Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 6, 2019; 7(3): 357-365
Published online Feb 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i3.357
Published online Feb 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i3.357
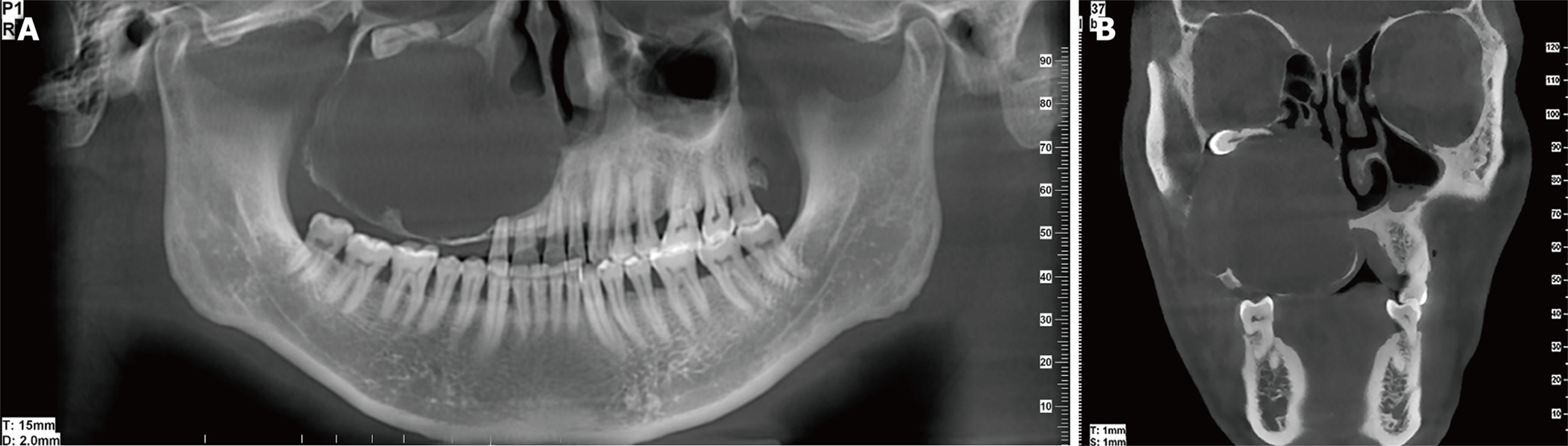
Figure 1 Cone-beam computed tomography images for case 1.
A: Orthopantomographic radiograph showing a round well-defined unilocular radiolucent lesion filling the right maxilla with tooth root resorption and impacted teeth; B: Cone-beam computed tomography image in the coronal plane showing extension of the tumor through the medial and anterior walls of the maxillary sinus.
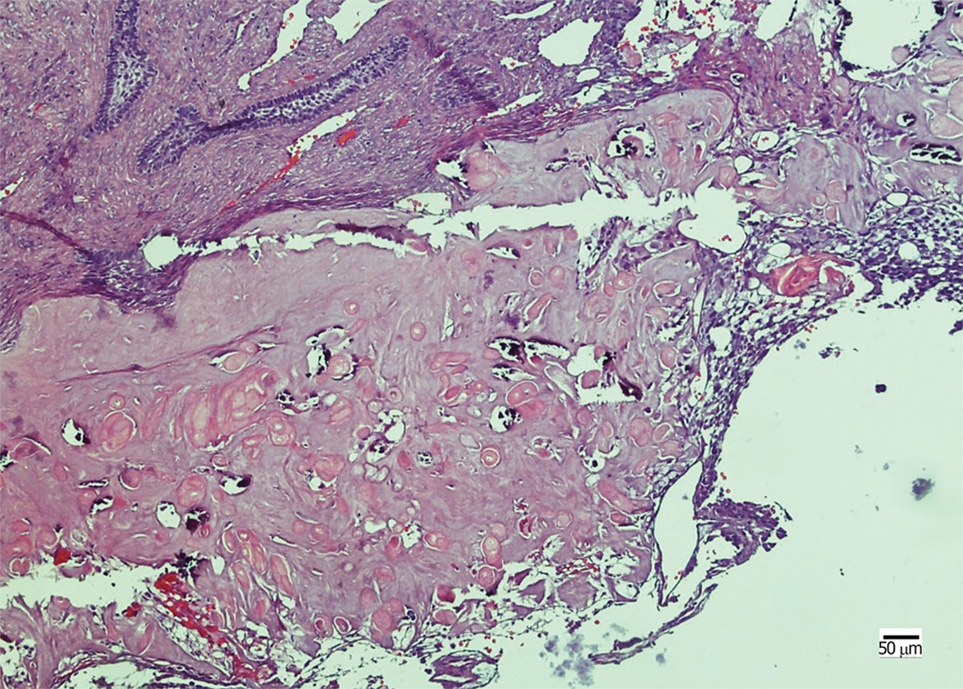
Figure 2 Histopathological examination in case 1.
The tumor nests comprise a well-defined basal layer of columnar cells and cells resembling the stellate reticulum forming an epithelial lining; masses of ghost cells are distributed along with calcification.
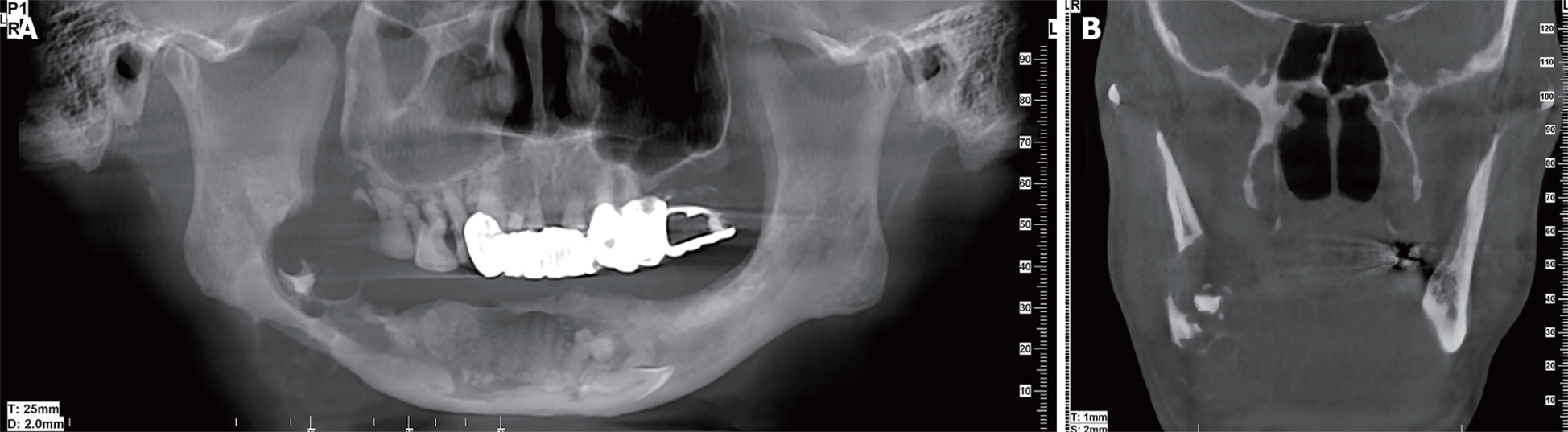
Figure 3 Cone-beam computed tomography images for case 2.
A: Orthopantomographic radiograph showing a multilocular cyst with ill-defined and extensive bony destructive lesion, with perforation of the buccal and lingual plates of the jaw and infiltration into the soft tissues; B: Cone-beam computed tomography image in the coronal plane showing extension of the tumor and perforation of the buccal and lingual plates of the mandible.
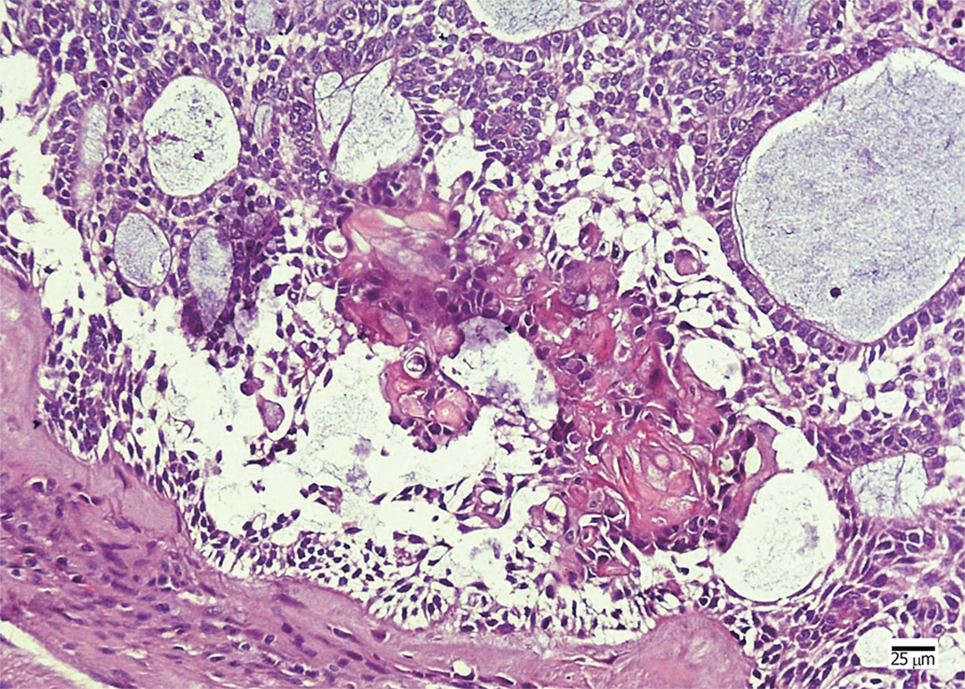
Figure 4 Histopathological examination in case 2.
The neoplastic tumor included an epithelial lining showing a basal layer of columnar cells arranged in a palisading pattern and an overlying layer of stratified cells resembling stellate reticulum, with clusters of ghost cells sporadically or intensively distributed in the tumor nests.
- Citation: Jia MQ, Jia J, Wang L, Zou HX. Ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma of the jaws: Report of two cases and a literature review. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(3): 357-365
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i3/357.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i3.357