Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 26, 2019; 7(16): 2322-2329
Published online Aug 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i16.2322
Published online Aug 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i16.2322
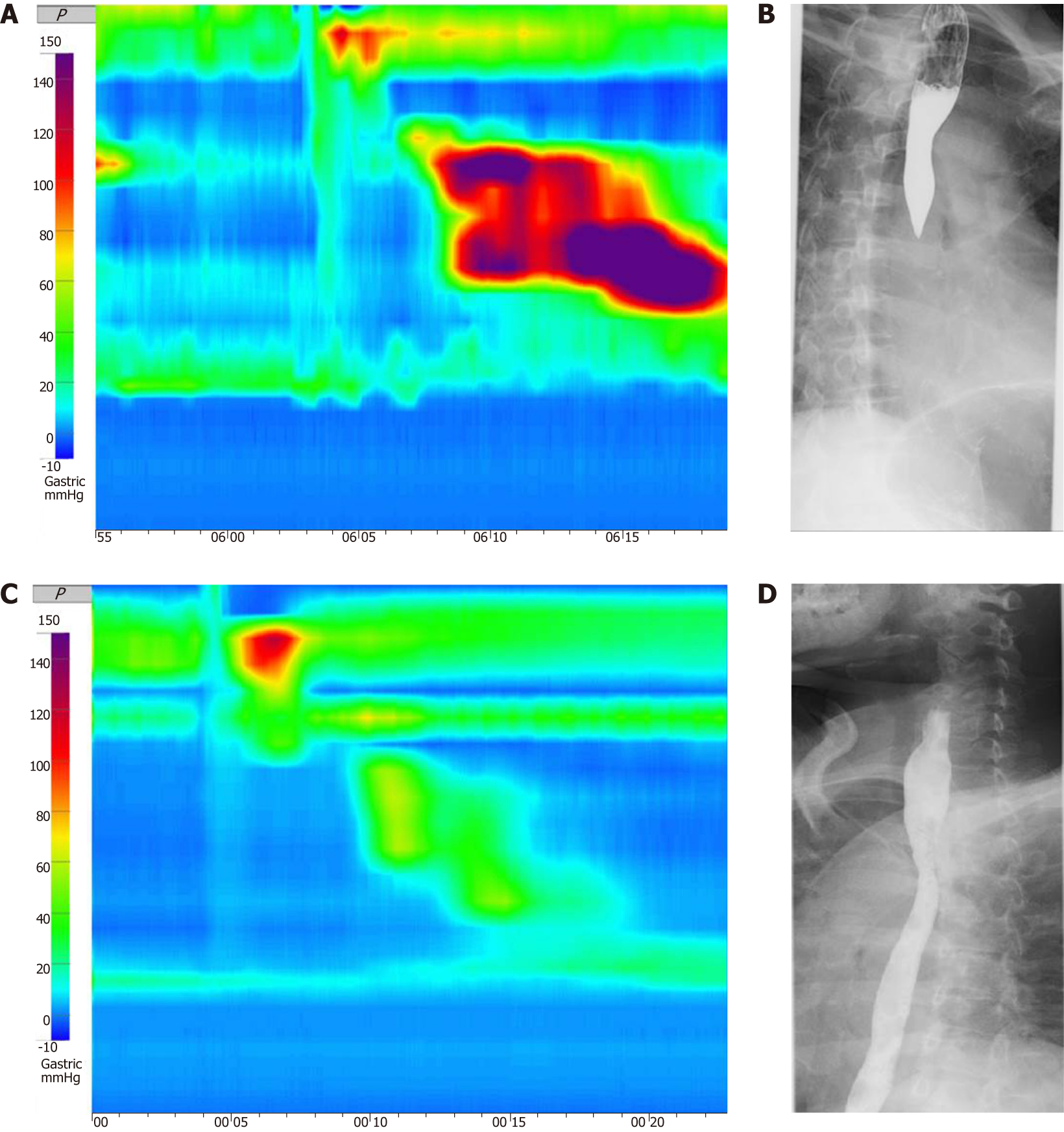
Figure 1 The examination of 53-year-old woman conducted before superficial circular muscle per-oral esophageal myotomy.
A: Pre-treatment high-resolution esophageal manometry (HRM) image depicted a jackhammer esophagus patient with distal contractile index over 8000 mmHg.s.cm; B-D: Barium radiography showed spasmodic contraction of the distal esophagus and a narrowing of the esophageal cavity (C) Post-treatment HRM revealed distal contractile integral of 980 mmHg.s.cm (D) Post-treatment esophagogram showed improved.
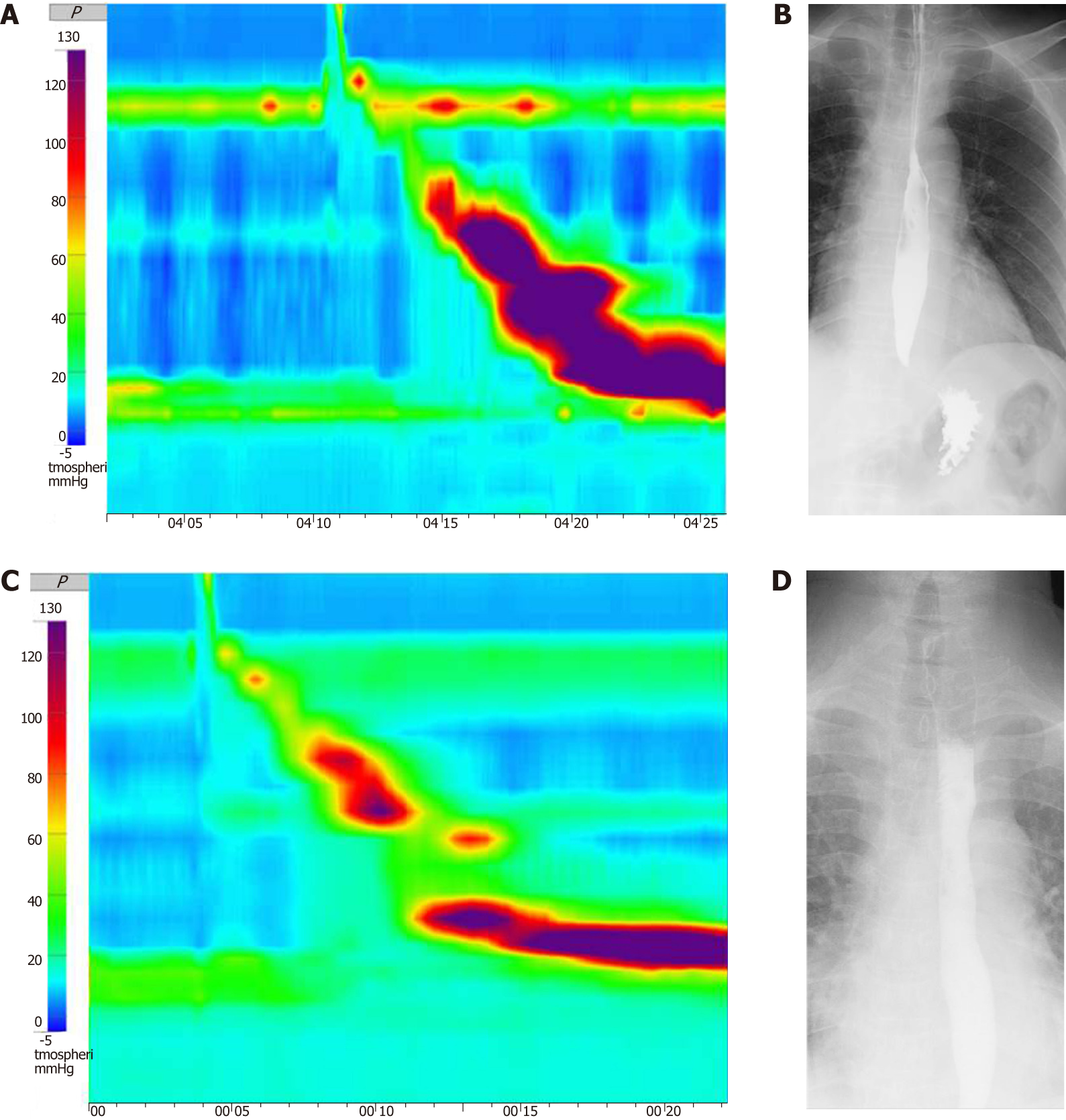
Figure 2 The examination of 47-year-old man conducted before superficial circular muscle per-oral esophageal myotomy.
A: Pre-treatment high-resolution manometry (HRM) showed high-amplitude distal esophageal contractions with a distal contractile integral (DCI) value > 8000 mmHg.s.cm for 8 of a total of 10 swallows and the highest DCI value was 13553 mmHg.s.cm; B-D: Pre-treatment esophagography showed spasmodic contraction of the distal esophagus (C) Post-treatment HRM revealed within normal range of DCI (D) Post-treatment esophagogram showed improved function of passage of esoaphagus.
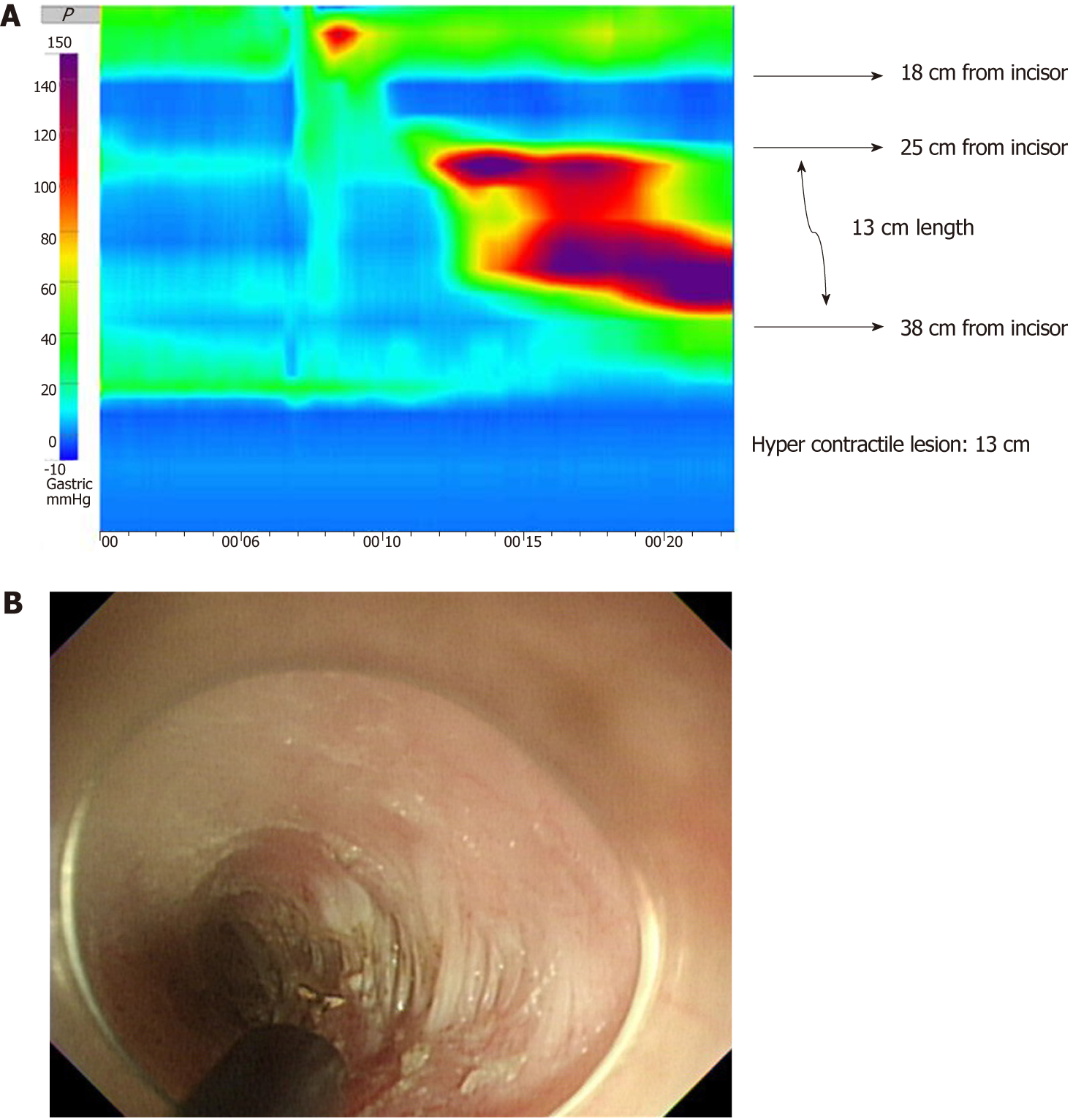
Figure 3 Procedures of high-resolution manometry guided superficial partial circular muscle myotomy.
A: We first detect the hypercontractile lesion through high-resolution manometry (HRM), and in this patients’ case, HRM showed high-amplitude distal esophageal contractions located 25-38 cm from the incisors according to the distance gauge of the pressure measuring tubes. B: Therefore, we performed superficial partial circular muscle myotomy of the esophageal muscle on the right side, (B) Superficial partial circular muscle myotomy during POEM. Remnant circular muscle.
- Citation: Choi YI, Kim KO, Park DK, Chung JW, Kim YJ, Kwon KA. Clinical outcomes and safety of high-resolution manometry guided superficial partial circular muscle myotomy in per-oral endoscopic myotomy for Jackhammer esophagus: Two cases report. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(16): 2322-2329
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i16/2322.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i16.2322