Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 16, 2023; 11(29): 7136-7143
Published online Oct 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i29.7136
Published online Oct 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i29.7136
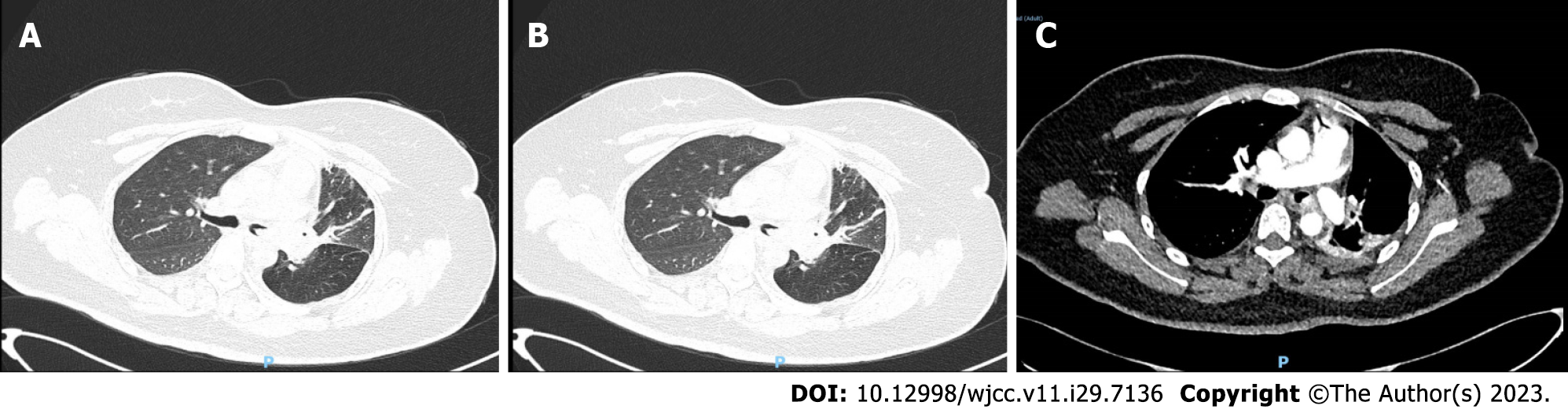
Figure 1 Preoperative chest computed tomography images.
A: Lung window; B: Mediastinal window; C: Enhanced computed tomography. The nodule of the left main trachea is seen, with obvious uniform enhancement.
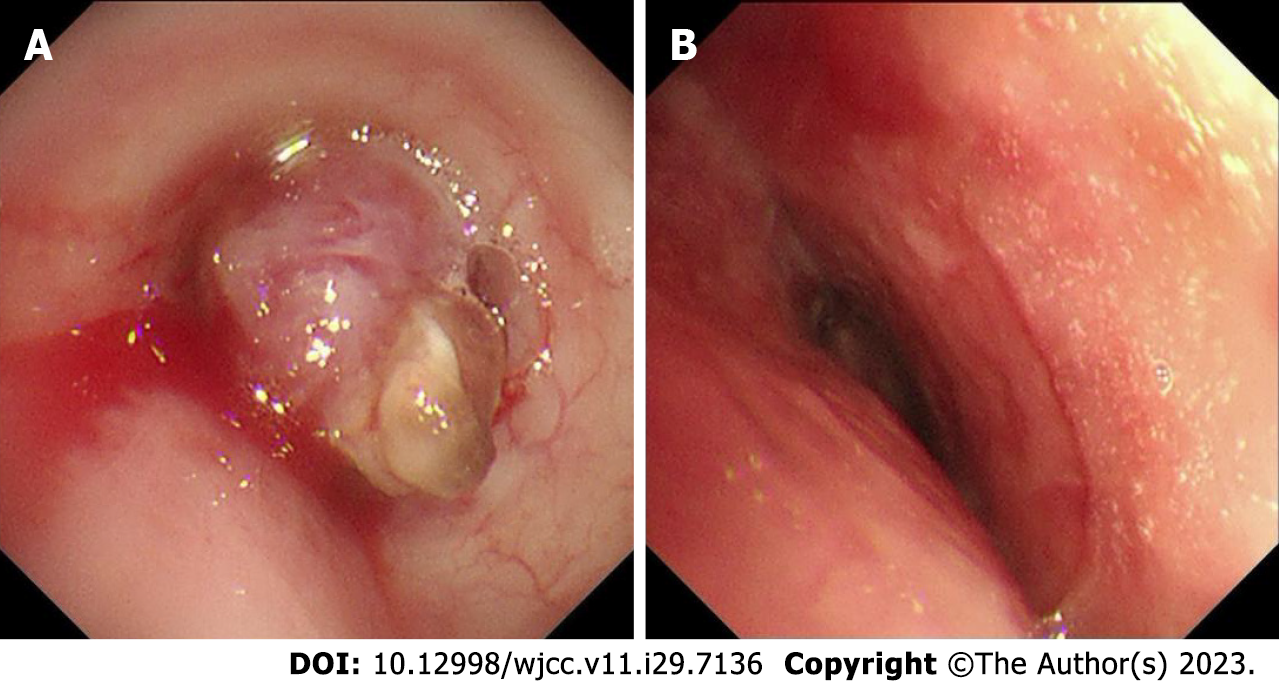
Figure 2 Electronic bronchoscopy.
A: Preoperative bronchoscopy Showing that a spherical lesion could be seen in the main bronchus 1.5 cm away from the protuberance; B: Postoperative bronchoscopy showing that the lumen was unobstructed.
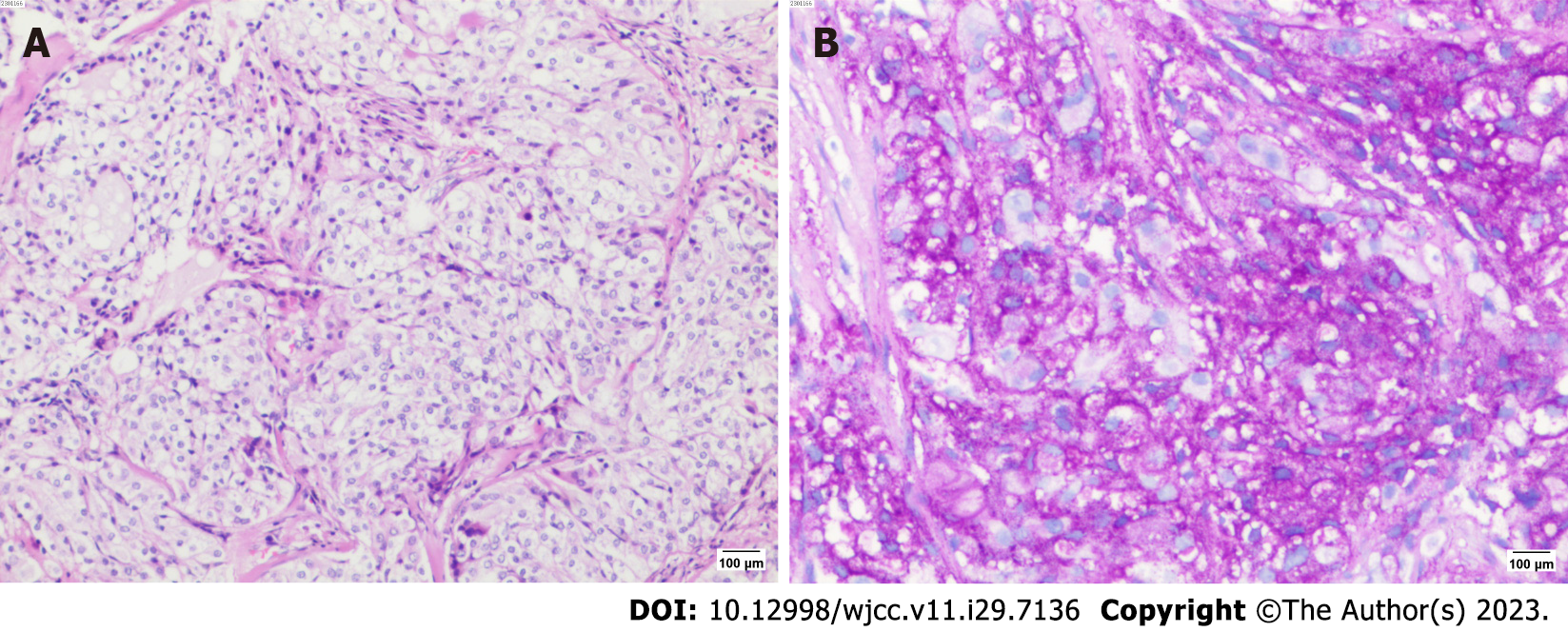
Figure 3 Pathological staining.
A: HE staining (10 × 10); B: PAS staining (+) (10 × 10).
Figure 4 Immunohistochemical results.
A: CD117 (+) (10 × 20); B: Carcinoembryonic antigen (+) (10 × 20); C: Cytokerain (+) (10 × 20); D: CK5/6 (+) (10 × 20); E: CK7 (+) (10 × 20); F: CK-H (+) (10 × 20); G: Ki67 (+) (10 × 20); H: P40 (+) (10 × 20); I: P63 (+) (10 × 20).
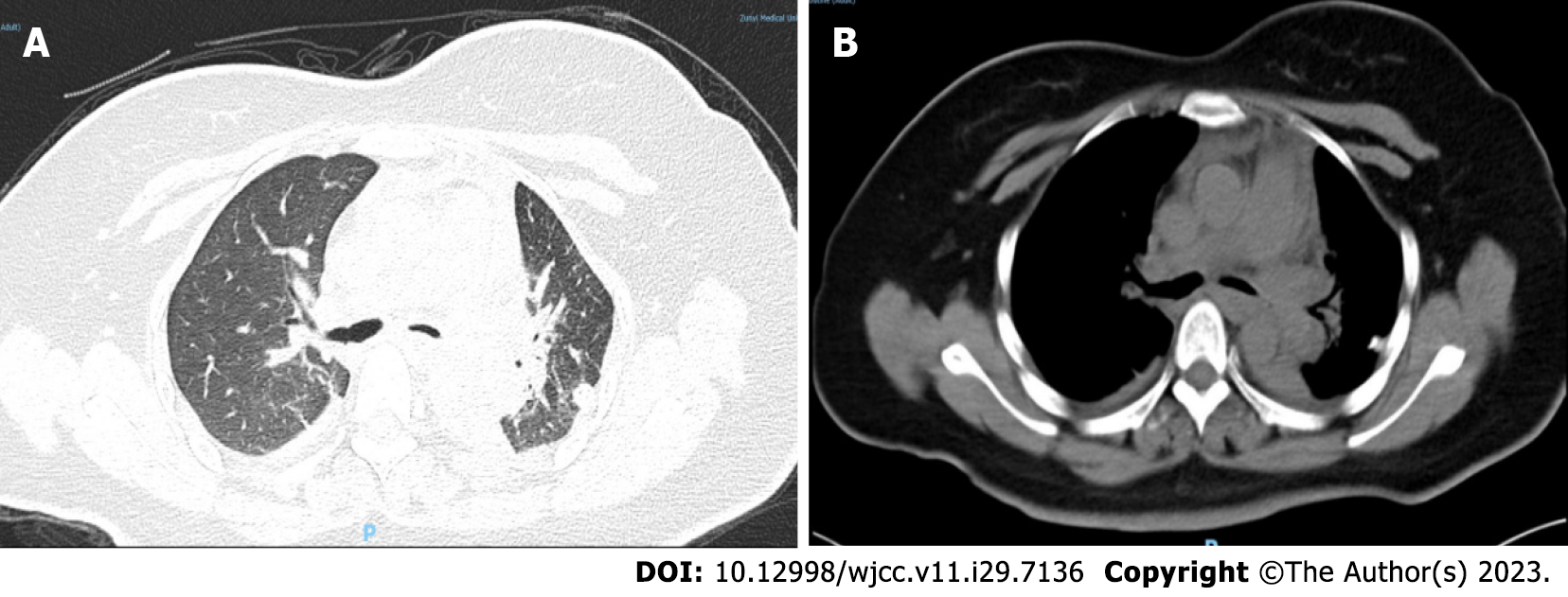
Figure 5 Postoperative chest computed tomography images.
The left main trachea is unobstructed. A: Lung window; B: Mediastinal window.
- Citation: Xie WX, Liu R, Li Z, Zhou PL, Duan LN, Fu DD. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the lung with hemoptysis as initial symptom: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(29): 7136-7143
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i29/7136.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i29.7136