Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Sep 19, 2025; 15(9): 110536
Published online Sep 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i9.110536
Published online Sep 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i9.110536
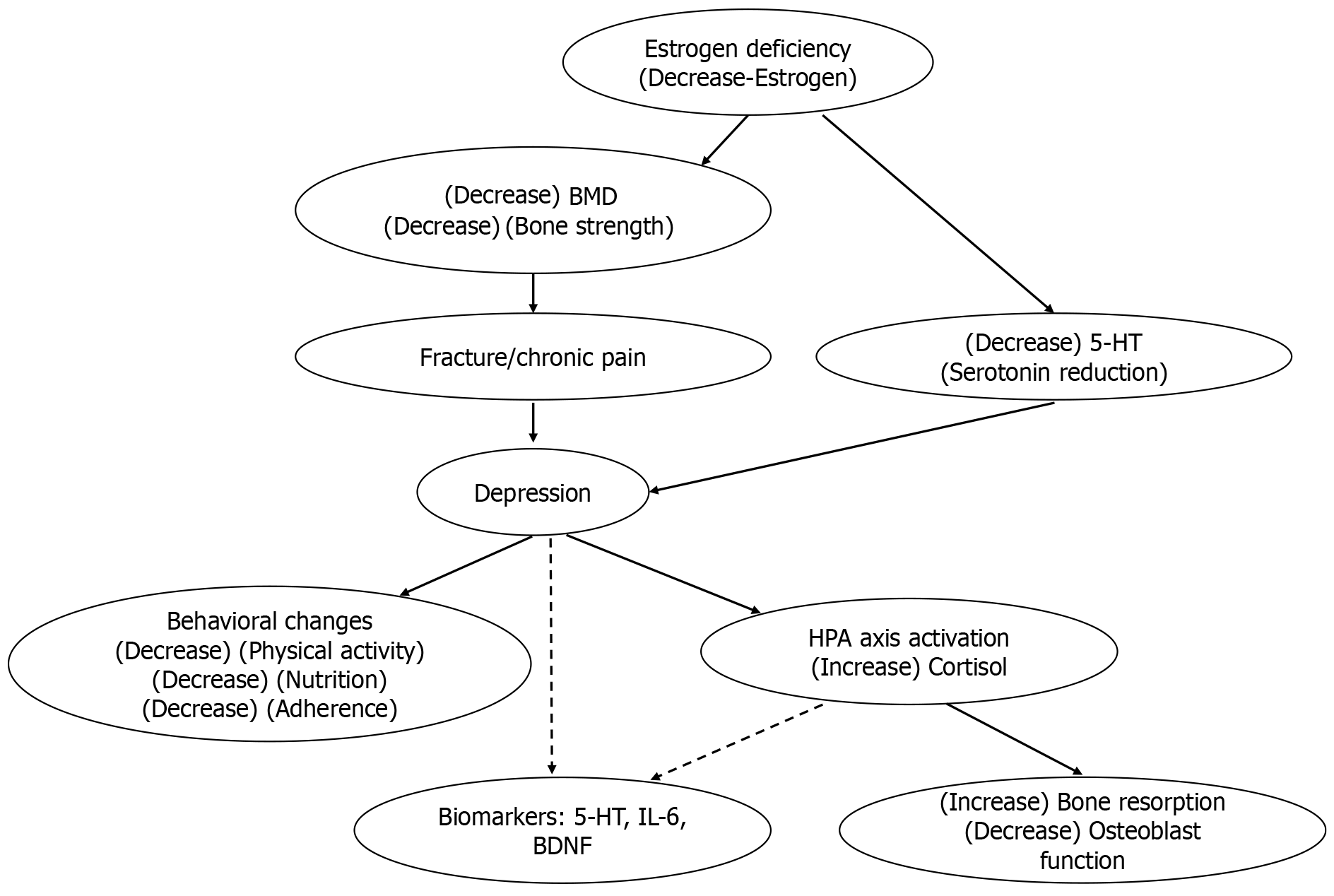
Figure 1 Bidirectional mechanisms between depression and osteoporosis in postmenopausal women.
Estrogen deficiency leads to reductions in bone mineral density and serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine), while depression triggers hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activation and elevated cortisol, exacerbating bone loss. Fractures, chronic pain, and behavioral factors further contribute to this cycle. BMD: Bone mineral density; 5-HT: 5-hydroxytryptamine; HPA: Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal; IL-6: Interleukin-6; BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor.
- Citation: Zhu JY, Yiming A, Zeng JQ. Depression in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: Integrating psychological nursing into holistic care. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(9): 110536
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i9/110536.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i9.110536