Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 6, 2022; 10(31): 11358-11370
Published online Nov 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i31.11358
Published online Nov 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i31.11358
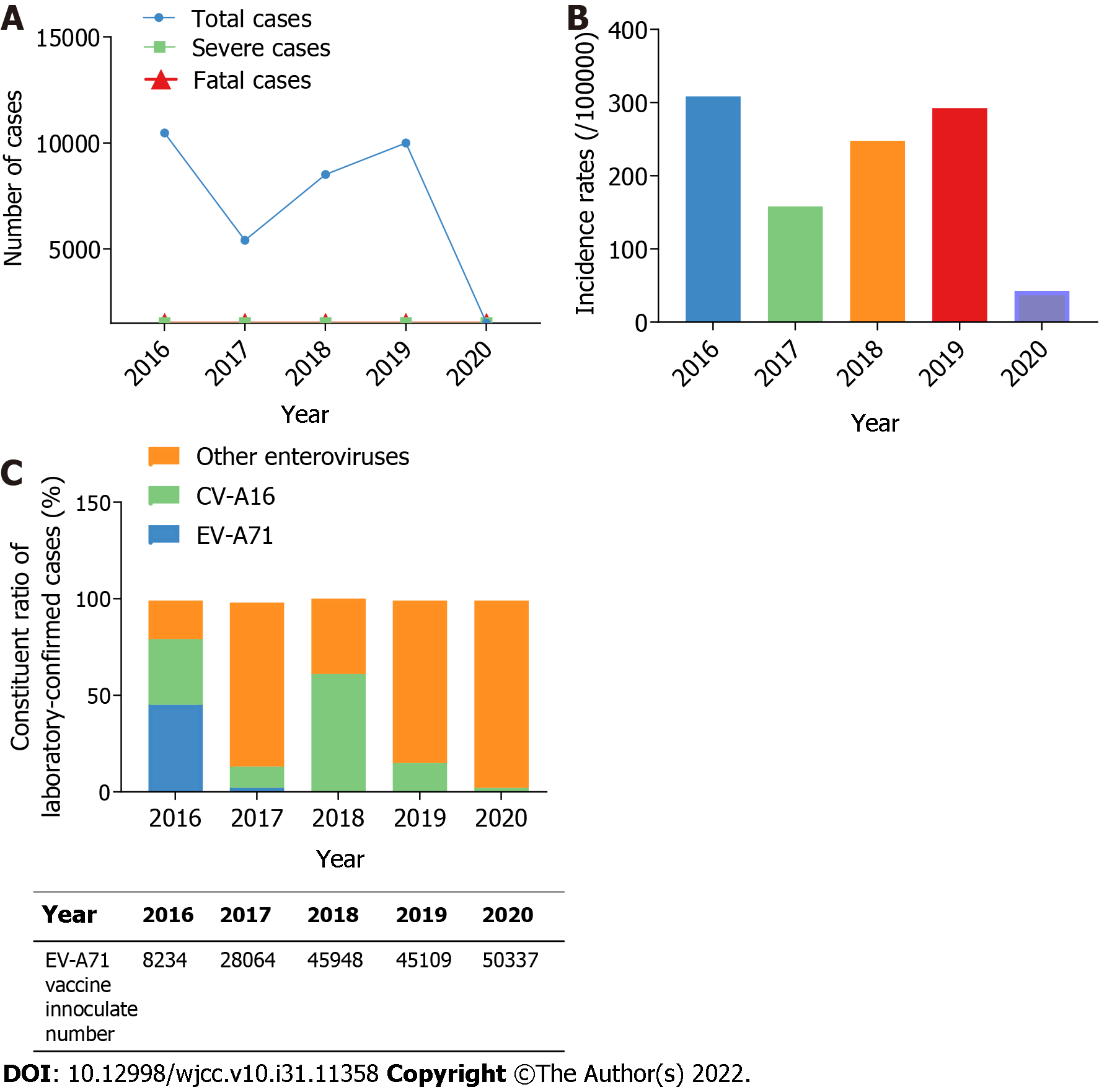
Figure 1 Yearly distribution of hand, foot, and mouth disease cases from 2016 to 2020, in Shiyan, central China.
A: Yearly distribution of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) cases, severe cases, and fatal cases; B: Yearly incidence rates of HFMD; C: Yearly distribution of laboratory-confirmed HFMD cases and enterovirus A71 vaccine inoculation numbers. CV-A16: Coxsackievirus A16; EV-A71: Enterovirus A71.
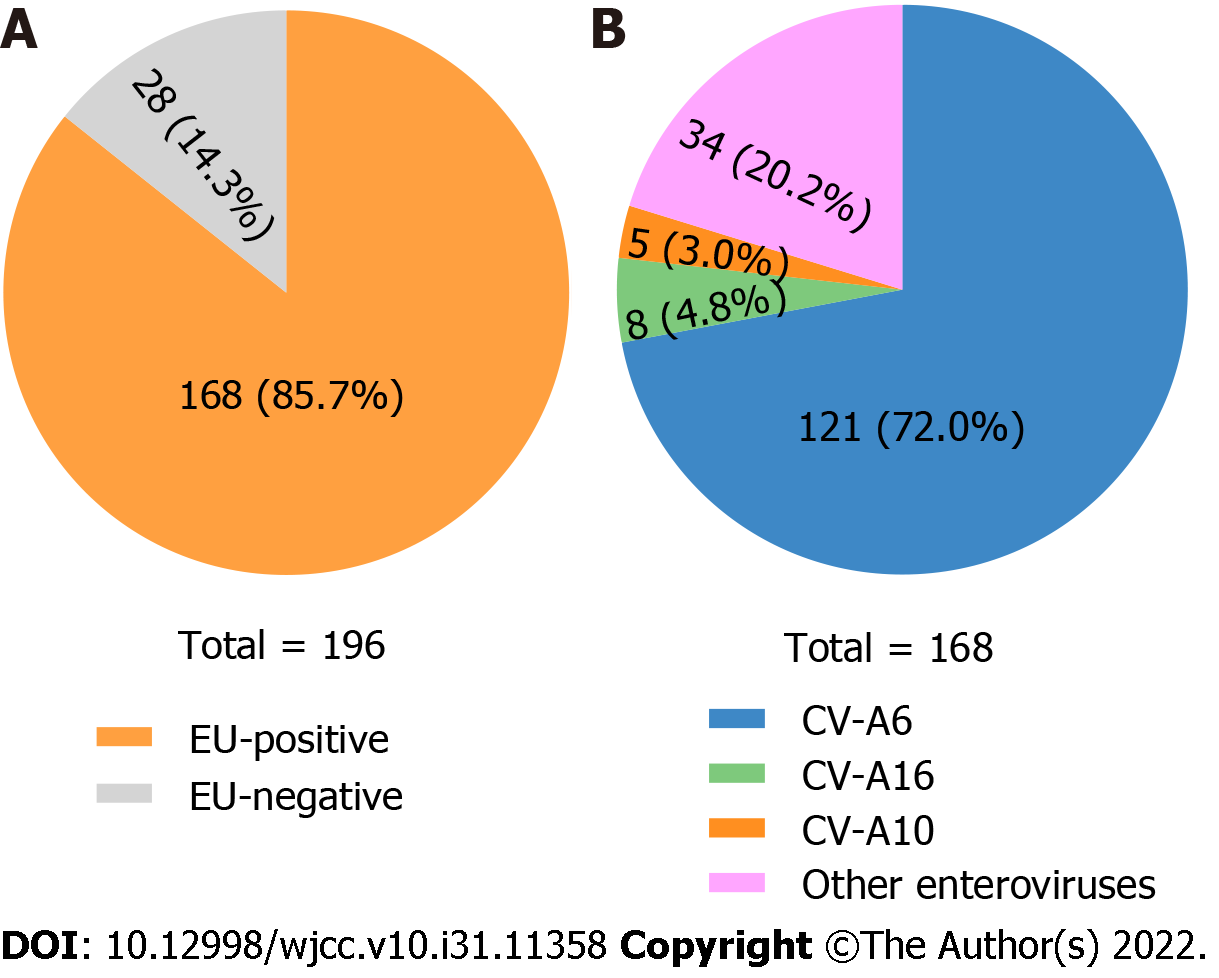
Figure 2 Enterovirus serotypes of 196 hospitalized hand, foot, and mouth disease patients enrolled in this study from 2018 to 2020 in Shiyan, central China.
A: Enterovirus A71 specific, coxsackievirus A16 specific, and pan-enterovirus real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction Kits were used to identify enterovirus-positive specimens; B: The 5'-untranslated region sequences identified enterovirus serotypes of 168 enterovirus-positive samples. EU-positive: Enterovirus-positive; CV: Coxsackievirus.
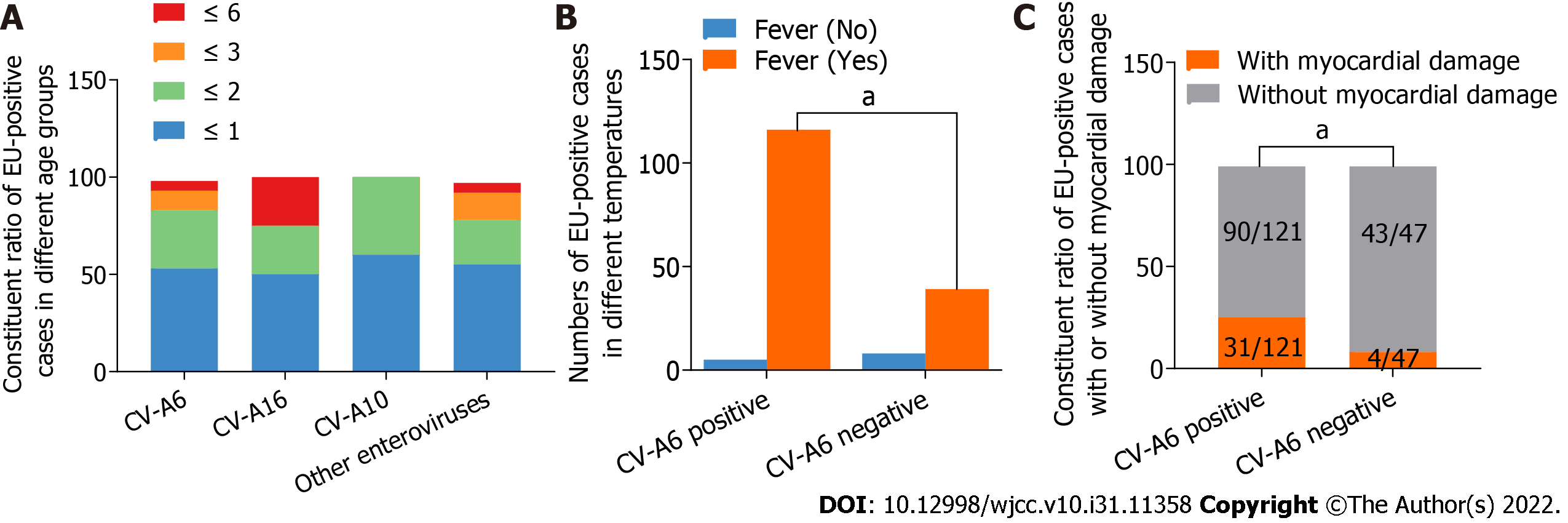
Figure 3 Clinical characteristics of hand, foot, and mouth disease in Shiyan from 2018 to 2020.
A: The constituent ratio of different enterovirus serotypes associated with hand, foot, and mouth disease cases in different age groups; B: Numbers of enterovirus-positive cases with or without fever; C: The constituent ratio of enterovirus-positive cases with or without myocardial damage. aP < 0.05. EU-positive: Enterovirus-positive; CV: Coxsackievirus.
- Citation: Li JF, Zhang CJ, Li YW, Li C, Zhang SC, Wang SS, Jiang Y, Luo XB, Liao XJ, Wu SX, Lin L. Coxsackievirus A6 was the most common enterovirus serotype causing hand, foot, and mouth disease in Shiyan City, central China. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(31): 11358-11370
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i31/11358.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i31.11358