Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 16, 2022; 10(29): 10663-10669
Published online Oct 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i29.10663
Published online Oct 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i29.10663
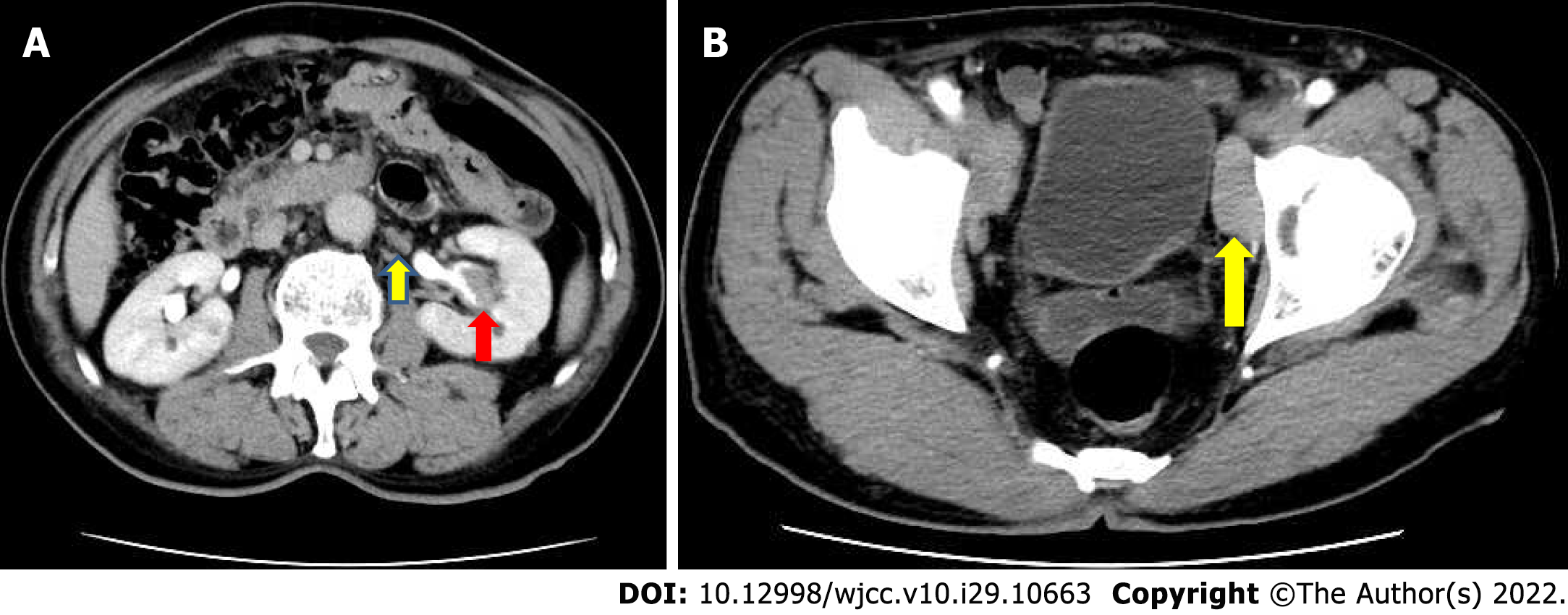
Figure 1 Multiple enlarged lymph nodes were noted in the retroperitoneal and pelvic walls.
A: Abdominal computed tomography imaging demonstrated a tumor mass of approximately 2.7 cm × 1.5 cm × 1 cm in the central part of the left renal pelvis cavity; B: Multiple enlarged lymph nodes were noted in the retroperitoneal and pelvic walls.
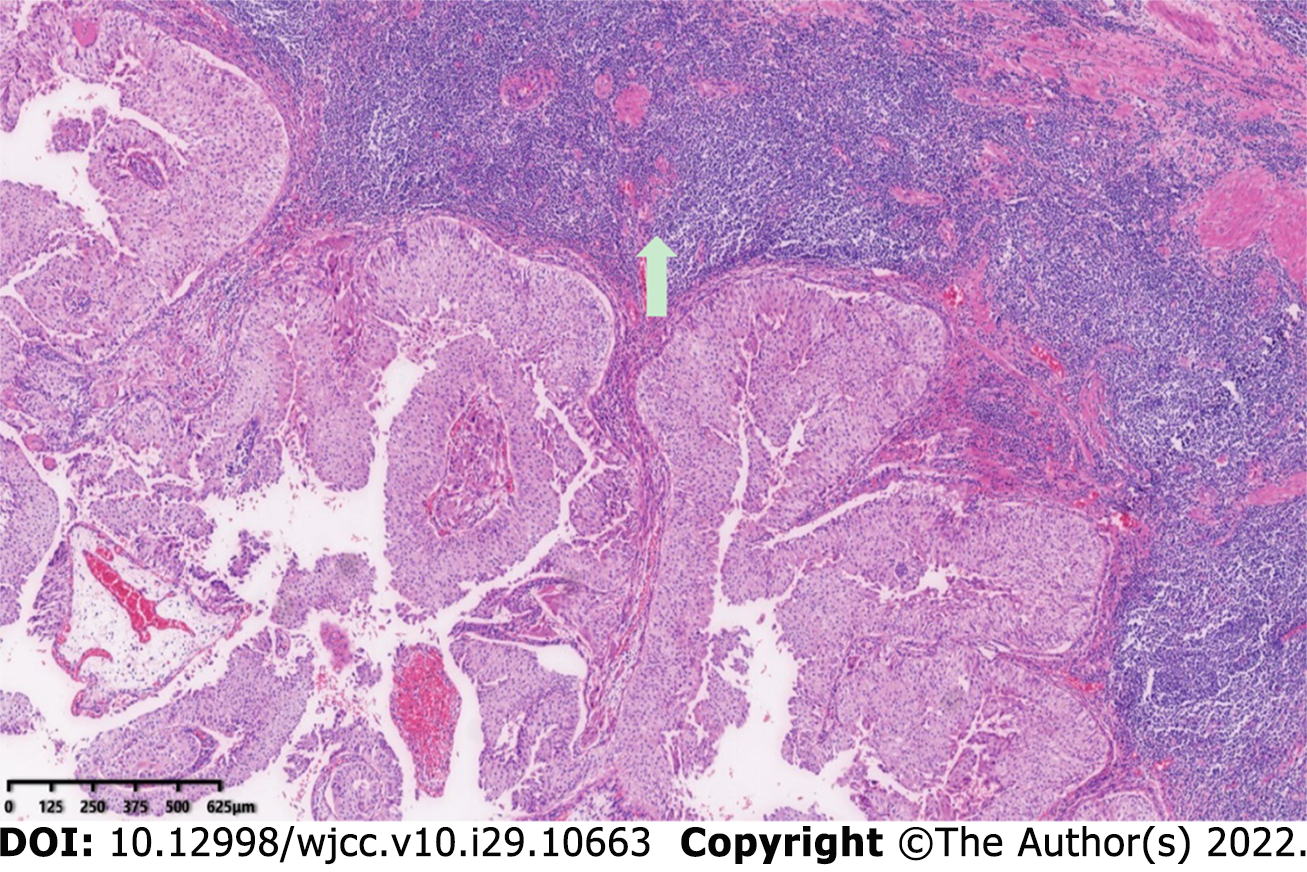
Figure 2 Light microscopic examination confirmed the diagnosis of upper tract urothelial carcinoma of the renal pelvis urothelium extending into the lamina propria.
Original magnification: 100 ×; scale bar: 100 μm.
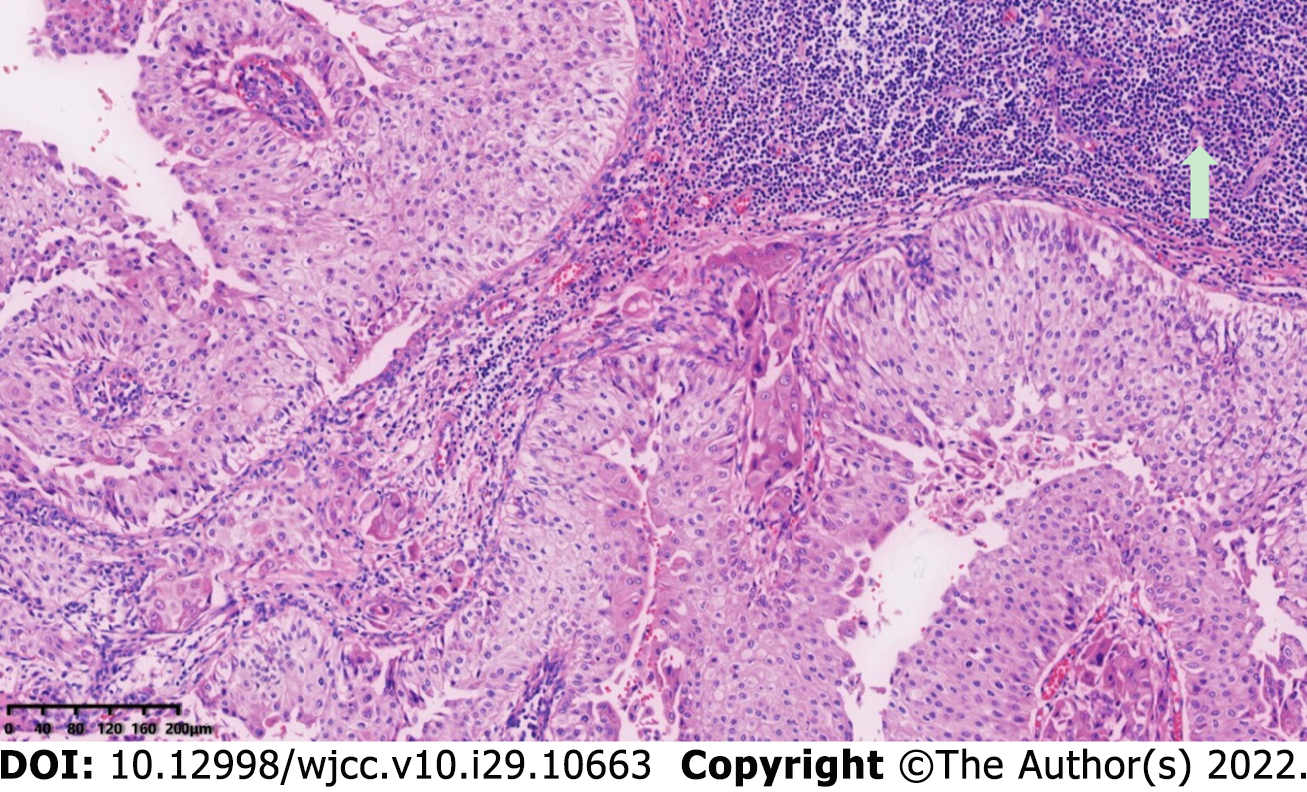
Figure 3 A large amount of diffuse small lymphocytic infiltration was observed along the periphery of the tumor mucosa.
Original magnification: 100 ×; scale bar: 100 μm.
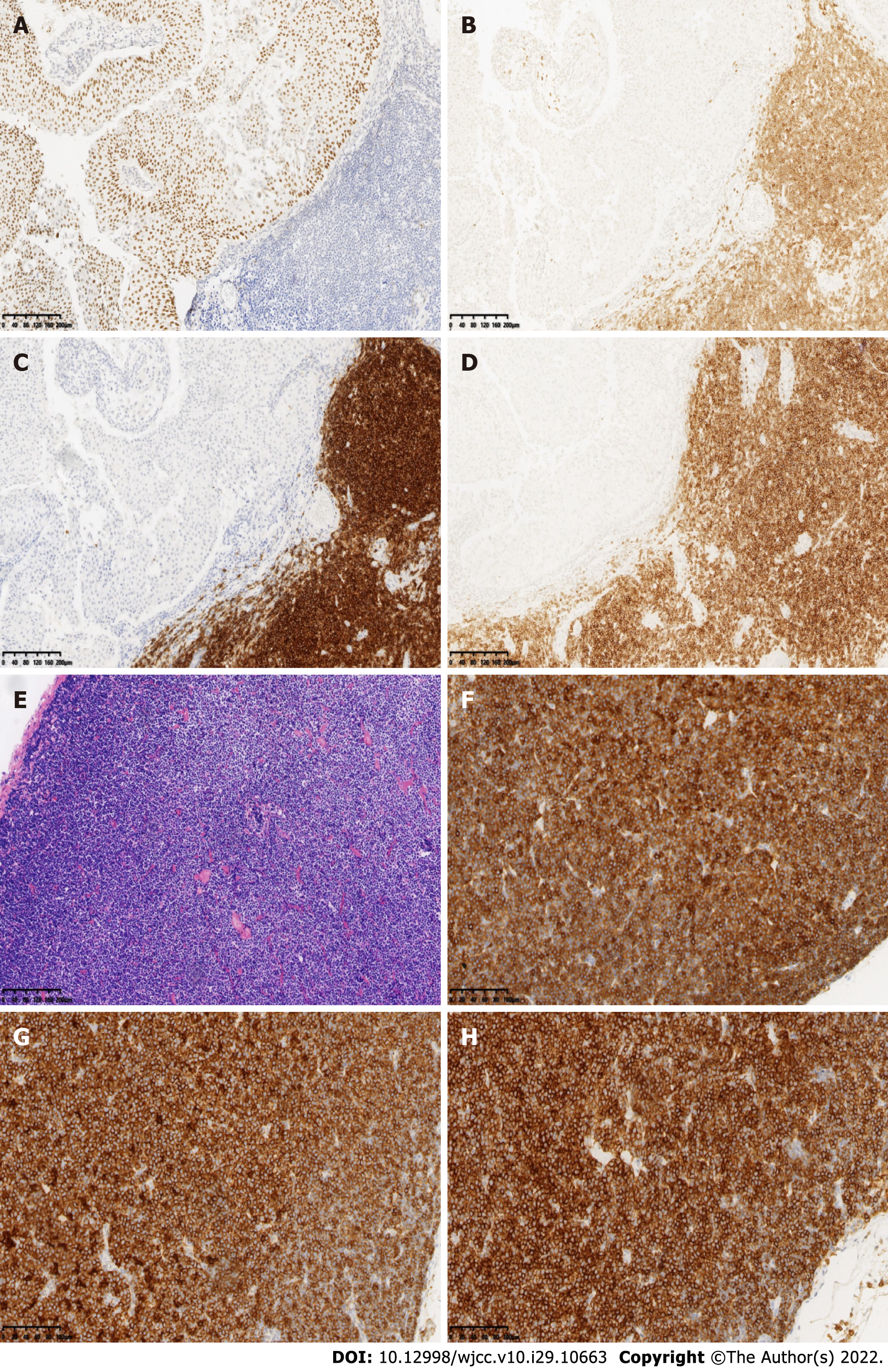
Figure 4 Immunohistochemistry studies revealed that the urothelial tumor cells were positive for P63.
A-E: Retroperitoneal renal pedicle enlarged lymph nodes showed diffuse architectural effacement due to the proliferation of small lymphocytes with variably prominent scattered proliferation centers composed of prolymphocytes and paraimmunoblasts, and were positive for CD5, CD20, and CD23; F-H: No urothelial carcinoma metastases were observed in the lymph nodes. Renal pelvis lymphatic tissue and lymphocytes were positive for CD5, CD20, and CD23. Original magnification: 100 ×; scale bar: 100 μm.
- Citation: Yang HJ, Huang X. Synchronous renal pelvis carcinoma associated with small lymphocytic lymphoma: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(29): 10663-10669
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i29/10663.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i29.10663