Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 26, 2018; 6(16): 1194-1198
Published online Dec 26, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i16.1194
Published online Dec 26, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i16.1194
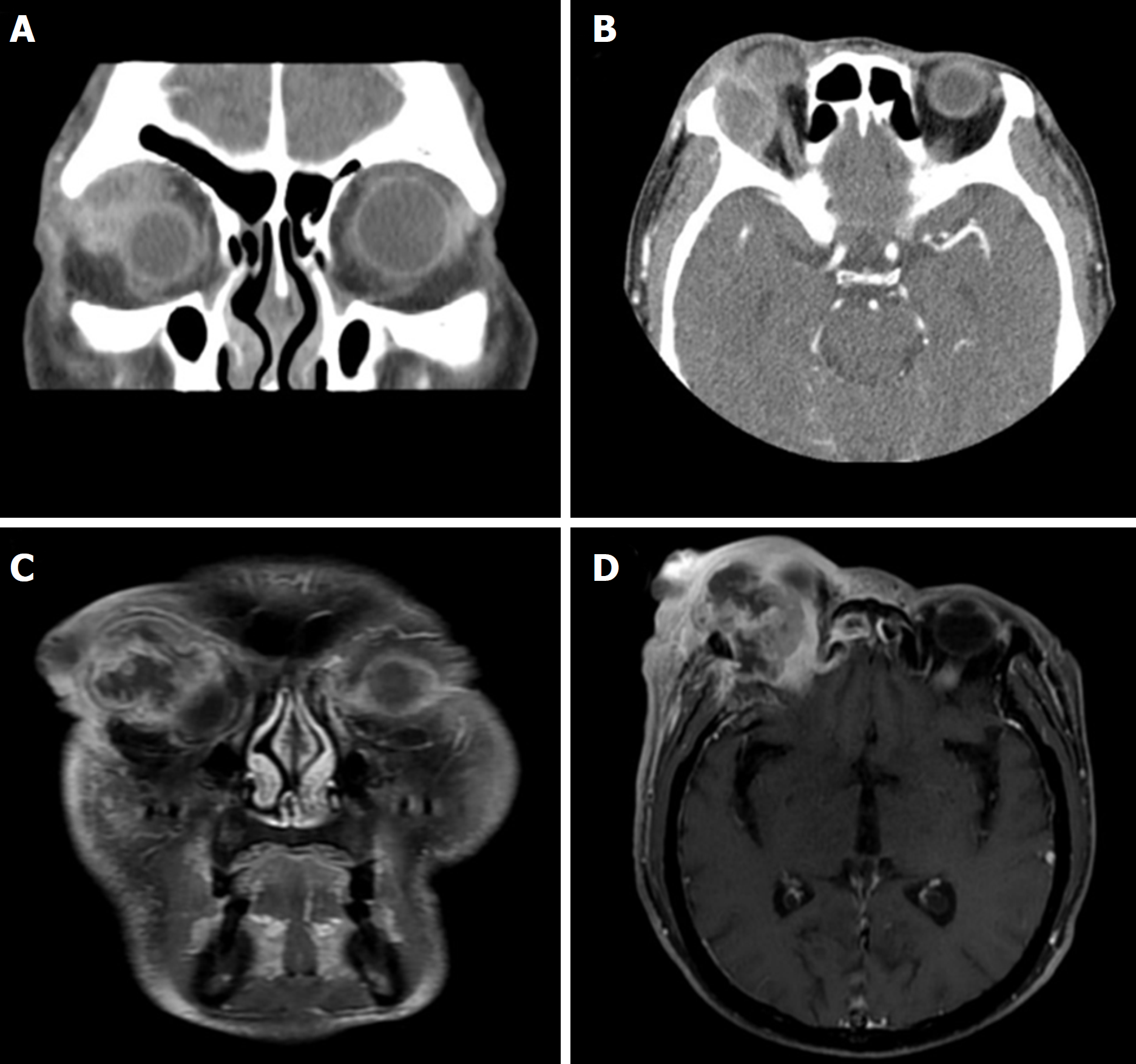
Figure 1 Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging images of the orbit.
A, B: Initial coronal (A) and axial (B) orbital computed tomography scans show enhanced mass at the superotemporal orbit of the extraconal space; C, D: Three months after initial diagnosis, coronal (C) and axial (D) orbital magnetic resonance scans show enhanced mass at the superotemporal orbit of the extraconal space. The mass compress right eyeball and protrude to intracranial cavity.
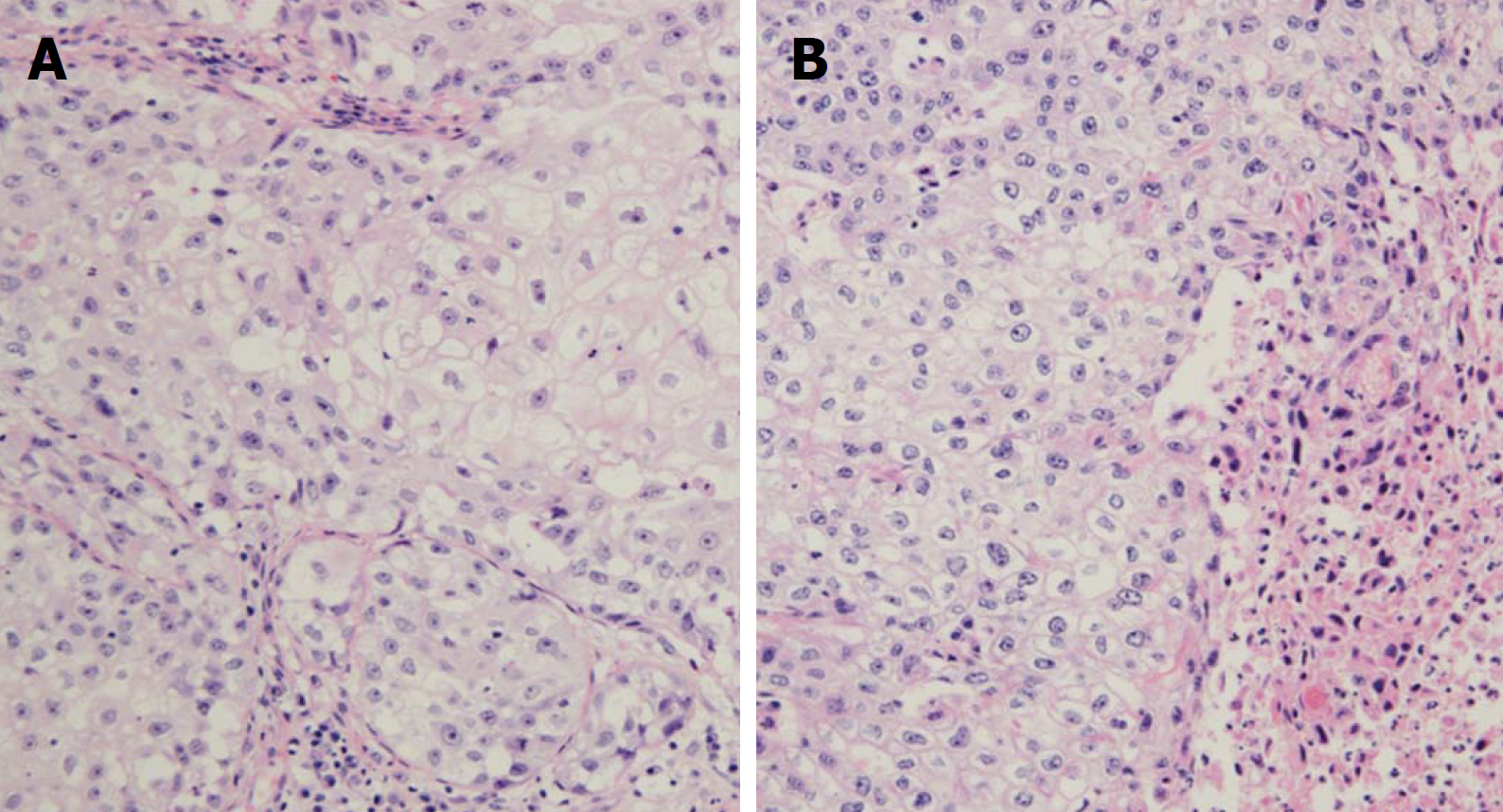
Figure 2 Microscopic view of the biopsied and resected specimen.
A: Histologic finding of the right orbital biopsy specimen shows infiltration of undifferentiated malignant cells suggesting squamous cell carcinoma; B: Histological finding of the surgical specimen shows large neoplastic cells with vacuolated cytoplasm mixed with squamous and sarcomatoid differentiation. H and E, × 200.
- Citation: Park H, Choi SG. Primary sebaceous carcinoma of lacrimal gland: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2018; 6(16): 1194-1198
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v6/i16/1194.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v6.i16.1194