Published online May 20, 2022. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v12.i3.122
Peer-review started: November 28, 2021
First decision: January 12, 2022
Revised: January 16, 2022
Accepted: March 16, 2022
Article in press: March 16, 2022
Published online: May 20, 2022
Processing time: 171 Days and 7.8 Hours
Several strategies have been implemented to reduce or abolish the life-threatening risk of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)-related multidrug-resistant infections due to duodenoscopes contaminations; among those strategies, serial microbiologic tests, thorough reprocessing schedules, and use of removable scope cap have been adopted, but the potential cross-infection risk was not eliminated.
To review available evidence in the field of single-use duodenoscopes (SUD) use for ERCP.
An overview on ongoing clinical studies was also performed to delineate which data will become available in the next future.
One bench comparative study and four clinical trials performed with EXALT model-D (Boston Scientific Corp., United States) have been identified. Of them, one is a randomized controlled trial, while the other three studies are prospective single-arm, cross-over studies. Pooled technical success rate (4 studies, 368 patients) was 92.9% [95% confidence interval (CI): 89.9-95.5; I2: 11.8%]. Pooled serious adverse event (4 studies, 381 patients) rate was 5.9% [3.7%-8.5%; I2: 0.0%].
Although few clinical trials are available, evidence is concordant in identifying an absolute feasibility and safety and feasibility for SUD use for ERCP. The expertise and quality of evidence in this field are going to be improved by further large clinical trials; data on cost-effectiveness and environmental impact will be needed for a worldwide spread of SUD use for ERCP.
Core Tip: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) has significantly changed the management and natural history of patients with biliary and pancreatic diseases. While in the past decades ERCP procedure were considered safe and bearing low-risk for exogenous pathogens transmission, the risk of duodenoscopes contaminations and related cross-infection was recently demonstrated and quantified. To overcome this issue, two different single-use duodenoscopes (SUD) have been developed and are commercially available. The sterile packaging and the disposable intent guarantee to avoid exogenous patient-to-patient cross-infections. A systematic review of all available clinical evidence on the use of SUD for ERCP was performed, demonstrating an overall pooled safety and efficacy. Although few clinical trials are available, evidence is concordant in identifying an absolute feasibility and safety and feasibility for single-use duodenoscopes (SUD) use for ERCP. Future large clinical trials are ongoing to increase the knowledge and quality of evidence in the field; data on cost-effectiveness and environmental impact will be needed for a worldwide spread of SUD use for ERCP.
- Citation: Lisotti A, Fusaroli P, Napoleon B, Cominardi A, Zagari RM. Single-use duodenoscopes for the prevention of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography -related cross-infection – from bench studies to clinical evidence. World J Methodol 2022; 12(3): 122-131
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v12/i3/122.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v12.i3.122
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) has significantly changed the management and natural history of patients with biliary and pancreatic diseases[1-3].
Millions of ERCP procedures have been performed annually and this worldwide amount is going to constantly increase due to epidemiological trends of main indications (i.e., biliary stone disease, malignant biliary obstruction), aging of population, and increasing therapeutic applications[4,5].
In recent years, several outbreaks of multi-drug resistant ERCP-related infections have been reported; main risk factors for ERCP-related infections are patients’ immunocompromised status and interventional procedures, such as biliary stenting for intrahepatic strictures[6,7]. Contamination of the biliary tract from endogenous gut microbiota bacteria is responsible for the vast majority of post-ERCP infections. However, several issues related to multidrug resistant infections related to duodenoscope contaminations have been reported (i.e. P. aeruginosa and carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae)[8,9].
While in the past decades ERCP procedure were considered safe and bearing low-risk for exogenous pathogens transmission, the risk of duodenoscopes contaminations and related cross-infection was recently demonstrated and quantified[10-12].
Food and Drug Administration alerted physicians’ community about duodenoscope-related infections in 2015. The peculiar design of these side-viewing instruments was identified as the potential sources of contamination. Indeed, in the tip of the scope is allocated the elevator mechanism with his dedicated cable passing through the scope body; this complex mechanism, despite adequate procedures, is difficult to accurately clean making reprocessing more challenging due to the possible formation of bacteria-containing biofilm[13].
Post-market studies conducted by main manufacturers demonstrated an unexpected higher rate of duodenoscope contamination. A recent meta-analysis tried to overcome the lack of data and quantify the risk of cross-infection in ready-to-use duodenoscopes. A pooled contamination rates up to 15% was identified and none of the available standard reprocessing protocols are able to correctly clean these instruments[14,15].
Several strategies have been proposed to overcome duodenoscope-related infections, such as deep bacterial coltures, improved protocol for reprocessing, and avoiding the use of scopes with fixed cap to allow decontamination. Unfortunately, duodenoscope contaminations could not be avoided with these strategies[16-19].
Four reusable duodenoscopes with detachable cap are available, from three manufacturers. For a detailed focus on this field, a recent American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) practice guideline was published[4,20].
Two different single-use duodenoscopes (SUD) are commercially available in the US. The sterile single-use package allow the avoidance of exogenous contaminations[4].
The aim of this study was to perform a systematic review of all available clinical evidence on the use of SUD for ERCP.
A systematic literature research was performed through MEDLINE using Pubmed, Google Scholar, and Embase interfaces at the end of November 2021. The search queries were ("duodenoscope"[all fields] OR "single-use"[all fields] OR "disposable"[all fields]) AND "ERCP"[all fields]). Institutional Review Board evaluation for this purpose was not required. Relevant studies were independently analyzed by two authors (AL, RMZ).
Inclusion criteria were: (1) Population: All adult individuals who underwent ERCP; (2) Interventions: SUD use for ERCP; (3) Objectives: Technical success (amount of successfully-completed procedures with SUD among all procedures); and (4) safety: Incidence of ERCP-related complications.
Technical success rate and other aims were pooled through a random-effects model based on DerSimonian and Laird test. Heterogeneity was estimated using I2 tests: I2 less than 30% was considered low, while I2 > 30% but < 60% was considered weak. Funnel plots inspection was used to assess possible publication bias.
Main objective was the technical success, (completed ERCP using SUD among the entire amount conducted). Secondary objectives were adverse events (AEs).
Statistical analysis was performed with MedCalc package v20 (MedCalc Software Ltd, Ostend, Belgium; https://www.medcalc.org; 2021).
In 2017, several animal studies on porcine and canine models have been conducted with ERCP experts, to evaluate duodenoscope prototypes. Simulated ERCP procedures have been tested with the SUD prototype (Boston Scientific, United States) and a reusable duodenoscope. Involved physicians were asked to rate specific endoscopes tasks qualitatively and quantitatively. These pre-clinical tests allowed the development of the EXALT model-D by Boston Scientific[21].
In 2019, ERCP experts from United States completed the first comparative study on two simulators. Three reusable duodenoscopes from the major companies in the field (Olympus Corp., Japan, Pentax Corp., Japan and Fujifilm Holdings Corp., Japan) were compared to EXALT-D using a 0-10 score in four different tasks (and 14 sub-tasks): Guidewire locking with elevator, plastic and metal stents placement and removal, and Dormia Basket passage. The technical success rate for each task and time to achieve the completion was recorded and compared.
The results of this bench study showed that EXALT-D SUD showed similar overall performance, task completion times, tip control and guidewire locking to three different reusable duodenoscopes. Moreover, mechanical scope navigation and image quality was considered excellent (≥ 8 on a scale of 10)[21].
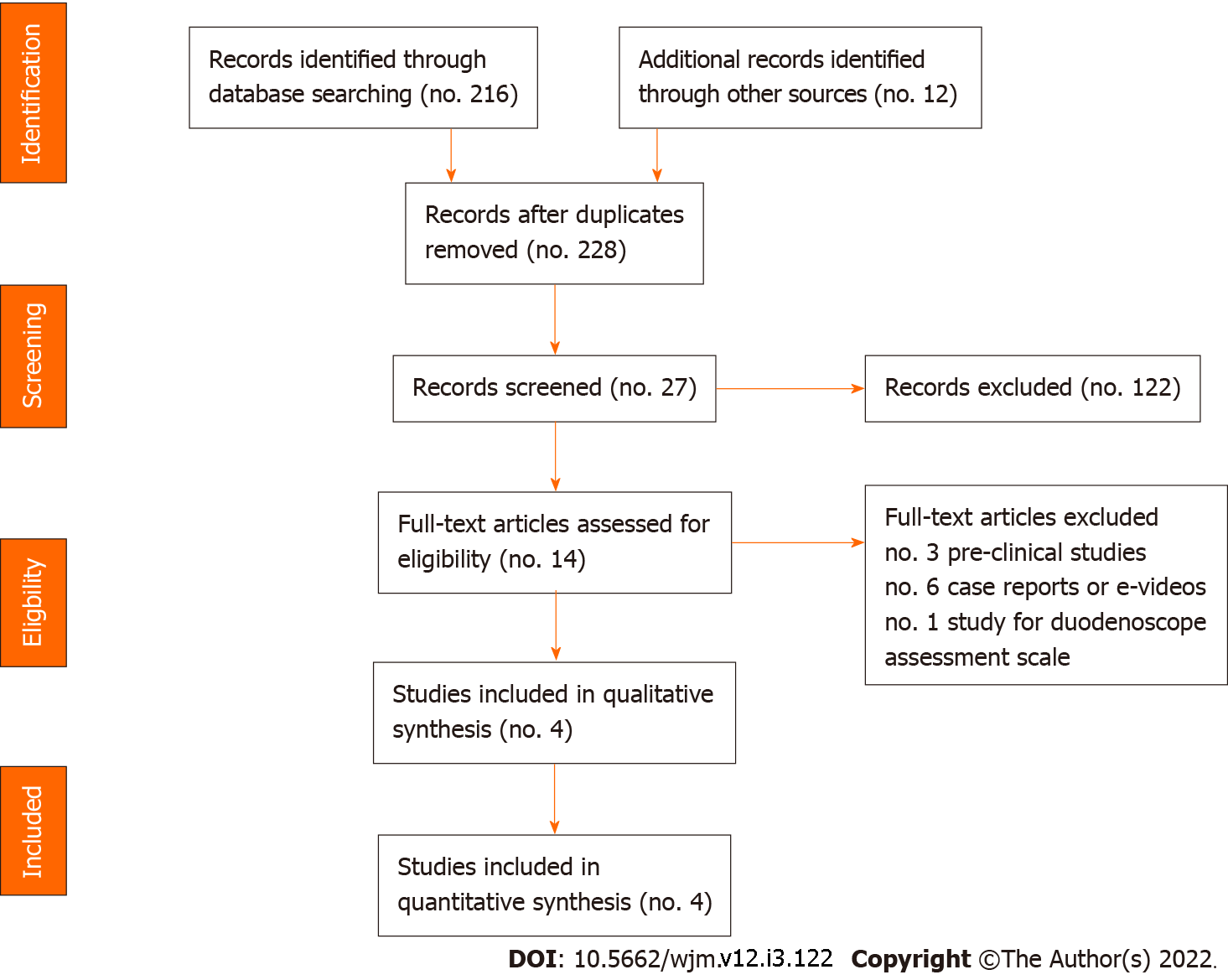
Four studies have been conducted since the introduction of SUD (study flow diagram according to PRISMA 2009 guidelines is shown in Figure 1); studies are summarized in Table 1.
| Ref. | Region, Study design | Population (no.); male gender (%) | Age (yr, SD) | Naïve papilla (%) | ASGE complexity 3-4 (%) | Technical success (%) | Serious AEs (%) | Note |
| Muthusamy et al[22], 2020 | United States, Case-series | No. 60, Male 61.7% | 64.4 ± 14.1 | 26.70% | 45.00% | 96.70% | 6.70% | The study included a roll-in phase with 13 patients |
| Bang JY et al[23], 2020 | United States, RCT | No. 48, Male 54.2% | 67.2 ± 14.4 | 100% | 16.70% | SUD: 95.8%; Reusable: 100% | 4.20% | Primary outcome was no. attempts to achieve cannulation (SUD median 2; reusable 5; P = 0.013) |
| Napoléon et al[24], 2022 | France, Prospective | No. 60, Male 43.3% | 65.5 ± 13.6 | 53.30% | 40.00% | 95% | 1.70% | 96.7% of cases with optimal operators’ satisfaction |
| Slivka et al[25], 2021 | United States, Prospective | No. 200, Male 48.5% | 62.6 ± 14.0 | 45.50% | 40.50% | 90.50% | 6.50% | Included 14 expert and 5 “non-expert” ERCP operators with similar outcomes |
Muthusamy et al[22] conducted in April-May 2019 a multicenter study involving ten US centers and seven ERCP experts; 73 consecutive patients undergoing ERCP have been enrolled. Thirteen patients entered a running “first-in-men study” evaluating the feasibility of ERCP maneuvers. All these “roll-in” procedures (100%) have been successfully completed and the operators stated that they feel confident to extremely-confident in performing ERCP with the SUD.
Sixty consecutive patients have been subsequently enrolled in the study. Most patients (61.7%) were male with a mean age of 64.4 ± 14.1 years. Most cases (73.3%) had a medical history of previous ERCP. In two cases (3.3%), cross-over to a reusable duodenoscope was required due to ERCP technical failure. In one case (tight intrahepatic stricture dilation in a patient with sclerosing cholangitis) the use of a reusable duodenoscope allowed a successful ERCP completion; in one case, papilla showed neoplastic infiltration.
Between January and March 2020, Bang et al[23] randomized 98 patients to underwent ERCP with a reusable duodenoscope (TJF-180, Olympus America Inc., United States) or a SUD (EXALT-D, Boston Scientific, United States). Forty-eight patients (54.2% male, 67.2 ± 14.1-year-old) were allocated to the SUD arm and compared to 50 patients (46.0% male, 60.8 ± 18.2-year-old) of the reusable duodenoscope arm; no patient had previous ERCP or bilio-pancreatic intervention. The Authors observed comparable selective cannulation rate (95.8% vs 100%), with similar time to reach the papilla (20 vs 20 sec); the authors observed that the number of attempt (2 vs 5) and time to achieve selective biliary cannulation (35 vs 99 sec) were significantly lower in the SUD group.
Napoléon et al[24] have recently published the first study conducted outside the US. In this French multicenter study involving six centres, 60 patients (43.3% male, median 65.5 [55-76] year-old) were prospectively enrolled. 95% of the procedures were successfully completed with the SUD, while in three cases the Authors switched to a reusable duodenoscope. In these 3 cases, ERCP could not be completed even with the use of a reusable duodenoscope because of a complete duodenal stricture, a neoplastic infiltration of the ampullary region and a complete biliary stricture; these patients were treated with surgery, EUS- hepaticogastrostomy and percutaneous trans-hepatic drainage, respectively. In this study, 46.7% of patients had previous ERCP. Among the remaining cases, selective biliary cannulation was achieved in 93.8% of cases, after a median of 1 minute and 1.5 guidewire attempts[24].
The results of a large prospective study, conducted in United States, have been published by Slivka et al[25]. The Authors enrolled 200 patients undergoing ERCP for various indications; in fact, 40.5% of ERCP procedures presented high complexity (ASGE 3-4). The Authors reported an overall 90.5% technical success rate. Interestingly, this is the first study that included not only expert operators (defined as > 2000 lifetime ERCP performed), but also five “non-expert” operators. The Authors observed that the crossover to a reusable duodenoscope rate (2.5% vs 11.3%), the ERCP completion rate (97.5% vs 96.3%) and procedure time (28.5 vs 25.0 min) were similar among expert and non-expert groups[25].
Muthusamy reported a case of post-ERCP pancreatitis in 1 out of 13 patients involved in the roll-in study. Moreover, they reported 2 post-ERCP pancreatitis (3.3%), one post-sphincterotomy bleeding (1.7%) and one infection of a walled-off pancreatic necrosis in the 60 patients included in the main study. The overall serious adverse event rate was 6.7%[22].
No difference was observed in term of adverse event (AE) and mortality, when ERCPs performed with the SUD were compared to those performed with a reusable duodenoscope. The authors observed two adverse events in the SUD arm (4.2%) compared to 8% adverse event rate in the control group. The Authors reported an ERCP-related mortality of 2.1% and 2%in the two groups, respectively[23].
Napoléon et al[24] reported 3 ERCP-related adverse events (5.0%). Of them, two cases were mild (biliary pain and one mild pancreatitis), while one patient (1.7%) presented worsening of underlying condition due to pancreatic cancer and died one week after the procedure[24].
Slivka et al[25] reported 13 serious adverse events (6.5%); of them, 5 bleeding, 3 post-ERCP pancreatitis and 2 cholangitis. The incidence of adverse events was similar in expert and non-expert groups (5.0% vs 6.9%) and was independent by ASGE complexity grade (low – ASGE 1-2: 7.0% vs high – ASGE 3-4: 6.2%).
All studies reported no SUD-related adverse event.
No data on specific SUD contamination after ERCP has been provided in the included studies.
Muthusamy reported a median overall satisfaction with the SUD of 9 (range, 1-10). In 4 cases (6.7%) the Authors observed a poor satisfaction (4 or less), due to difficulty of stent insertion, low image quality, and technical issue with the device (turning off during the procedure)[22].
Bang et al[23] observed that the SUD present lower image quality and stability comparing to a reusable duodenoscope. From a mechanical point of view, the Authors reported a lower ease to pass into the stomach and frequent dysfunction of air-water valve.
Napoléon et al[24] reported a median overall satisfaction of 9 on a scale of 10. In two cases (3.3%), the operator reported a low satisfaction (less than 5) due to malfunction of the insufflation valve leading to irrigation water in the lumen, limiting the visibility. Among 22 different tasks, the authors considered the SUD clinically-satisfactory in 100% and comparable to a reusable duodenoscope in 97.9%of cases.
The recently published study by Slivka et al[25] confirmed an optimal overall satisfaction with the SUD [median 8 (range VAS 1-10)]. Among 23 evaluated maneuvers, all obtained a median of at least 4 (range 1 to 5).
Our study group recently conducted a meta-analysis including all clinical studies assessing the safety and efficacy of SUD use for ERCP, identifying 4 studies (368 patients) [26]. We observed a 92.9% [89.9 – 95.5; I2 11.8%] overall success rate and 5.9% [3.7 – 8.5; I2 0%] overall incidence of serious AEs. Overall incidence of pancreatitis (2.5%), infections (1.8%) and bleeding (1.8%) was very low, in line with suggested threshold and confirming the optimal safety[26].
Five clinical studies on the use of SUD for ERCP are ongoing (no. 2) or ready to start recruitment (no. 3); these studies and contact information are summarized in Table 2.
| Title, reference | Region | Investigators | Design, population, Duodenoscope | Primary outcome | Status |
| Single Use ERCP -SURE Study (SURE). NCT04671095 | Nottingham, United Kingdom | Dr. Suresh Vasan Venkatachalapathy; suresh.venkatachalapathy@nuh.nhs.uk | Prospective, 50 patients, EXALT-D1 | Technical success (ERCP completion) | Not yet recruiting |
| International Study to Evaluate Outcomes and Safety of Patients Undergoing ERCP Using a Single-use Cholangioscope and Single-use Duodenoscope (MESE). NCT04712253 | Rozzano (MI), Italy | Prof. Alessandro Repici alessandro.repici@hunimed.eu; Dr. Andrea Anderloni andrea.anderloni@humanitas.it | Retrospective, 50 patients, EXALT-D1 | Technical success, clinical outcomes | Recruiting |
| Global Prospective Case Series Using a Single-Use Duodenoscope. NCT04103749 | United States | Gregory Tirrell; gregory.tirrell@bsci.com; Pooja Goswamy; pooja.goswamy@bsci.com | Prospective, 1000 patients, EXALT-D1 | Technical success (ERCP completion) | Not yet recruiting |
| Exalt D Single-use Duodenoscope in ERCP Procedures in China (ExaltDScope). NCT04687774 | China | Zhiwei Guzhiwei.gu@bsci.com; Jingjing Gu | Observational, 30 patients, EXALT-D1 | Technical success (ERCP completion) | Not yet recruiting |
| A Single-Use Duodenoscope in a Real-World Setting. NCT04628949 | United States | Elizabeth Smith; elsm@ambu.comTrine; Højgaard Tølbøll; trht@ambu.com | Prospective, 550 patients, aScope | Technical success (ERCP completion) | Recruiting |
Two of them are planned to be conducted in US, while the remaining two studies in Europe (Italy and UK) and one in China.
Following the feasibility and safety studies performed in high-volume centers by extremely experienced operators, one study (NCT04103749) will include large real-life experience with operators with various expertise.
Interestingly, an Italian study is going to assess the performance of SUD in combination with single-use digital cholangioscope in a tertiary referral center.
Finally, a large multicenter study is testing the performance of another SUD, namely the aScope™ Duodeno, manufactured by Ambu A/S (Denmark) on 550 patients undergoing ERCP. In less than 12 mo, the knowledge and quality of evidence in the field of SUD use for ERCP is going to be strongly expanded. The introduction of a validated tool for duodenoscope assessment will allow physician to utilize a reproducible and reliable tool for the assessment of technical performance of duodenoscopes[27].
A recently published study, based on a “Montecarlo model” assessed the cost-effectiveness of different approaches adopted for the reduction of duodenoscope-related cross-infections[28]. The cost for each ERCP procedure, based on United States data, performed with SUD has been estimated in $2991. The analysis, based on an estimated < 1% risk of duodenoscope-related cross-infections did not identified routinely SUD use as a cost-effective strategy. The Authors acknowledged that these results should be contextualized based on duodenoscope-related cross-infection rate, local ERCP volume, quality adjusted life years, post-ERCP lifespan and environmental costs[28,29].
The lack of a reliable quantification of the impact of duodenoscope contamination-related infections does not allow to correctly evaluate the benefit of the systematic use of a SUD.
Indeed, all the published studies have been designed to compare SUD to standard reusable duodenoscopes with a non-inferiority purpose, in terms of technical and clinical success rate. Since the estimated rate of duodenoscope-related cross-infection was < 8% published studies are underpowered to detect any clinical difference.
Another point of critical discussion will be the ecological impact of production and wasting of a single-use endoscope.
A recent international named “Green Endoscopy” (Twitter account @GreenEndoscopy) wrote an inspiring editorial on this issue. The Authors estimated a mean 1.5 kg of waste for each single endoscopic procedure, with very-low amount of recyclable materials.
The disposal SUD is equivalent up to 400 g of household waste and this weight should be added to this waste. The Authors considered “unthinkable” that each ERCP could be performed with SUD based both on cost and environmental burdens.
A comparative study on two different approaches adopted with bronchoscopes [http://ambu.co.uk/pulmonology/environmental-impact] has reported that single-use endoscopy does not much differ since the cost of disposing plastic endoscopes should be balanced with sterilization process, disinfecting equipment and consumable costs.
On the other hand, SUDs are made from recycled plastic and are claimed to be recyclable through third party companies, even if material from these duodenoscopes will not be used for production of medical devices[29].
In conclusion, the recent identification of several cluster of exogenous multidrug-resistant bacterial infection caused by duodenoscope cross-contamination necessitated the implementation of various strategies for at least prevention or abolition of that life-threatening risk. Among those strategies, the introduction of sterile, disposable duodenoscopes is able to completely abolish the contamination and cross-transmission of bacteria.
Although there are only few clinical trials available, evidence is concordant in identifying an absolute safety and feasibility. Indeed, no SUD-related adverse event is still reported, and overall risk of adverse events and mortality is comparable to ERCP performed with reusable duodenoscopes. Moreover, the pooled technical success rate in expert hands stands at optimal values, with no significant heterogeneity among studies.
Future studies will deepen the knowledge in this field; data on cost-effectiveness and environmental impact will be needed for a worldwide spread of SUD use for ERCP.
In conclusion, the recent identification of several cluster of exogenous multidrug-resistant bacterial infection caused by duodenoscope cross-contamination necessitated the implementation of various strategies for at least prevention or abolition of that life-threatening risk. Among those strategies, the introduction of sterile, disposable duodenoscopes is able to completely abolish the contamination and cross-transmission of bacteria.
Although there are only few clinical trials available, evidence is concordant in identifying an absolute safety and feasibility. Indeed, no SUD-related adverse event is still reported, and overall risk of adverse events and mortality is comparable to ERCP performed with reusable duodenoscopes. Moreover, the pooled technical success rate in expert hands stands at optimal values, with no significant heterogeneity among studies.
However, further studies are needed to provide high-quality data, in terms of cost-effectiveness and environmental impact, potentially allowing a worldwide spread of SUD use for ERCP.
Single-use duodenoscope use has been proposed as an effective strategy to avoid the risk of duodenoscope-related cross-infections in patients undergoing endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP).
Recentaly, several manuscript have been published reporting the ouctomes of clinical studies on single-use duodenoscope use for ERCP.
To perform a systematic review of the literature and report qualitative and quantitative results in terms of technical success rate, clinical success, and safety.
Systematic review and quantitative analysis.
Five original articles have been identified. One bench comparative study and four clinical trials performed with EXALT model-D (Boston Scientific Corp., United States) have been identified. Of them, one is a randomized controlled trial, while the other three studies are prospective single-arm, cross-over studies. Pooled technical success rate (4 studies, 368 patients) was 92.9% [95% confidence interval (CI): 89.9-95.5; I2: 11.8%]. Pooled serious adverse event (4 studies, 381 patients) rate was 5.9% [3.7%-8.5%; I2: 0.0%].
Although few clinical trials are available, evidence is concordant in identifying an absolute feasibility and safety and feasibility for single-use duodenoscopes (SUD) use for ERCP. Data on cost-effectiveness and environmental impact will be needed for a worldwide spread of SUD use for ERCP.
Future perspective and study pipelines should assess the use of other models of single-use duodenoscope, cost-effectiveness of single-use duodenoscope use for ERCP and environmental sustainability.
Provenance and peer review: Invited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: Italy
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B, B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Tang J, China; Yang X, China; Yao D, China S-Editor: Liu JH L-Editor: A P-Editor: Liu JH
| 1. | Boxhoorn L, Voermans RP, Bouwense SA, Bruno MJ, Verdonk RC, Boermeester MA, van Santvoort HC, Besselink MG. Acute pancreatitis. Lancet. 2020;396:726-734. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 276] [Cited by in RCA: 584] [Article Influence: 116.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Williams E, Beckingham I, El Sayed G, Gurusamy K, Sturgess R, Webster G, Young T. Updated guideline on the management of common bile duct stones (CBDS). Gut. 2017;66:765-782. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 212] [Cited by in RCA: 259] [Article Influence: 32.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 3. | Dumonceau JM, Kapral C, Aabakken L, Papanikolaou IS, Tringali A, Vanbiervliet G, Beyna T, Dinis-Ribeiro M, Hritz I, Mariani A, Paspatis G, Radaelli F, Lakhtakia S, Veitch AM, van Hooft JE. ERCP-related adverse events: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline. Endoscopy. 2020;52:127-149. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 249] [Cited by in RCA: 501] [Article Influence: 100.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 4. | Ehrlich D, Muthusamy VR. Device profile of the EXALT Model D single-use duodenoscope for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: overview of its safety and efficacy. Expert Rev Med Devices. 18: 421-427. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Beilenhoff U, Biering H, Blum R, Brljak J, Cimbro M, Dumonceau JM, Hassan C, Jung M, Neumann C, Pietsch M, Pineau L, Ponchon T, Rejchrt S, Rey JF, Schmidt V, Tillett J, van Hooft J. ESGE-ESGENA technical specification for process validation and routine testing of endoscope reprocessing in washer-disinfectors according to EN ISO 15883, parts 1, 4, and ISO/TS 15883-5. Endoscopy. 2017;49:1262-1275. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Akshintala VS, Sperna Weiland CJ, Bhullar FA, Kamal A, Kanthasamy K, Kuo A, Tomasetti C, Gurakar M, Drenth JPH, Yadav D, Elmunzer BJ, Reddy DN, Goenka MK, Kochhar R, Kalloo AN, Khashab MA, van Geenen EJM, Singh VK. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, intravenous fluids, pancreatic stents, or their combinations for the prevention of post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;6:733-742. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 11.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Higa JT, Ross AS. Duodenoscope as a Vector for Transmission. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2020;30:653-663. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Humphries RM, Yang S, Kim S, Muthusamy VR, Russell D, Trout AM, Zaroda T, Cheng QJ, Aldrovandi G, Uslan DZ, Hemarajata P, Rubin ZA. Duodenoscope-Related Outbreak of a Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Identified Using Advanced Molecular Diagnostics. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;65:1159-1166. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 42] [Cited by in RCA: 63] [Article Influence: 10.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Ofstead CL, Buro BL, Hopkins KM, Eiland JE, Wetzler HP, Lichtenstein DR. Duodenoscope-associated infection prevention: A call for evidence-based decision making. Endosc Int Open. 2020;8:E1769-E1781. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Holzwanger EA, Bilal M, Saperia J, Cohen J, Sawhney MS, Berzin TM, Pleskow DK. Duodenoscope-related infections and potential role of single-use duodenoscopes. VideoGIE. 2020;5:628-629. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Rubin ZA, Kim S, Thaker AM, Muthusamy VR. Safely reprocessing duodenoscopes: current evidence and future directions. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3:499-508. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 41] [Article Influence: 6.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Ellison PL Jr, Freeman J, Elmunzer BJ, Cote GA, Brock AS. Review of Duodenoscope Infection Prevention Practices at the Medical University of South Carolina. Gastroenterol Nurs. 2020;43:E214-E216. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Bomman S, Kozarek RA, Thaker AM, Kodama C, Muthusamy VR, Ross AS, Krishnamoorthi R. Economic burden of enhanced practices of duodenoscopes reprocessing and surveillance: balancing risk and cost containment. Endosc Int Open. 2021;9:E1404-E1412. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Larsen S, Russell RV, Ockert LK, Spanos S, Travis HS, Ehlers LH, Mærkedahl A. Rate and impact of duodenoscope contamination: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine. 2020;25:100451. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 57] [Cited by in RCA: 63] [Article Influence: 12.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Hutfless S. Endoscope infection transmission state-of-the-art: beyond duodenoscopes to a culture of infection prevention. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2020;36:366-369. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Mehrotra P, Weber DJ, Sarpatwari A. Preventing medical-device-borne outbreaks: High-level disinfection policy for duodenoscopes. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2021;42:334-337. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Snyder GM, Wright SB, Smithey A, Mizrahi M, Sheppard M, Hirsch EB, Chuttani R, Heroux R, Yassa DS, Olafsdottir LB, Davis RB, Anastasiou J, Bapat V, Bidari K, Pleskow DK, Leffler D, Lane B, Chen A, Gold HS, Bartley A, King AD, Sawhney MS. Randomized Comparison of 3 High-Level Disinfection and Sterilization Procedures for Duodenoscopes. Gastroenterology. 2017;153:1018-1025. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 65] [Cited by in RCA: 75] [Article Influence: 9.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Benowitz I, Moulton-Meissner HA, Epstein L, Arduino MJ. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Guidance on Flexible Gastrointestinal Endoscopes: Lessons Learned from Outbreaks, Infection Control. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2020;30:723-733. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Haugen SP, Ferriter A, Connell J, Min LJ, Wiyor HD, Cole S. Recent Actions by the US Food and Drug Administration: Reducing the Risk of Infection from Reprocessed Duodenoscopes. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2020;30:711-721. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Edmundowicz SA. Is a Solution to Duodenoscope-transmitted Infections Good Enough and Can We Afford it? Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18:1933-1934. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Ross AS, Bruno MJ, Kozarek RA, Petersen BT, Pleskow DK, Sejpal DV, Slivka A, Moore D, Panduro K, Peetermans JA, Insull J, Rousseau MJ, Tirrell GP, Muthusamy VR. Novel single-use duodenoscope compared with 3 models of reusable duodenoscopes for ERCP: a randomized bench-model comparison. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91:396-403. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 50] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 9.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Muthusamy VR, Bruno MJ, Kozarek RA, Petersen BT, Pleskow DK, Sejpal DV, Slivka A, Peetermans JA, Rousseau MJ, Tirrell GP, Ross AS. Clinical Evaluation of a Single-Use Duodenoscope for Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18:2108-2117.e3. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 78] [Cited by in RCA: 67] [Article Influence: 13.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Bang JY, Hawes R, Varadarajulu S. Equivalent performance of single-use and reusable duodenoscopes in a randomised trial. Gut. 2021;70:838-844. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 36] [Cited by in RCA: 61] [Article Influence: 15.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Napoléon B, Gonzalez JM, Grandval P, Lisotti A, Laquière AE, Boustière C, Barthet M, Prat F, Ponchon T, Donatelli G, Vanbiervliet G. Evaluation of the performances of a single-use duodenoscope: Prospective multi-center national study. Dig Endosc. 2022;34:215-221. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 29] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 7.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Slivka A, Ross AS, Sejpal DV, Petersen BT, Bruno MJ, Pleskow DK, Muthusamy VR, Chennat JS, Krishnamoorthi R, Lee C, Martin JA, Poley JW, Cohen JM, Thaker AM, Peetermans JA, Rousseau MJ, Tirrell GP, Kozarek RA; EXALT Single-use Duodenoscope Study Group. Single-use duodenoscope for ERCP performed by endoscopists with a range of experience in procedures of variable complexity. Gastrointest Endosc. 2021;94:1046-1055. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 5.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Lisotti A, Zagari RM, Fusaroli P, Napoléon B. Optimal safety and pooled technical success rate for ERCP performed with single-use duodenoscopes. Dig Liver Dis. 2022;54:291-292. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Bang JY, Rösch T, Kim HM, Thakkar S, Robalino Gonzaga E, Tharian B, Inamdar S, Lee LS, Yachimski P, Jamidar P, Muniraj T, DiMaio C, Kumta N, Sethi A, Draganov P, Yang D, Seoud T, Perisetti A, Bondi G, Kirtane S, Hawes R, Wilcox CM, Kozarek R, Reddy DN, Varadarajulu S. Prospective evaluation of an assessment tool for technical performance of duodenoscopes. Dig Endosc. 2021;33:822-828. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Barakat MT, Ghosh S, Banerjee S. Cost utility analysis of strategies for minimizing risk of duodenoscope related infections. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 8.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Dhar A, Hayee B, Wesley E, Stableforth W, Sebastian S. Reducing low risk of transmissible infection in duodenoscopes: at what cost to the planet? Gut. 2022;71:655-656. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |