Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Orthop. Sep 18, 2017; 8(9): 697-704
Published online Sep 18, 2017. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v8.i9.697
Published online Sep 18, 2017. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v8.i9.697
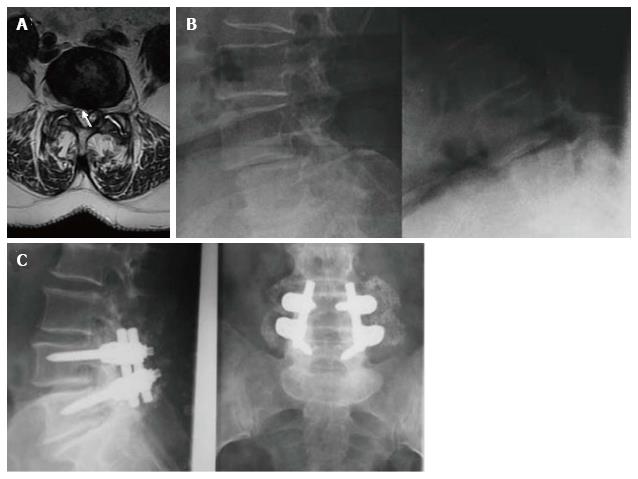
Figure 1 Case 2, Table 1.
Preoperative axial T2-weighted MR image (A) showing a dehydrated and hypointense disk with a hyperintense cystic formation at right L4-L5 level (arrow). The cyst appeared to be of the internal or flavum type (see text for the classification). Sagittal dynamic images (B) 12 mo after the first surgical treatment showed an unstable olisthesis at L4-L5 level. Standard X-rays performed 1 year after surgical stabilization (C) showed the instrumentation to be well-positioned with an optimal profile and fusion at L4-L5.
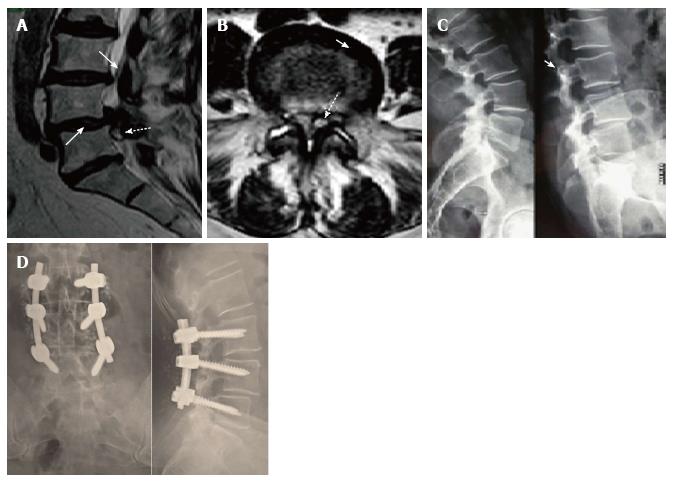
Figure 2 Case 12, Table 1.
Preoperative sagittal T2-weighted MR image (A) showing a spinal ganglion cyst (dotted arrow) accompanied by olisthesis at L4/L5 with a dehydrated intervertebral disk (arrow), partially herniated into the spinal canal. On axial images (B) the cyst (dotted arrow) appeared to be of the medium or articular type (see text for classification). The interfacetal space contained an anomalous abundance of “sinovia” (commonly called synovial fluid), as the contralateral one did. Dynamic X-rays (C) showed an unstable olisthesis at L4/L5 and L3/L4. Postoperative outcome of the L3/L5 stabilization is documented by standard X-ray films (D) which confirmed good stability and fusion of the lumbar spine.
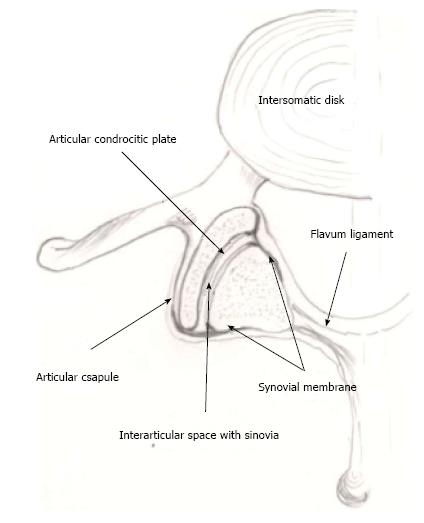
Figure 3 Schematic drawing of a lumbar facet joint showing the extension and distribution of the synovial membrane localized on the internal face of the articular capsule, extending to the external margins of the joint, up to the chondrocytic plates.
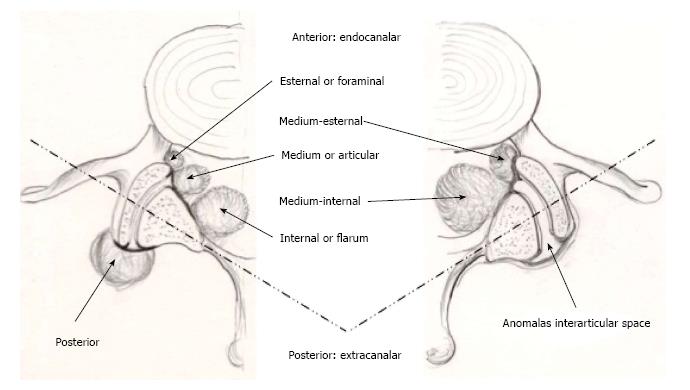
Figure 4 Localizations of lumbar spinal ganglion cysts (see text for the classification).
The drawing on the right shows the joint with signs of instability (widened and misaligned interarticular space and increased amount of sinovia).
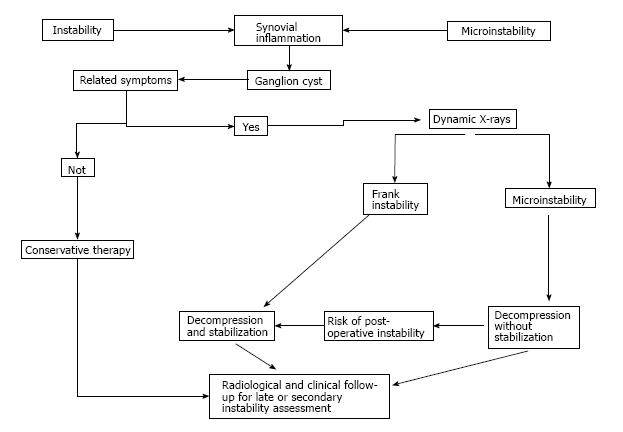
Figure 5 Flow-chart depicting options for the most appropriate approach to the lumbar spinal ganglion cysts.
- Citation: Domenicucci M, Ramieri A, Marruzzo D, Missori P, Miscusi M, Tarantino R, Delfini R. Lumbar ganglion cyst: Nosology, surgical management and proposal of a new classification based on 34 personal cases and literature review. World J Orthop 2017; 8(9): 697-704
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v8/i9/697.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v8.i9.697