Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 6, 2019; 7(7): 819-829
Published online Apr 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i7.819
Published online Apr 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i7.819
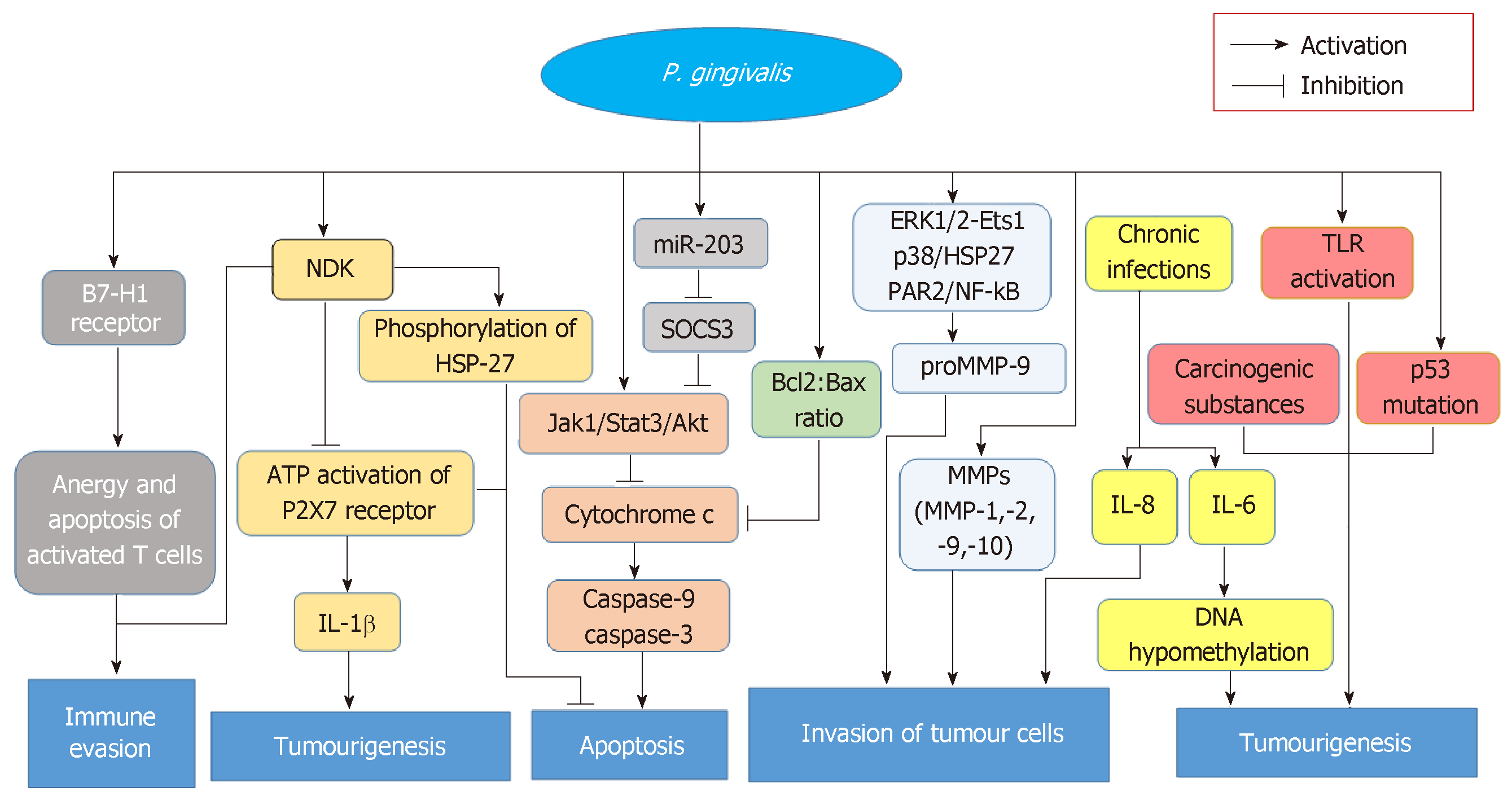
Figure 1 Possible mechanisms of cancers caused by Porphyromonas gingivalis.
When Porphyromonas gingivalis (P. gingivalis) infects the host, the expression of the B7-H1 receptor is activated, contributing to anergy and apoptosis of activated T cells, which eventually leads to immune evasion. Nucleoside diphosphate kinas (NDK) from P. gingivalis antagonizes ATP activation of purinergic receptor (P2X7) receptors and thus reduces the production of interleukin-1β and promotes tumourigenesis. NDK also phosphorylates heat shock protein 27 (HSP27); the phosphorylation of HSP27 and ATP activation of P2X7 receptor both inhibit apoptosis. The upregulation of miRNA-203 leads to inhibition of the negative regulator suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 (SOCS3), and SOCS3 can play a role of inhibiting JAK/STAT3 signalling, while the activation of Jak1/Akt/Stat3 signalling pathways and the increased Bcl2: Bax ratio induced by P. gingivalis infection both curtail the release of cytochrome c and block the activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3 that positively correlate with apoptosis. By activating the ERK1/2-Ets1, p38/HSP27, and PAR2/NF-kB signalling pathways, P. gingivalis induces the expression of proMMP-9, and the levels of MMPs also substantially increase after P. gingivalis infection; both consequently promote the invasion of tumour cells. P. gingivalis causes the host to be in a chronic inflammatory state. Inflammatory factors, such as IL-6 and IL-8, are subsequently released; the former causes DNA hypomethylation and tumourigenesis, and the latter inhibits the levels of MMPs and makes connections with the invasion of tumour cells. Additionally, the metabolism of carcinogenic substances and the activation of TRL are involved in tumourigenesis as well. NDK: Nucleoside diphosphate kinase; P2X7: Purinergic receptor; IL-1β: Interleukin-1β; HSP27: Heat shock protein 27; miR-203: miRNA-203; SOCS3: Suppressor of cytokine signaling-3; Jak1: Janus kinase 1; Stat3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3; Akt: Protein kinase B; Jak1/Stat3/Akt: Jak1/Stat3/Akt pathway; ERK1/2: Extracellular signal‐regulated kinase 1 and 2; Ets1: Ever shorter telomere 1; PAR2: Protease-activated receptor 2; NF-kB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; proMMP-9: Pro-matrix metalloproteinase-9; MMPs: Matrix metalloproteinase; IL-8/IL-6: Interleukin 8/interleukin 6; TLR: Toll-like receptor; BCL-2: B cell CLL/lymphoma-2.
- Citation: Zhou Y, Luo GH. Porphyromonas gingivalis and digestive system cancers. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(7): 819-829
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i7/819.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i7.819