Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 6, 2020; 8(15): 3267-3279
Published online Aug 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i15.3267
Published online Aug 6, 2020. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i15.3267
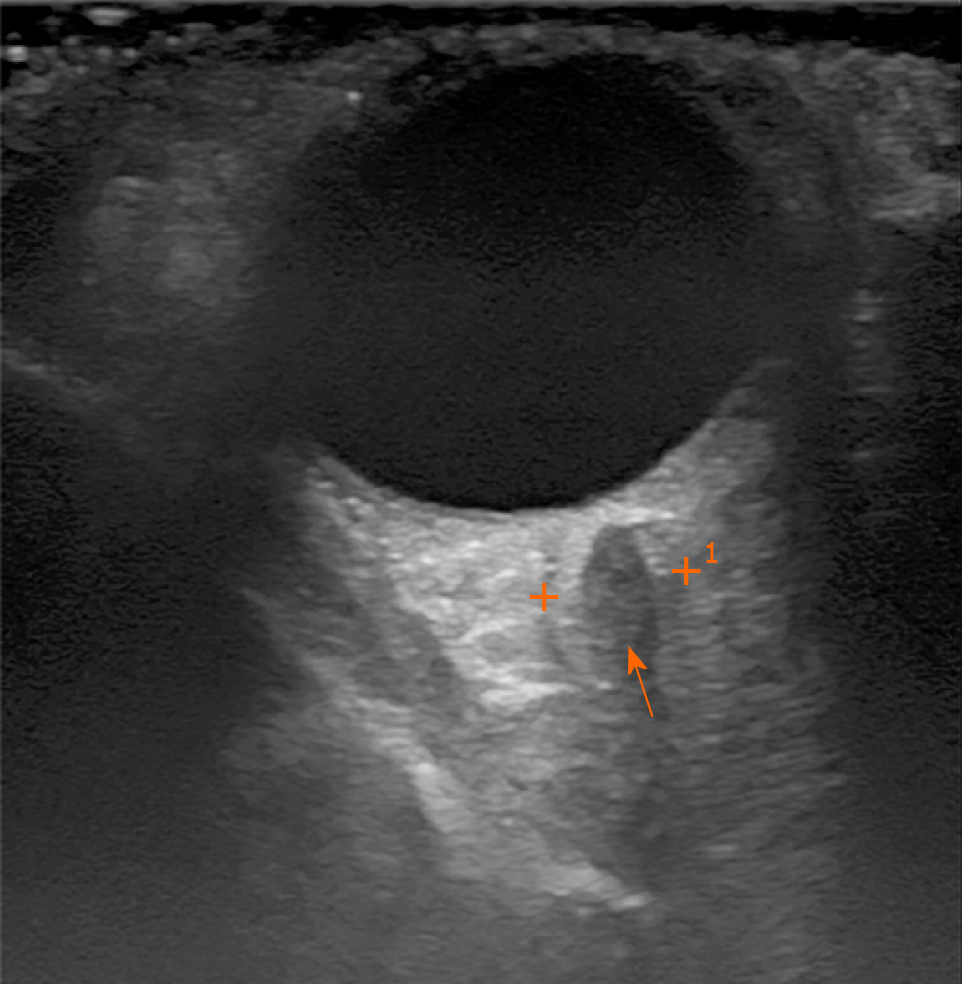
Figure 1 Orbital sonography.
Orbital sonography showing an irregular size heterogenic mass transorbitally on the left orbital cavity (arrow).
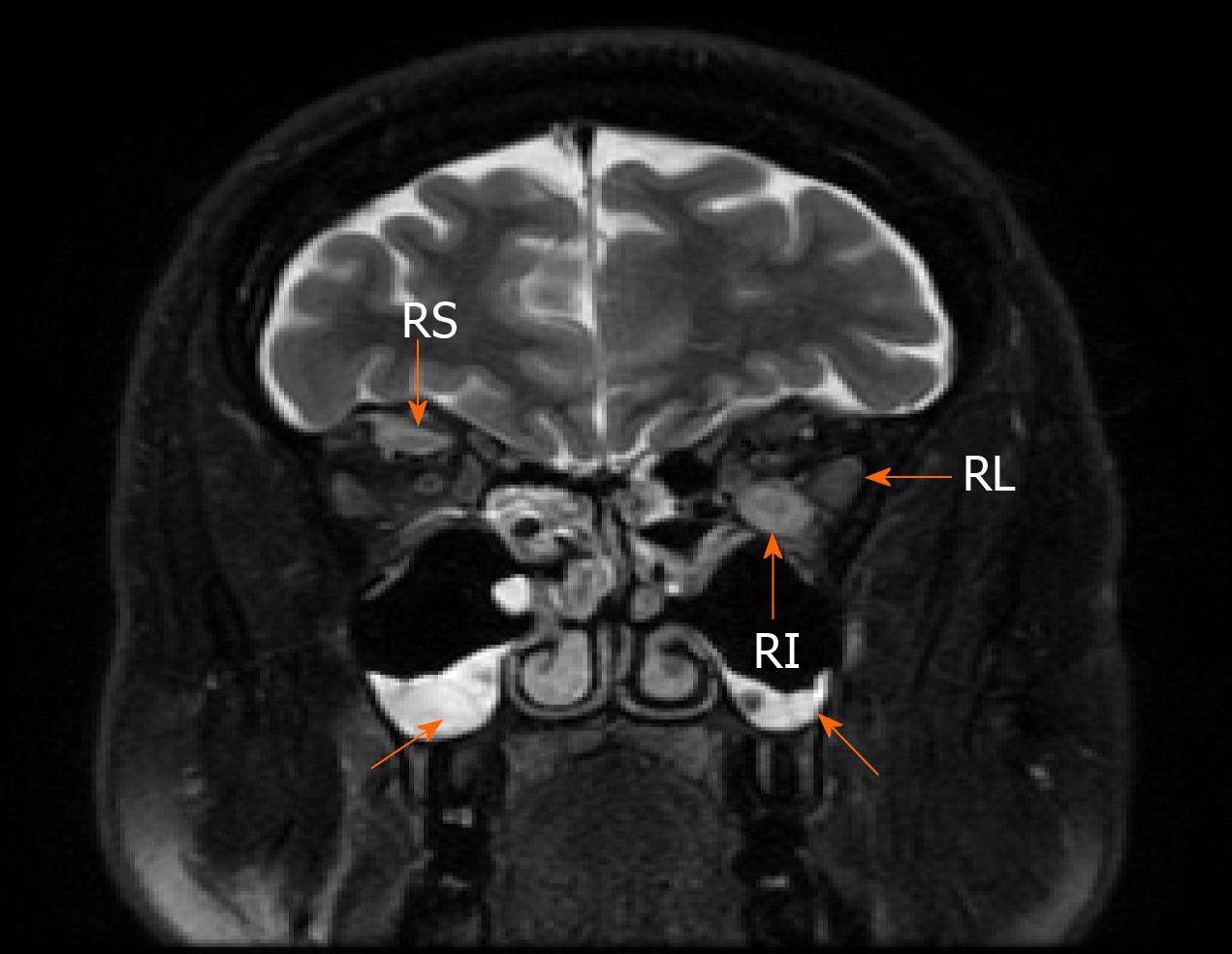
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging of the orbital cavity.
1.5-T Magnetic resonance imaging of the orbital cavity showing the swelling of the extra orbital muscles and sinusitis (T2-weighed image) (arrows): RL – musculus rectus lateralis sinister [5.5 mm (normal range 3.3 mm)], RI – musculus rectus inferior sinister [8 mm (normal range 4.6 mm)], RS – musculus rectus superior dexter [5 mm (normal range 4.6 mm)].
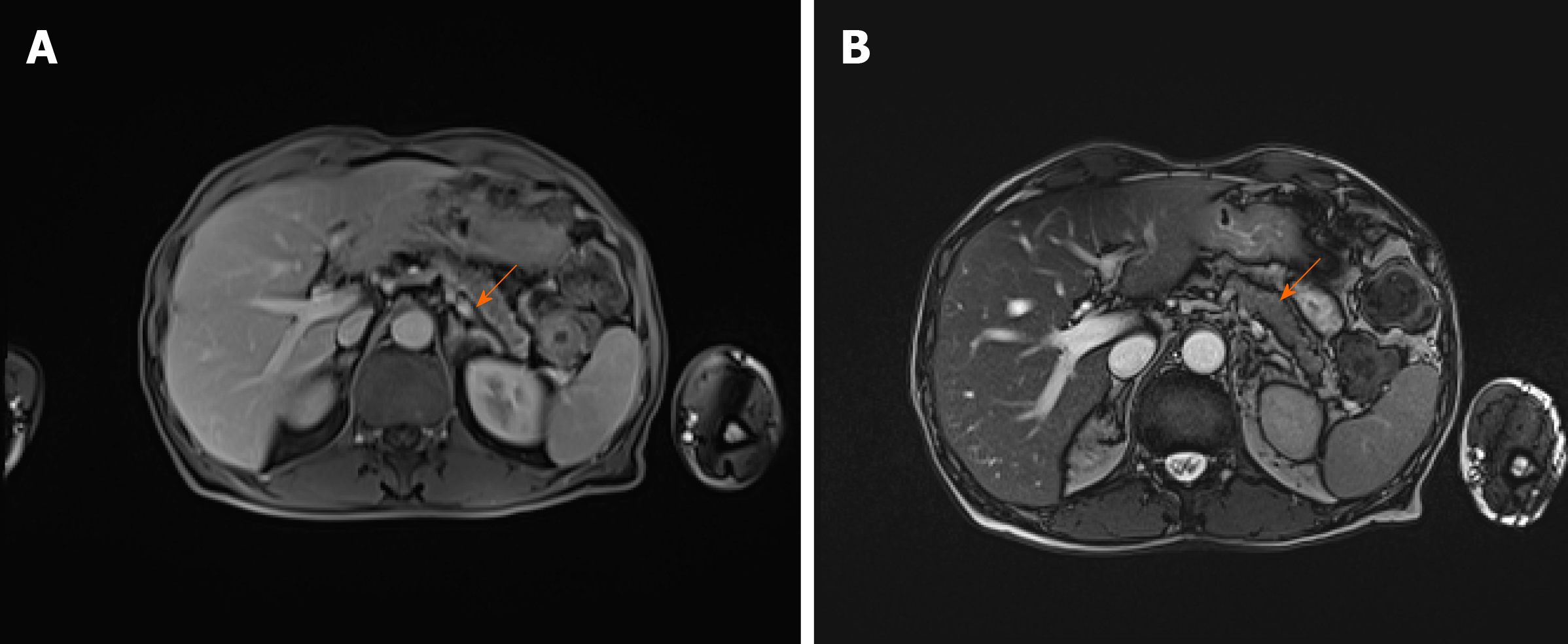
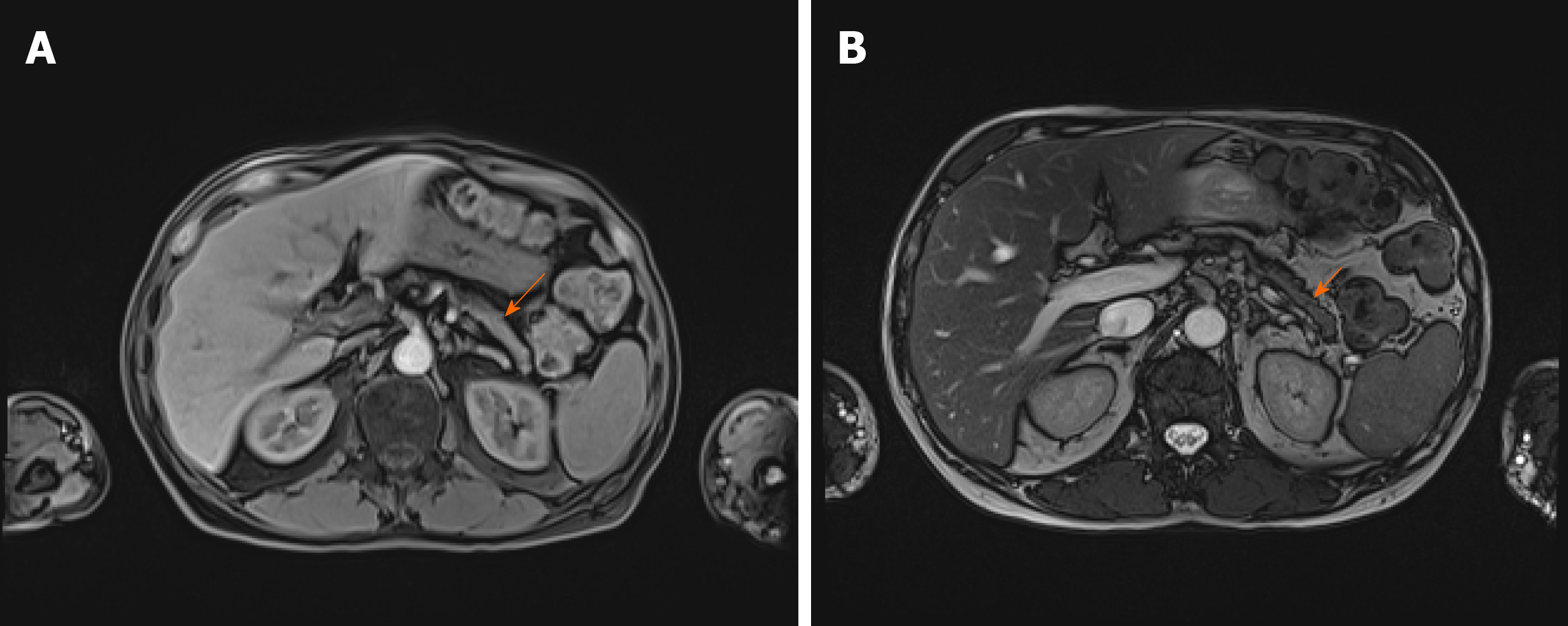
Figure 3 Abdominal magnetic resonance imaging before the treatment.
Abdominal magnetic resonance imaging before the treatment showing diffusely enlarged pancreas with a "halo" - peripancreatic rim with low attenuation (arrows) [T1-weighed (A) and T2-weighed (B) images].
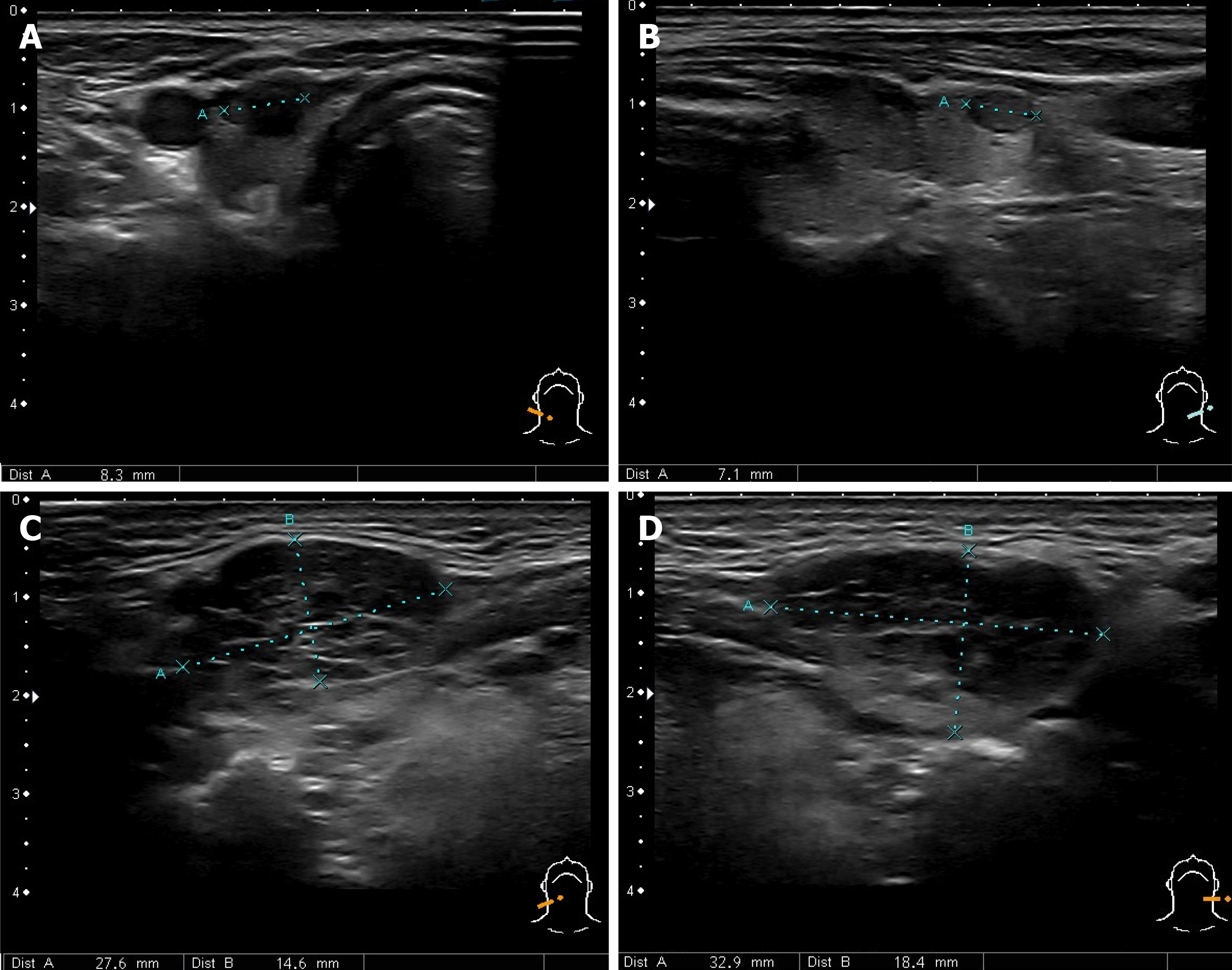
Figure 4 Ultrasound of the neck.
A and B: Ultrasound imaging showing thyroid gland nodules; C and D: Enlarged submandibular glands.
Figure 5 Abdominal magnetic resonance imaging after the treatment.
Abdominal magnetic resonance imaging one month after the treatment with prednisolone showing the notable pancreas size reduction and no presence of the peripancreatic rim (arrows) [T1-weighed (A) and T2-weighed (B) images].
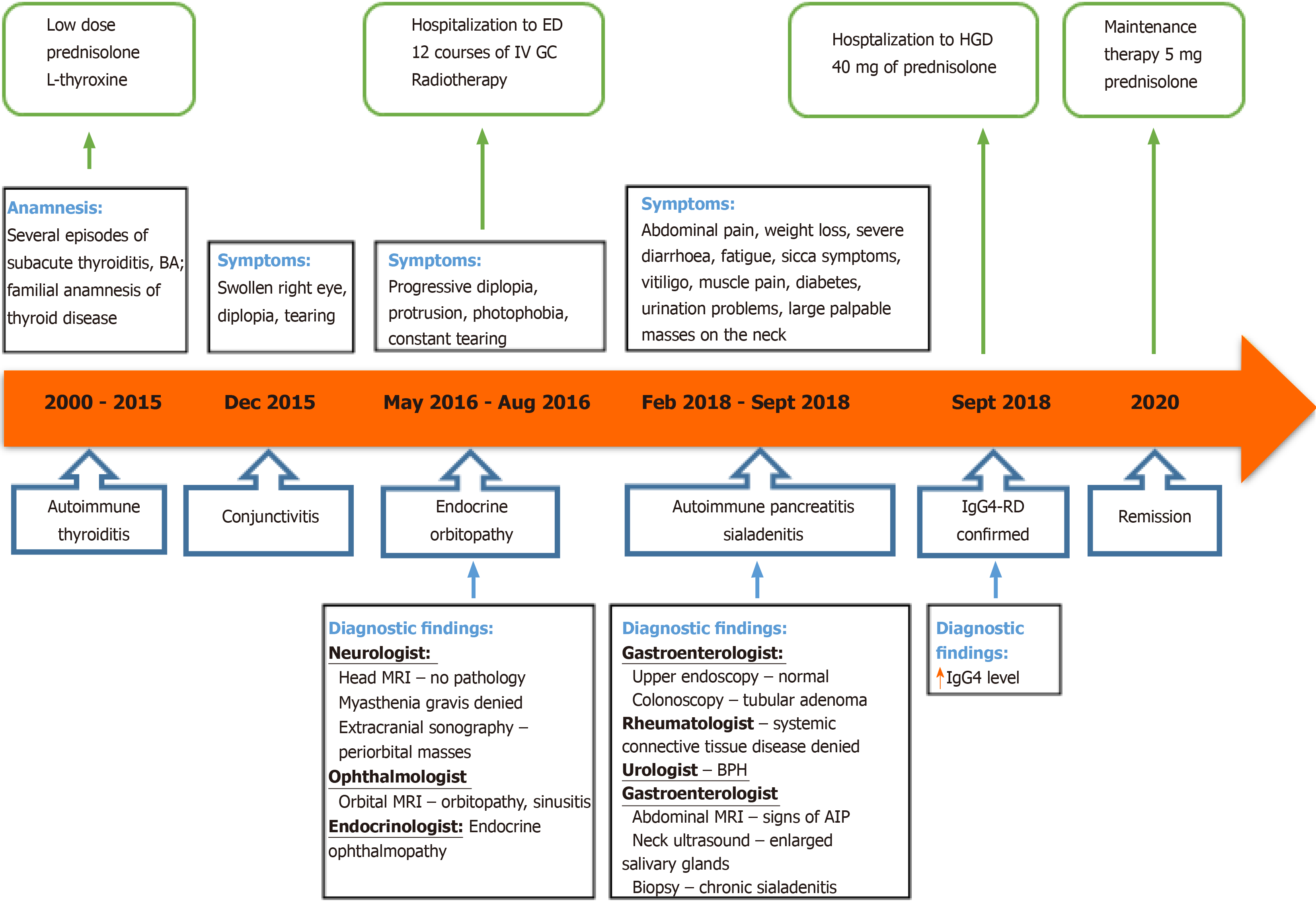
Figure 6 Case history timeline.
BA: Bronchial asthma; IV: Intravenous; GC: Glucocorticosteroids; ED: Endocrinology department; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; BPH: Benign prostatic hyperplasia; AIP: Autoimmune pancreatitis; HGD: Hepatology and gastroenterology department; IgG4–RD: Immunoglobulin G4 - related disease.
- Citation: Strainiene S, Sarlauskas L, Savlan I, Liakina V, Stundiene I, Valantinas J. Multi-organ IgG4-related disease continues to mislead clinicians: A case report and literature review. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8(15): 3267-3279
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v8/i15/3267.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v8.i15.3267