Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 6, 2022; 10(31): 11630-11637
Published online Nov 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i31.11630
Published online Nov 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i31.11630
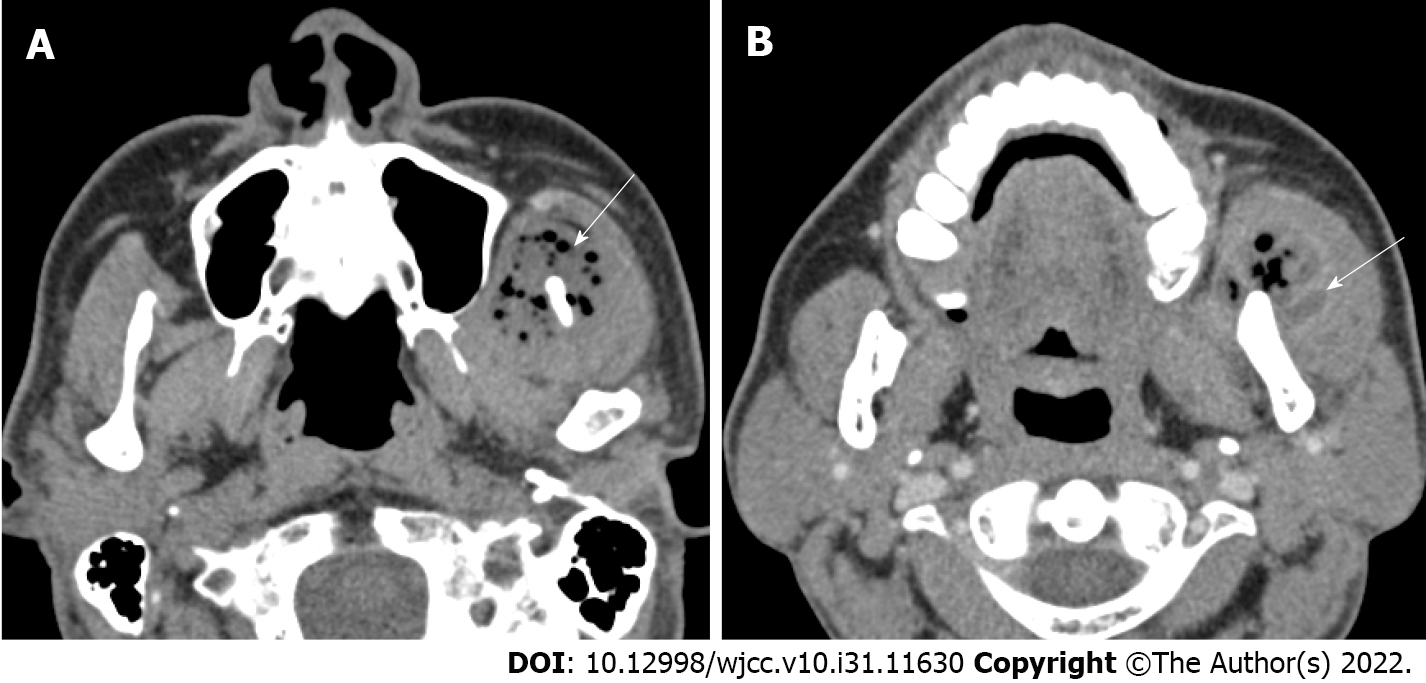
Figure 1 Preoperative computed tomographic imaging.
A: Axial computed tomography (CT) showing multiple soft tissue abscesses with air bubbles (white arrow); B: In the enhanced phase, axial CT showing a polymorphic wall with enhancing lesions in the muscle (white arrow).
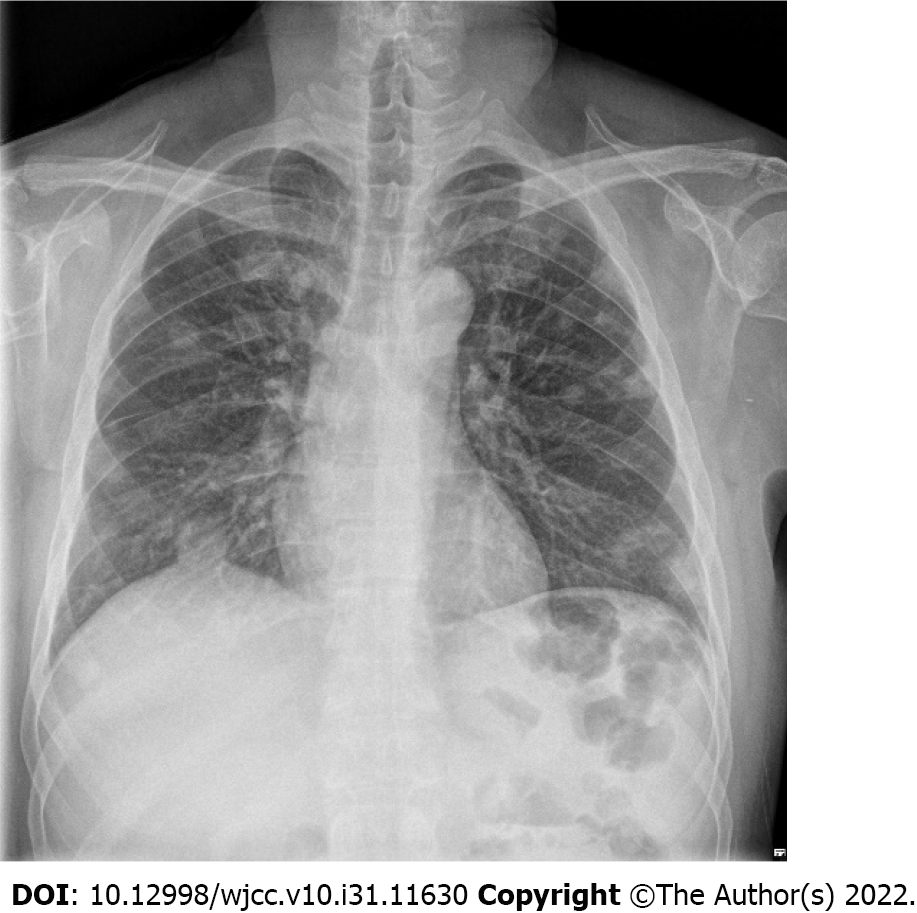
Figure 2 Chest X ray taken at the time of admission of the patient.
Multiple masses and nodules are observed as findings of septic pneumonia caused by hematogenous metastasis.
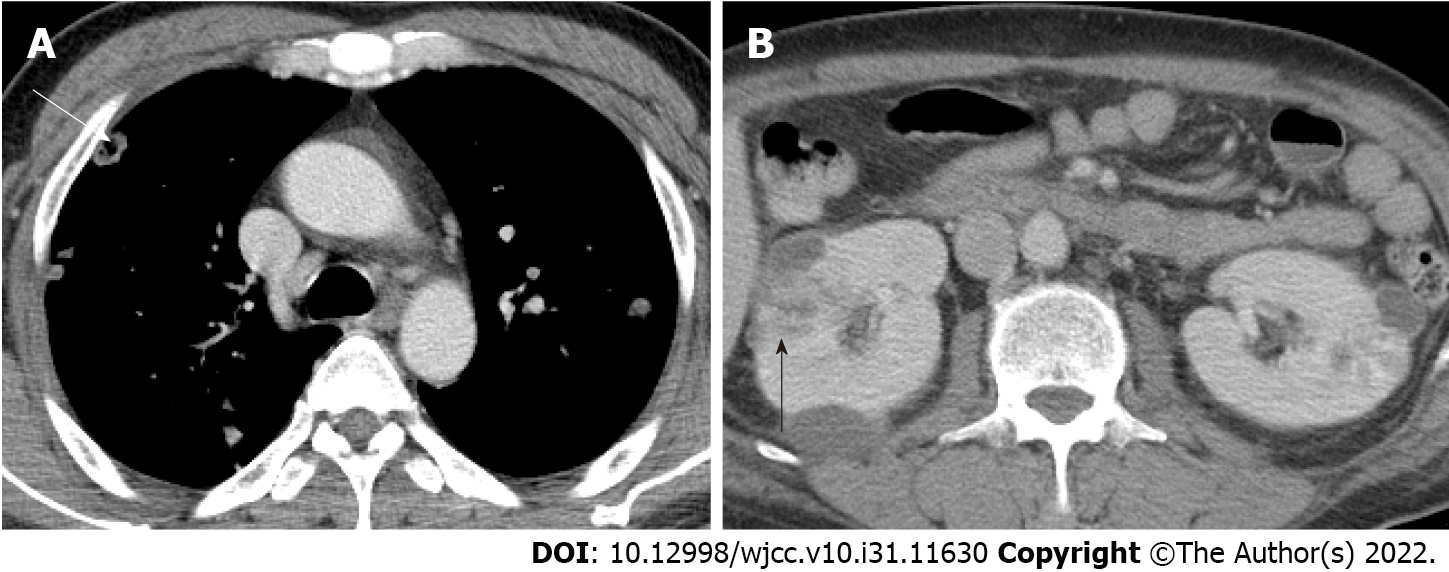
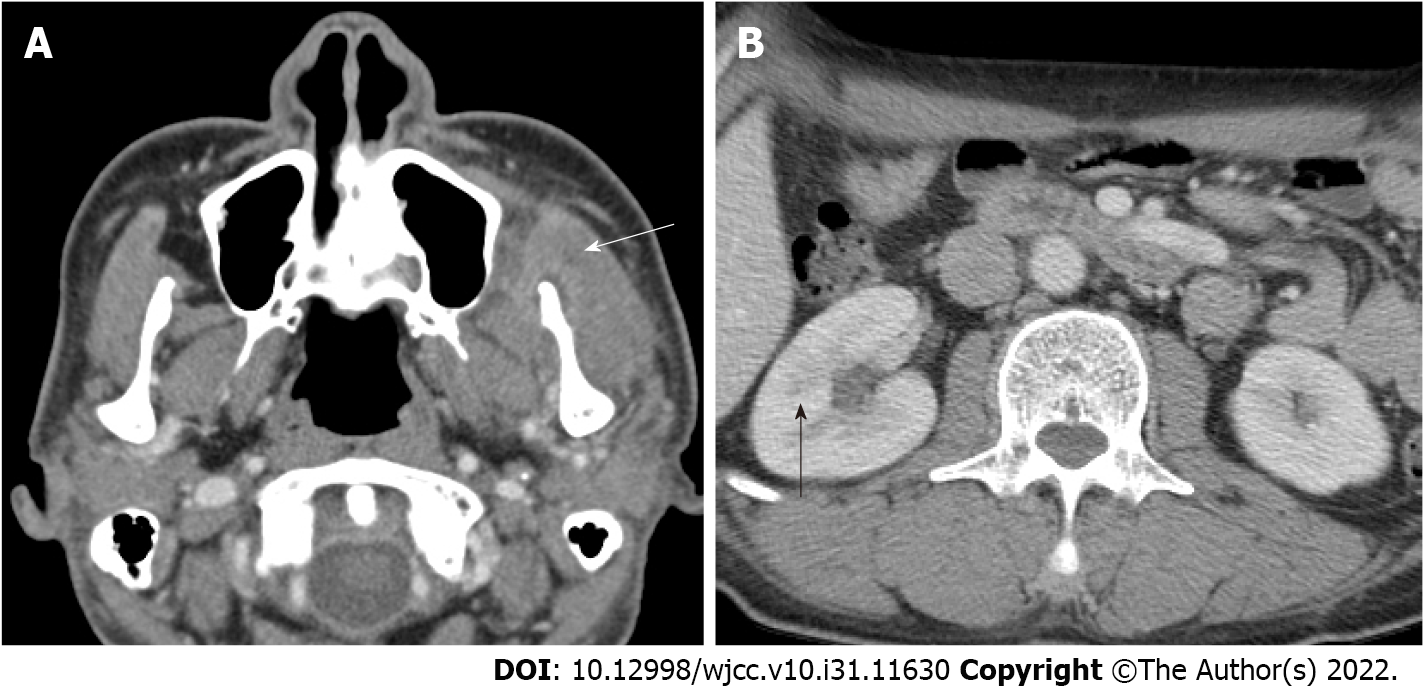
Figure 3 Computed tomographic imaging of internal organ abscesses.
A: Septic emboli on chest computed tomography (white arrow); B: Large renal abscess lesions are observed on abdominopelvic computed tomography (black arrow).
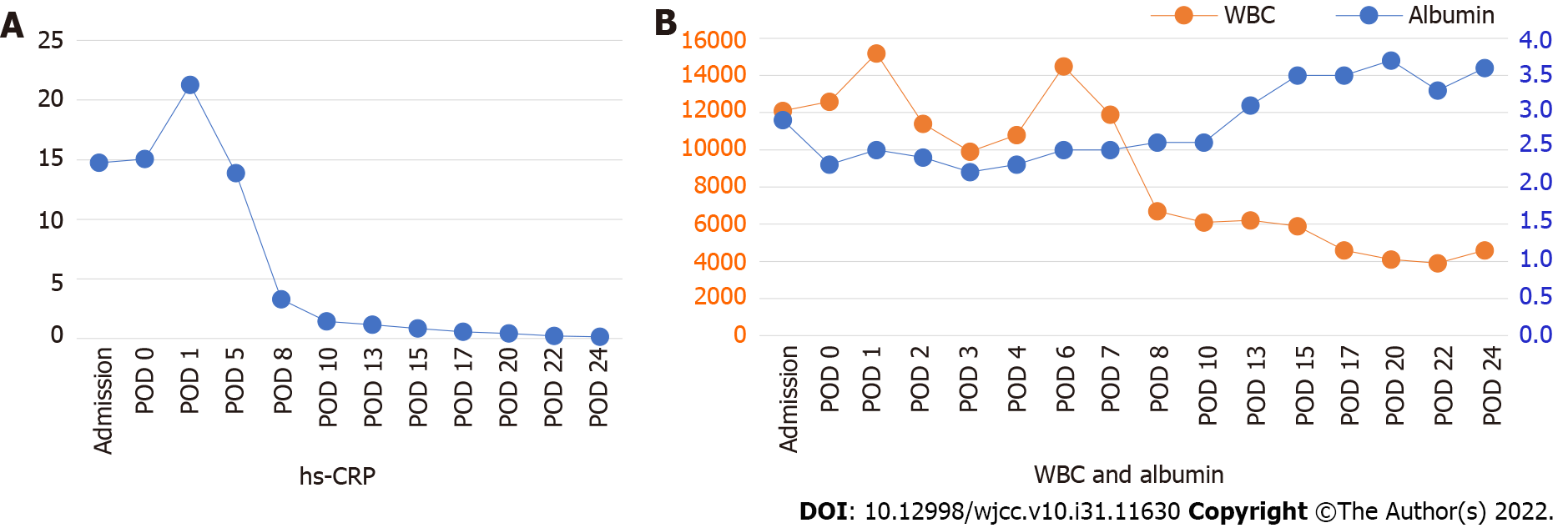
Figure 4 The graph of quantitative change of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, white blood cell and albumin in laboratory findings.
Before and after percutaneous catheter drainage insertion, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and white blood cell decreased, and albumin recovered to 3 or higher as the patient’s clinical symptoms improved. hs-CRP: High-sensitivity C-reactive protein; WBC: White blood cell; POD: Postoperative day.
Figure 5 Postoperative computed tomographic imaging.
A: At postoperative day 25 showing a greater decrease in the size of abscess formation in the left masseter and temporalis muscles (white arrow); B: Abdominopelvic computed tomographic images. On postoperative day 45, The abscess is in remission and is not observed (black arrow).
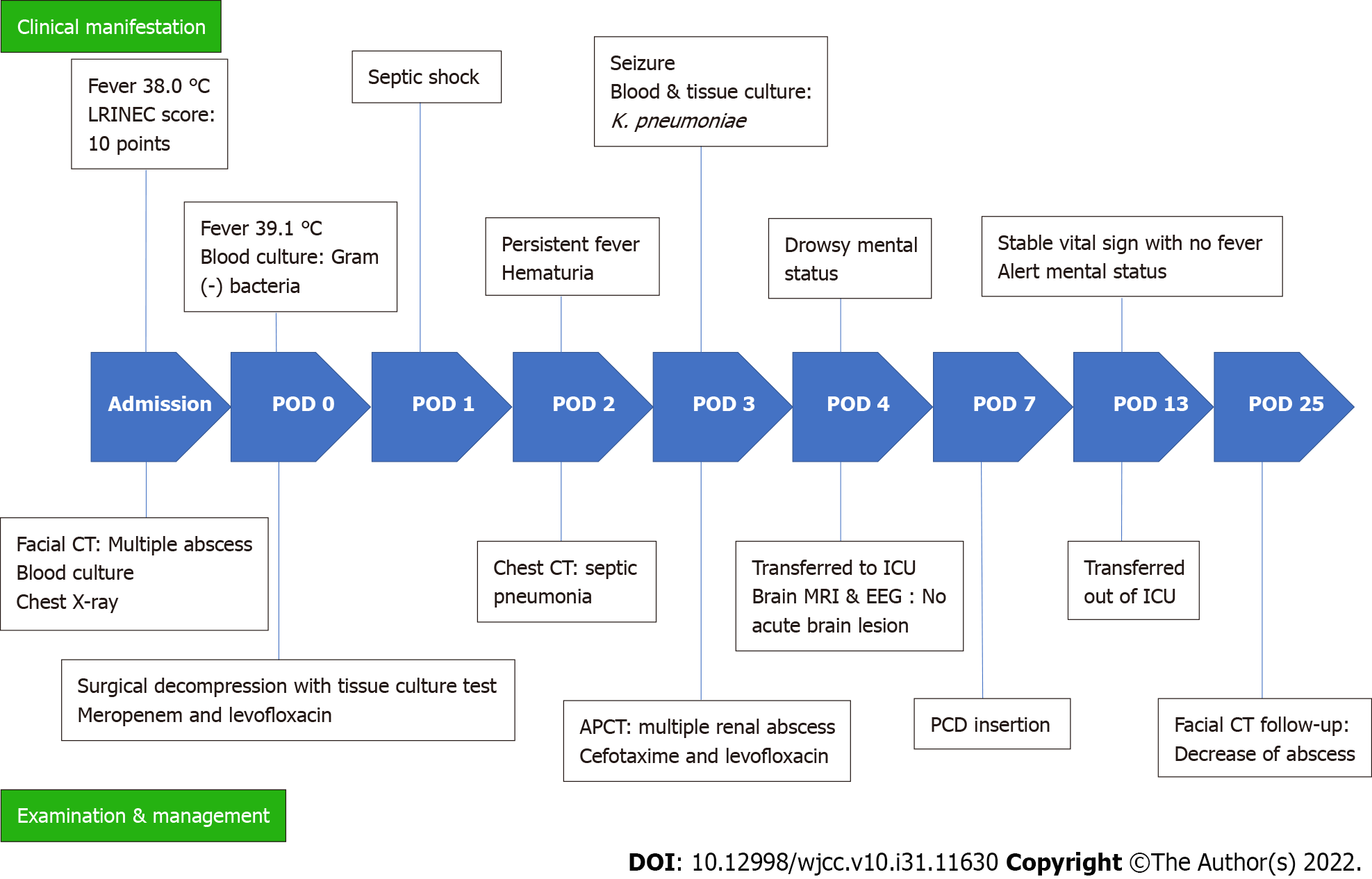
Figure 6 Timeline of reported events.
The chronological sequence of changes in clinical manifestation, examination and management was recorded. LRINEC: Laboratory risk indicator for necrotizing fasciitis; POD: Postoperative day; CT: Computed tomography; hs-CRP: High-sensitivity C-reactive protein; APCT: Abdominal and pelvic computed tomography; ICU: Intensive care unit; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; EEG: Electroencephalography; PCD: Percutaneous catheter drainage.
- Citation: Lee DW, Kwak SH, Choi HJ. Secondary craniofacial necrotizing fasciitis from a distant septic emboli: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(31): 11630-11637
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i31/11630.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i31.11630