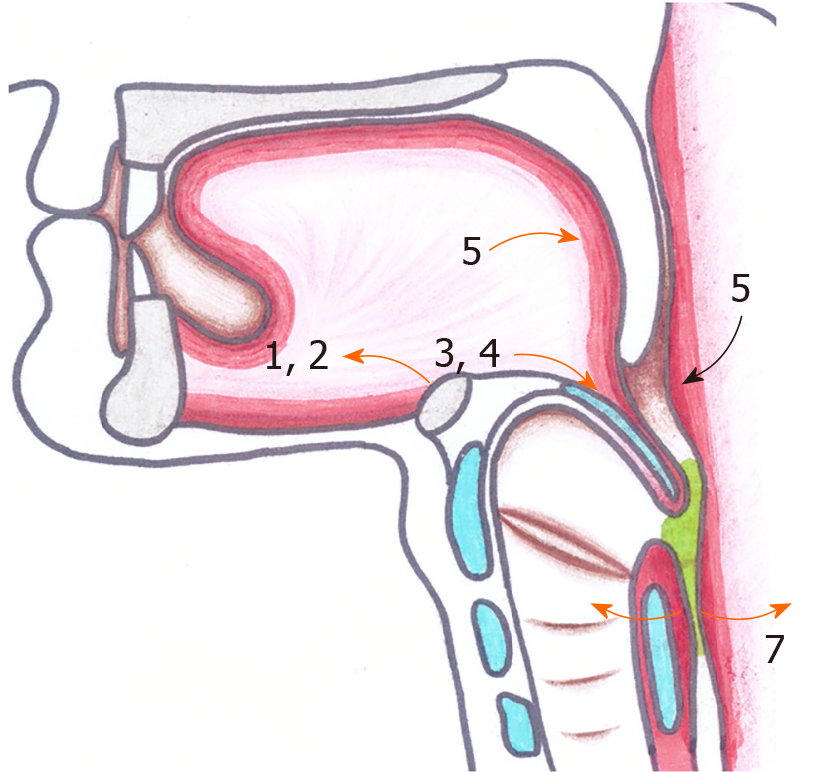
Figure 1 Placement of electrical stimulation and balloon dilatation in the hyoid-complex elevation and stimulation technique.
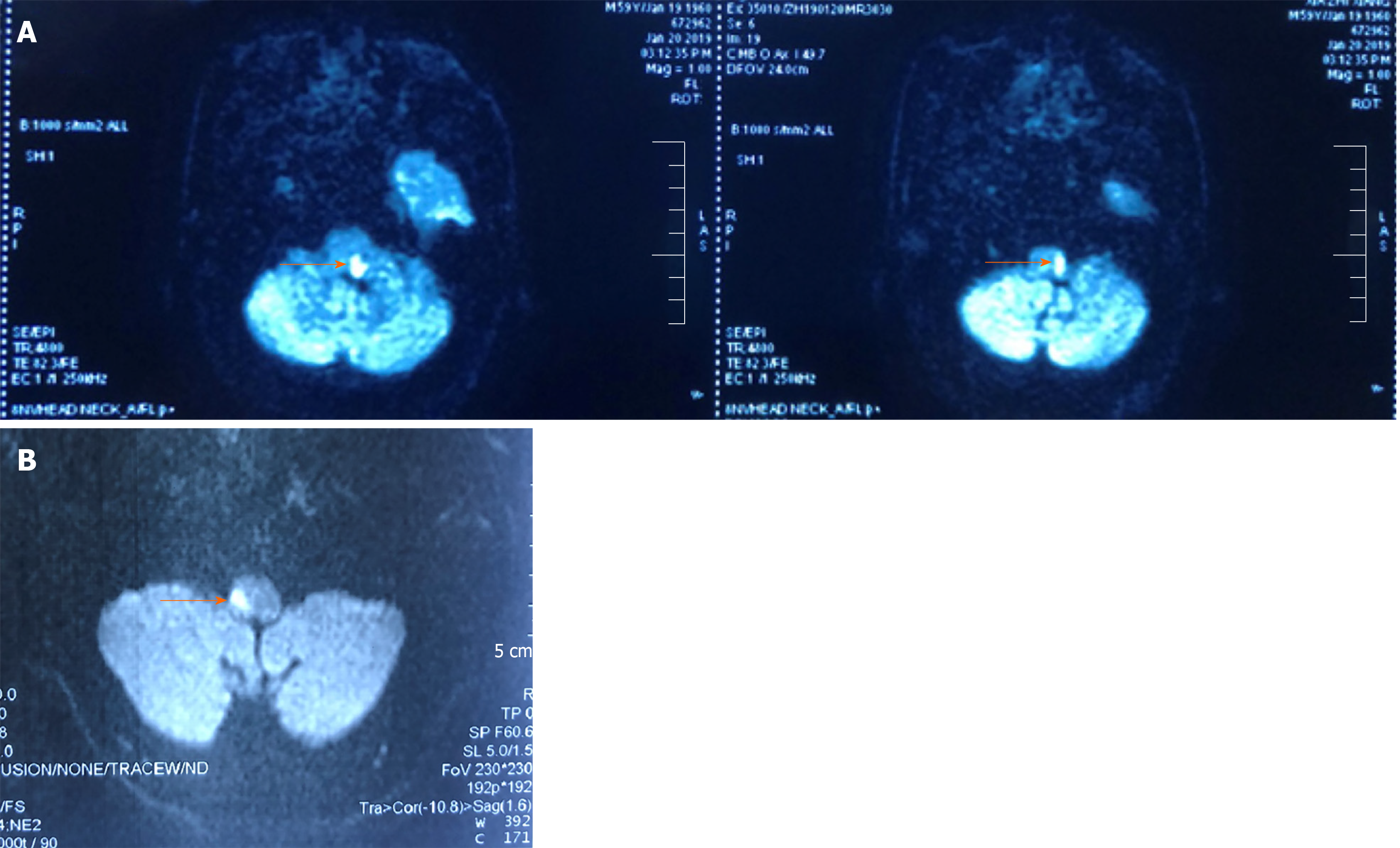
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging of the head.
A: Diffusion-weighted axial magnetic resonance image showing a left lateral medullary infarction in Case 1 (see arrow); B: Diffusion-weighted axial magnetic resonance image showing a right lateral medullary infarction in Case 2 (see arrow).
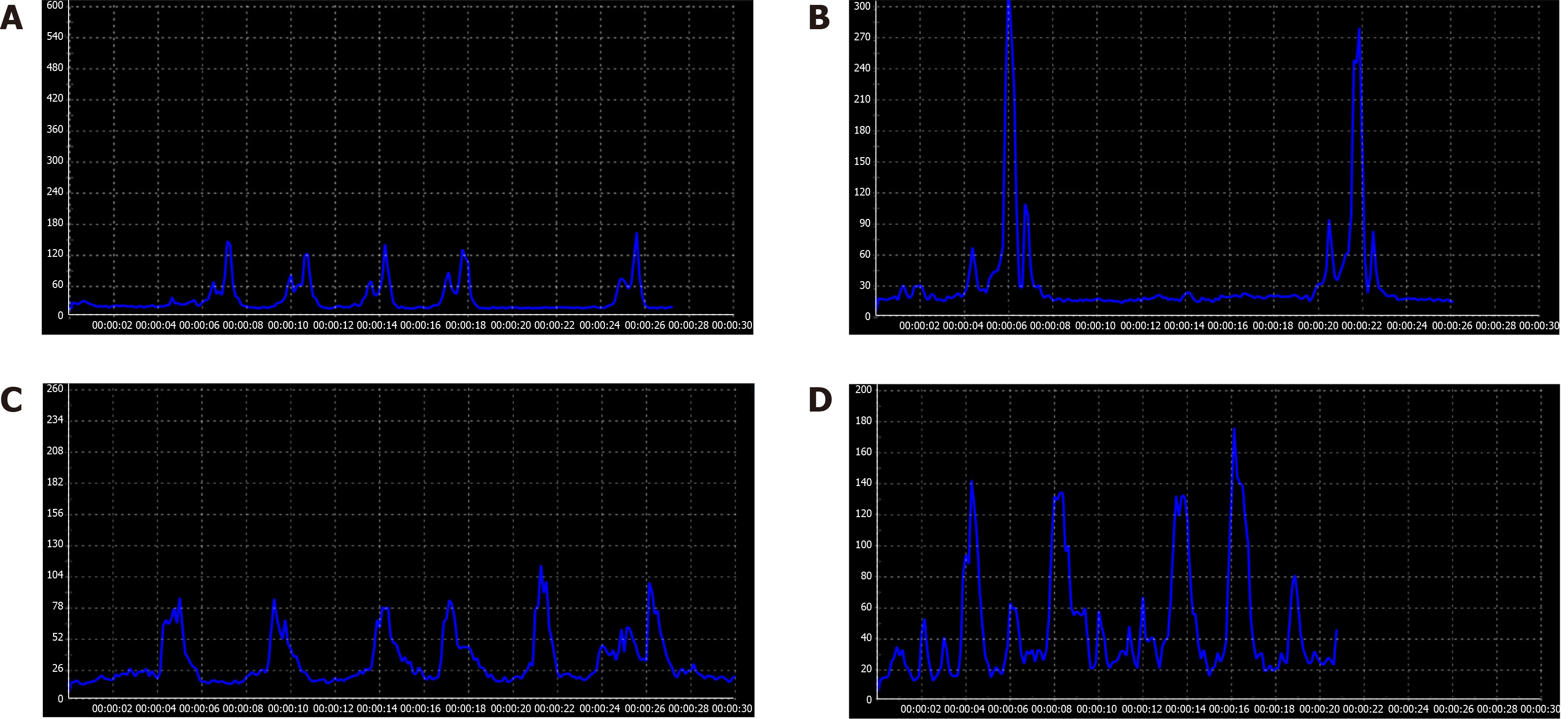
Figure 3 Surface electromyographic signal recording of two patients before and after hyoid-complex elevation and stimulation technique treatment.
A, B: For Case 1, the surface electromyographic signal recording peaked lower than 180 mV after 4-d traditional therapy (A) and higher than 270 mV after the hyoid-complex elevation and stimulation technique (B); C, D: For Case 2, the surface electromyographic signal recordings differed before (C) and after the hyoid-complex elevation and stimulation technique (D).
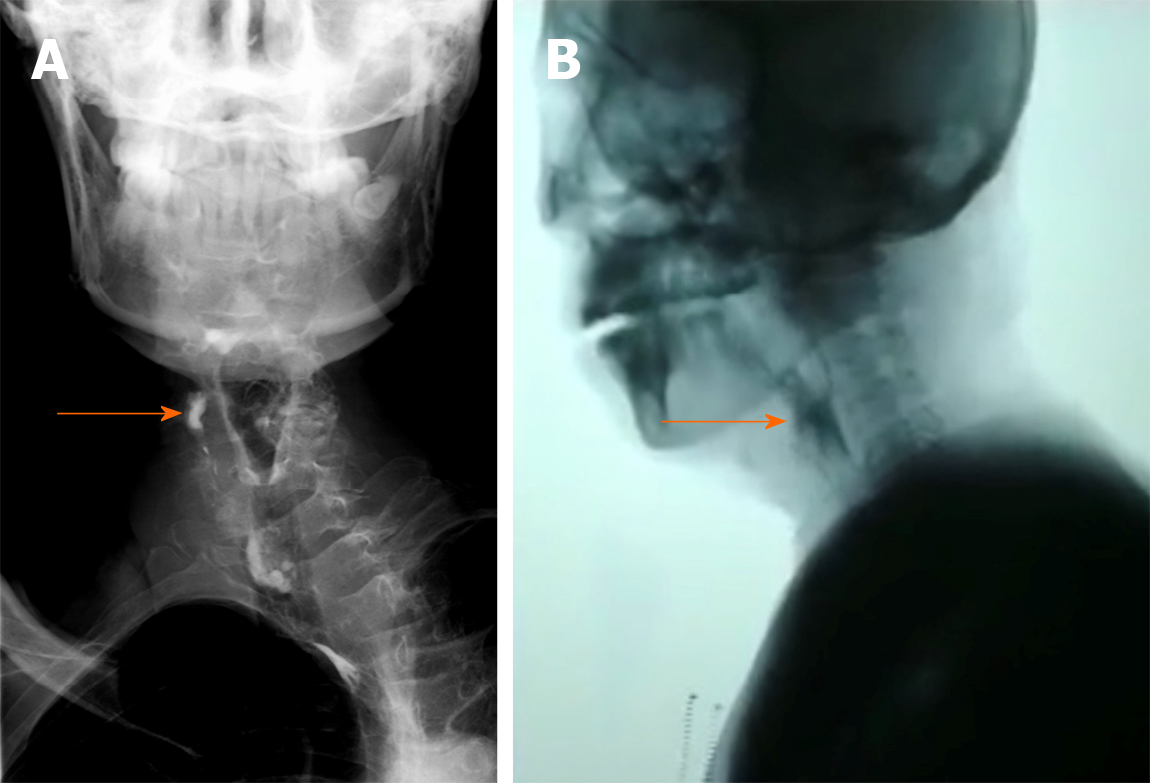
Figure 4 Initial video fluorography swallowing study showing pharyngeal residue (see arrow).
A: Case 1; B: Case 2.
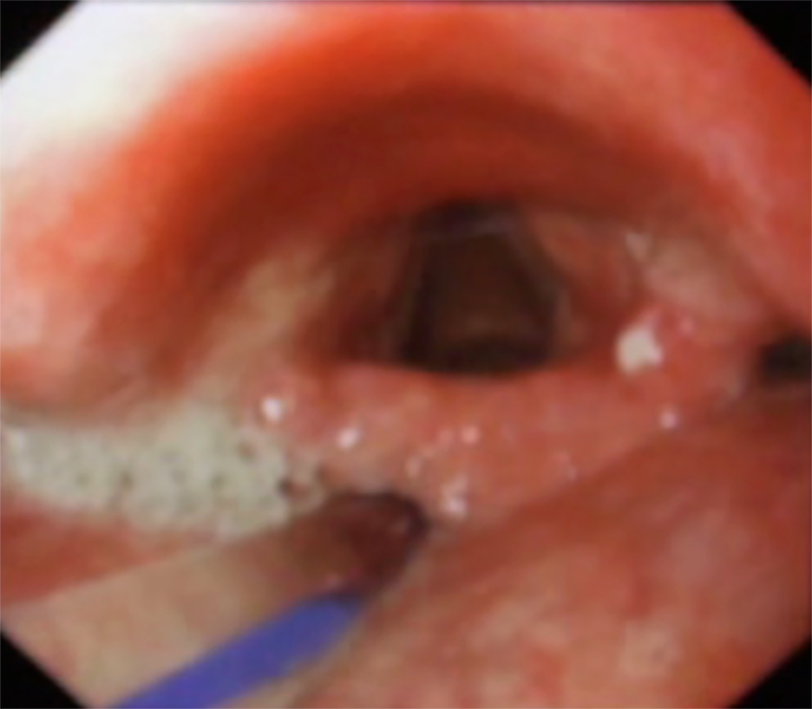
Figure 5 Initial fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing examination showing epiglottis insufficiency in Case 1.
Figure 6 The swallowing sequence of pharyngeal movement.
- Citation: Jiang YE, Lyu QQ, Lin F, You XT, Jiang ZL. Hyoid-complex elevation and stimulation technique restores swallowing function in patients with lateral medullary syndrome: Two case reports. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(6): 1142-1149
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i6/1142.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i6.1142